(Press-News.org) This press release is available in Spanish.
The study, published by Professor Eduardo Pérez Asenjo of UC3M's Economics Department, shows that relative earnings affect our happiness and our job performance. Summing up: if the people with whom I compare myself earn more than I do, I will be unhappier and I will work more. "This confirms the hypothesis of what I perceived, but not the way I would like things to be," the author of the study comments. "I would find it healthier not to compare what we earn to what others earn and I think it would be 'better' if these things didn't affect our happiness," he states.
In his analysis, he found that if an individual's earnings are less than those of her/his peers, s/he will work more hours. What causes this effect? "The most likely explanation lies in social comparisons, although it could also be due to the idea that if those around me earn more than I do, it might indicate that if I work hard I will end up earning as much as they do," explains Professor Pérez Asenjo, who also works at the Banco de España (the National Bank of Spain). The explanation derived from empirical analysis is the first one. "Therefore, the effect of others' earnings on my happiness is negative, because I compare myself to them and it makes me unhappy to earn less than them; so I work more hours so that I can earn the same as or more than them," he maintains.
VIDEO:
One of the keys to happiness at work is earning a lot of money, but what is equally important, if not more important, is that our earnings not be inferior...
Click here for more information.
This finding can be applied to labor management or to human resource management in companies. "It might be a relevant criterion to keep in mind, when setting salaries, that an employee is concerned not only with what s/he earns, but also with what those around her/him earn," comments the researcher, whose perception is that a happy worker is much more productive than an unhappy one. "My personal opinion is that employees' happiness is not really taken into account in work environments, from the company's perspective," he concludes.
This line of research presents many challenges and aspects that can be delved into further: How are peer groups formed? Do the effects of relative income on happiness vary with the level of income? Or with age? This researcher's hypothesis, which is still to be tested, is that, paradoxically, the richer you are, the more important it is to compare yourselves with others and to do better than them. "If the absolute quantity of money one earns were the only thing that mattered, at a certain very high level, the only thing left would be to stop working, but that is not what happens and I think one of the reasons for this is social comparisons", he speculates.
INFORMATION:
Happiness at work depends on a good salary, but also on how much colleagues earn
UC3M research
2012-10-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Length matters in gene expression
2012-10-02
Gene ends communicate
Human genomes harbour thousands of genes, each of which gives rise to proteins when it is active. But which inherent features of a gene determine its activity? Postdoctoral Scholar Pia Kjølhede Andersen and Senior Researcher Søren Lykke-Andersen from the Danish National Research Foundation's Centre for mRNP Biogenesis and Metabolism have now found that the distance between the gene start, termed the 'promoter', and the gene end, the 'terminator', is crucial for the activity of a protein-coding gene. If the distance is too short, the gene is transcriptionally ...
Intelligence is in the genes, but where?
2012-10-02
You can thank your parents for your smarts—or at least some of them. Psychologists have long known that intelligence, like most other traits, is partly genetic. But a new study led by psychological scientist Christopher Chabris reveals the surprising fact that most of the specific genes long thought to be linked to intelligence probably have no bearing on one's IQ. And it may be some time before researchers can identify intelligence's specific genetic roots.
Chabris and David Laibson, a Harvard economist, led an international team of researchers that analyzed a dozen ...
Superman-strength bacteria produce gold
2012-10-02
EAST LANSING, Mich. — At a time when the value of gold has reached an all-time high, Michigan State University researchers have discovered a bacterium's ability to withstand incredible amounts of toxicity is key to creating 24-karat gold.
"Microbial alchemy is what we're doing – transforming gold from something that has no value into a solid, precious metal that's valuable," said Kazem Kashefi, assistant professor of microbiology and molecular genetics.
He and Adam Brown, associate professor of electronic art and intermedia, found the metal-tolerant bacteria Cupriavidus ...
Solar cell consisting of a single molecule
2012-10-02
This press release is available in German.
