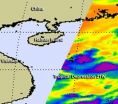
(Press-News.org) The twenty-first tropical depression of the northwestern Pacific Ocean was born as a NASA satellite flew overhead on Oct. 1, capturing its "baby picture" in infrared light.
On Monday, Oct. 1 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Tropical Depression 21W (TD21W) had maximum sustained winds near 25 knots. It was centered about300 nautical miles south of Hong Kong, near 17.4 North latitude and 114.8 East longitude. TD21W has tracked northward at 5 knots and is expected to curve to the northwest and west.
On Oct. 1, 2012, infrared imagery from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite shows that the center of circulation is well-defined and the strongest thunderstorms are building in the southeastern quadrant of the storm and wrapping into the center.
The system has been quasi-stationary over the past 12 hours, because it is in a weak steering environment with nothing to push the storm in any direction.
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect that Tropical Depression 21W will start moving to the west and approach the central Vietnam coast by Oct. 6 or Oct. 7.
INFORMATION:
NASA observes another tropical depression birth in northwestern Pacific
2012-10-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
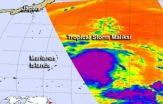
Tropical Storm Maliksi forms, Iwo To on guard
2012-10-02
The western North Pacific is in full swing, tropically speaking and NASA observed the birth of Tropical Storm Maliksi on Sept. 30. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of the storm when it was a depression and revealed a large area of powerful thunderstorms around its center that hinted at its strengthening.
Tropical Storm Maliksi formed from the twentieth tropical depression of the western North Pacific typhoon season. Tropical Depression 20W formed on Sept. 20 about 305 nautical miles from Guam near 16.3 North and 149.0 East. It is moving to the north-northwest ...
Digital mammography improves population-based breast cancer screening
2012-10-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. – New research from the Netherlands shows that the switch from screen film mammography (SFM) to digital mammography (DM) in large, population-based breast cancer screening programs improves the detection of life-threatening cancer without significantly increasing detection of clinically insignificant disease. Results of the study are published online in the journal Radiology.
DM's higher sensitivity at detecting breast cancer raised concerns that its introduction into screening programs would increase the diagnosis of clinically unimportant cancers—cancers ...
Novel MRI technique could reduce breast biopsies
2012-10-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Water diffusion measurements with MRI could decrease false-positive breast cancer results and reduce preventable biopsies, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology. Researchers said the technique also could improve patient management by differentiating high-risk lesions requiring additional workup from other non-malignant subtypes.
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) has emerged in recent years as a useful tool in breast cancer detection and staging. One of its primary limitations is a substantial number of false-positive ...
PETA scientists analyze animal use in HPV chemicals challenge program
2012-10-02
Washington — In an article published today (October 2, 2012) in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Health Perspectives (EHP), People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals reports that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) High Production Volume (HPV) Chemicals Challenge Program had the potential to use 3.5 million animals in new testing, but after the application of animal-saving measures, approximately 127,000 were actually used. Although this toll in animal lives is high, it would have been many times worse had PETA not obtained major concessions from the ...
Provincial effort to improve stroke care in Alberta is 'paying off'
2012-10-02
Stroke care has improved considerably in Alberta following the implementation of the Alberta Provincial Stroke Strategy (APSS), leading to more targeted patient care and fewer health complications, according to a study presented today at the Canadian Stroke Congress.
Nearly 97 per cent of stroke patients received a brain-imaging scan during their admission to hospital in 2011, compared to 88 per cent before the APSS was implemented in 2006.
"The faster a patient has access to brain imaging, the faster they get the right diagnosis and the right treatment," says lead ...
Sleep apnea plays dual role in stroke
2012-10-02
Improvements to the diagnosis and screening of sleep apnea are critical to stroke prevention, according to new stroke care guidelines released today at the Canadian Stroke Congress.
Obstructive sleep apnea, a disorder where the flow of air to the brain pauses or decreases during sleep, is both a risk factor for stroke and a complication following stroke, according to the Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care.
Among the general population sleep apnea increases the likelihood of having a stroke, even after controlling for other stroke risk factors, such ...
Smoking clouds the brain after stroke
2012-10-02
A study of stroke patients from Southern Ontario found those who smoke have more difficulty with problem-solving and decision-making than non-smokers.
The study, presented today at the Canadian Stroke Congress, tested mental abilities of 76 patients, including 12 smokers, with an average age of 67.5 years, using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) tool. The MoCA exam tests patients with memory and problem solving questions and gives them a score out of 30.
Smokers had a median MoCA score two points lower than non-smokers -- 22 out of 30 compared to 24 out of 30. ...
Expand telestroke in all provinces to save lives, reduce disability
2012-10-02
Widespread use of telestroke -- two-way audiovisual linkups between neurologists in stroke centres and emergency rooms in underserved and rural areas -- would save lives, reduce disability and cut health-care costs in all parts of Canada, according to a major national report released today at the Canadian Stroke Congress.
However, despite repeated research that shows telestroke delivers quality stroke care to underserviced areas, few stroke patients in Canada are benefiting from this lifesaving service.
"The case for telestroke is compelling and the need is urgent," ...
Alzheimer's disease in men linked to low levels of hormone, IGF-1
2012-10-02
Chevy Chase, MD— Low serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) are associated with Alzheimer's Disease in men, but not women, according to a recent study accepted for publication in The Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 are involved in longevity and could be beneficial to cognition, especially in Alzheimer's disease where experimental studies have shown that IGF-1 opposes the main pathological processes of Alzheimer's disease. The current study ...
Study uncovers racial disparities in diabetic complications among underinsured
2012-10-02
Chevy Chase, MD— Diabetes is among the ten leading causes of death in both white and African American patients, but the prevalence of diabetic complications are race-specific, according to a recent study accepted for publication in The Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
"This study is one of only a few to assess whether there is a racial difference in the incidence of diabetic complications," said Gang Hu, MD, PhD, of Pennington Biomedical Research Center in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, and lead author of the study. "Our findings suggest ...