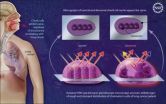
(Press-News.org) Accurate duplication of genetic material and the faithful segregation of chromosomes are critical for cell survival. The initiation of DNA replication is linked both to cell cycle progression and chromatin organization. In plants, animals and other "eukaryotes," the assembly of a multi-protein complex called pre-replicative complex (preRC) is the first step in the initiation of DNA replication. As the name implies, origin recognition complex (ORC) proteins bind to origins of DNA replication. Subsequently, other components of preRC are assembled at these sites. In addition to its role in DNA replication, ORC is also involved in gene silencing and organization of the tightly packed DNA, called heterochromatin. How ORC is brought to the DNA in human cells had previously remained a mystery.
Researchers at the University of Illinois, led by Professor Supriya Prasanth from the school of molecular and cellular biology, have identified a novel protein that is highly conserved in higher eukaryotes. They have shown that in human cells, this protein (once known as LRWD1 but renamed ORCA, for "ORC-associated" protein) associates with ORC and shows similar cell cycle dynamics to ORC. Along with ORC, this protein binds to heterochromatic structures, including centromeres and telomeres, which are important to cell division and chromosome maintenance.
The researchers further demonstrated that ORCA efficiently recruits ORC to chromatin, the DNA and proteins that make up the chromosome. Depletion of ORCA in human primary cells as well as in embryonic stem cells results in the loss of ORC binding to chromatin and subsequent arrest of cells in a vital phase of the cell cycle. Loss of ORCA results in defects in cellular proliferation, suggesting that a fine-tuned balance in the levels of ORCA is maintained in a normal cell. These results suggest that a novel protein, ORCA, is critical for initiation of DNA replication and heterochromatin organization in mammalian cells.
This work appears in the October 8, 2010 issue of the journal Molecular Cell.
"The discovery of this new protein is going to be revolutionary in the field of replication and cell cycle," Prasanth said. "We all know that diseases like cancer are caused by uncontrolled proliferation of cells, and our data demonstrates that ORCA controls proliferation of cells. This work is going to have important implications in cancer biology."
INFORMATION:
The study was spearheaded by Zhen Shen, a graduate student, with assistance from post-doctoral fellows Kizhakke M. Sathyan and Arindam Chakraborty. Other Illinois researchers on the study include Kannanganattu Prasanth, a professor in the department of cell and developmental biology; his graduate student Ruiping Zheng; Brian Freeman, a professor in the department of cell and developmental biology; Fei Wang, a professor in cell and developmental biology; and his graduate student Yejie Geng. The funding for this study was provided by National Science Foundation, and The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, through a Special Fellow Award granted to Supriya Prasanth.
Novel protein critical for cellular proliferation discovered
2010-10-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
An X-ray for your genes
2010-10-08
Prescription drugs and their dosages may be standardized, but not every patient reacts to a medicine in the same way. The personal genetic characteristics of individuals and populations can explain why a specific prescription successfully treats one patient and not another, so medical researchers are adopting the new approach called "personalized medicine" and a Tel Aviv University lab is leading the way.
Dr. Noam Shomron of Tel Aviv University's Sackler Faculty of Medicine is developing a new method for the advancement of personalized medicine, an expanding area of ...
Queen's University discovery could impact how the body receives medicine
2010-10-08
Researchers at Queen's University have discovered how molecules in glass or plastic are able to move when exposed to light from a laser. The findings could one day be used to facilitate medicinal drug distribution by allowing doctors to control the time and rate at which drugs are delivered into the body. The drugs, in a solid plastic carrier, could be released through the body when exposed to light.
Lead researcher Jean-Michel Nunzi, a professor in the departments of Chemistry and Physics, has determined that "molecular cooperation" is what allows the molecules to move ...
You may not be able to say how you feel about your race
2010-10-08
INDIANAPOLIS –A new study from the School of Science at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis looks at how much African Americans and whites favor or prefer their own racial group over the other, how much they identify with their own racial group, and how positively they feel about themselves.
The work, by Leslie Ashburn-Nardo, Ph.D., associate professor of psychology in the School of Science at IUPUI, looked at both consciously controllable sentiments and gut feelings about social stigma and found a significant difference in both groups between what people ...
Cheek swab may detect lung cancer
2010-10-08
Early detection is critical for improving cancer survival rates. Yet, one of the deadliest cancers in the United States, lung cancer, is notoriously difficult to detect in its early stages.
Now, researchers have developed a method to detect lung cancer by merely shining diffuse light on cells swabbed from patients' cheeks.
In a new clinical study, the analysis technique--called partial wave spectroscopic (PWS) microscopy--was able to differentiate individuals with lung cancer from those without, even if the non-cancerous patients had been lifetime smokers or suffered ...
Water discovered on second asteroid, may be even more common
2010-10-08
Water ice on asteroids may be more common than expected, according to a new study that will be presented today at the world's largest gathering of planetary scientists.
Two teams of researchers who made national headlines in April for showing the first evidence of water ice and organic molecules on an asteroid have now discovered that asteroid 65 Cybele contains the same material.
"This discovery suggests that this region of our solar system contains more water ice than anticipated," said University of Central Florida Professor Humberto Campins. "And it supports the ...
Childhood adversity may lead to unhealthy stress response in adult life
2010-10-08
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Seemingly healthy adults, if they were abused or neglected during childhood, may suffer physiological consequences decades later. In research published online last week by the journal Neuropsychopharmacology, a team led by psychiatrists at Brown University and Butler Hospital found that healthy adults who reported being mistreated as kids appear to have an elevated inflammatory response to stress compared to adults who had happier childhoods.
Lead author Linda Carpenter, associate professor of psychiatry and human behavior, said that ...
New study shows benefits of Bt corn to farmers
2010-10-08
A group of agricultural scientists reported in today's issue of the journal Science that corn that has been genetically engineered to produce insect-killing proteins isolated from the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) provides significant economic benefits even to neighboring farmers who grow non-transgenic varieties of corn.
"Modern agricultural science is playing a critical role in addressing many of the toughest issues facing American agriculture today, including pest management and productivity," said Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack. "This study provides ...
Stem cells shape up to their surroundings
2010-10-08
London, UK (October, 07, 2010) –Many scientists aspire to take control over the stem cell differentiation process, so that we can grow organs and implants perfectly matched to each patient in the future. Now research in the Journal of Tissue Engineering, published by SAGE-Hindawi, explains how engineering the topography on which stem cells grow, and the mechanical forces working on them, can be as powerful an agent for change as their chemical environment.
Stem cells respond to the stiffness, chemistry and topography of the environments they find themselves in – and scientists ...
Election forecasts favor Republican gains in midterm
2010-10-08
WASHINGTON, DC-In the weeks leading up to the 2010 midterm elections, five forecasters or teams of forecasters offer models and predictions for the House in the most recent issue (October 2010) of PS: Political Science and Politics, a journal of the American Political Science Association. The models offer a broad consensus that the Republicans will make substantial gains in the House, although there is not a consensus over how large those gains will be. A 30-seat spread between the low and high end of the seat change forecast range exists, with two forecasters giving an ...
Structure of plastic solar cells impedes their efficiency
2010-10-08
A team of researchers from North Carolina State University and the U.K. has found that the low rate of energy conversion in all-polymer solar-cell technology is caused by the structure of the solar cells themselves. They hope that their findings will lead to the creation of more efficient solar cells.
Polymeric solar cells are made of thin layers of interpenetrating structures from two different conducting plastics and are increasingly popular because they are both potentially cheaper to make than those currently in use and can be "painted" or printed onto a variety ...