A team of scientists, led by Joachim Reichert, Johannes Barth, and Alexander Holleitner (Technische Universitaet Muenchen, Clusters of Excellence MAP and NIM), and Itai Carmeli (Tel Aviv University) developed a method to measure photocurrents of a single functionalized photosynthetic protein system. The scientists could demonstrate that such a system can be integrated and selectively addressed in artificial photovoltaic device architectures while retaining their biomolecular functional properties. The proteins represent light-driven, ...
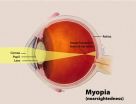
Specialty contact lenses may one day help halt the progression of nearsightedness in children
2012-10-02
WASHINGTON, Oct. 2—Nearsightedness, or myopia, affects more than 40 percent of people in the U.S. and up to 90 percent of children in some parts of Asia. The problem begins in childhood and often progresses with age. Standard prescription lenses can correct the defocus but do not cure nearsightedness, and do not slow progression rates as children grow. But recent experimental work by biomedical scientist David Troilo and colleagues at the State University of New York (SUNY) College of Optometry in New York City supports the development of a potential cure for myopia by ...
3-D medical scanner: New handheld imaging device to aid doctors on the 'diagnostic front lines'
2012-10-02
WASHINGTON, Oct. 2, 2012—In the operating room, surgeons can see inside the human body in real time using advanced imaging techniques, but primary care physicians, the people who are on the front lines of diagnosing illnesses, haven't commonly had access to the same technology – until now. Engineers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) have created a new imaging tool for primary care physicians: a handheld scanner that would enable them to image all the sites they commonly examine, and more, such as bacterial colonies in the middle ear in 3-D, or monitor ...
Sea Education Association tall ship departs on major marine debris research cruise
2012-10-02
(San Diego, California – October 2, 2012) A tall ship owned and operated by Sea Education Association (SEA) will depart port tomorrow on a research expedition dedicated to examining the effects of plastic marine debris, including debris generated by the 2011 Japanese tsunami, in the ocean ecosystem.
During their 37-day cruise, the crew of the Woods Hole, Mass.-based sailing oceanographic research vessel Robert C. Seamans will explore a region between San Diego and Honolulu, popularly dubbed the "Great Pacific Garbage Patch", where high concentrations of plastic debris ...
RI Hospital: Differences in diagnosis, treatment of nonepileptic seizures in US, Chile
2012-10-02
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – Epileptic and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) may look similar, but actually have different causes and treatments. Up to 20 percent of patients diagnosed with epilepsy actually have PNES, which are not treated by antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). According to a new study by Rhode Island Hospital researcher W. Curt LaFrance Jr., M.D., M.P.H., director of neuropsychiatry and behavioral neurology, increasing access to video electroencephalography (video-EEG) may aid in distinguishing between epilepsy and PNES. The study is published online in advance ...
Gene responsible for many spontaneous breast cancers identified
2012-10-02
BETHESDA, MD – October 2, 2012 -- Cancerous tumors contain hundreds of mutations, and finding these mutations that result in uncontrollable cell growth is like finding the proverbial needle in a haystack. As difficult as this task is, it's exactly what a team of scientists from Cornell University, the University of North Carolina, and Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York have done for one type of breast cancer. In a report appearing in the journal GENETICS, researchers show that mutations in a gene called NF1 are prevalent in more than one-fourth of all noninheritable ...
Amazonian tribal warfare sheds light on modern violence, says MU anthropologist
2012-10-02
In the tribal societies of the Amazon forest, violent conflict accounted for 30 percent of all deaths before contact with Europeans, according to a recent study by University of Missouri anthropologist Robert Walker. Understanding the reasons behind those altercations in the Amazon sheds light on the instinctual motivations that continue to drive human groups to violence, as well as the ways culture influences the intensity and frequency of violence.
"The same reasons - revenge, honor, territory and jealousy over women - that fueled deadly conflicts in the Amazon continue ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Happiness at work depends on a good salary, but also on how much colleagues earnUC3M research