(Press-News.org) Pop quiz! Tests are good for: (a) Assessing what you've learned; (b) Learning new information; (c) a & b; (d) None of the above.
The correct answer?
According to research from psychological science, it's both (a) and (b) – while testing can be useful as an assessment tool, the actual process of taking a test can also help us to learn and retain new information over the long term and apply it across different contexts.
New research published in journals of the Association for Psychological Science explores the nuanced interactions between testing, memory, and learning and suggests possible applications for testing in educational settings.
Appropriate Multiple-Choice Tests Can Foster Test-Induced Learning
One of the criticisms of multiple-choice tests is that they expose test takers to the correct answer among the available options. This means that you only have to recognize the correct answer, you don't have to rely on retrieval processes that are known to enhance later recall. Psychological scientist Jeri Little and her colleagues investigated whether multiple-choice tests could actually be designed to call upon these retrieval processes. If the alternative answers are all plausible enough, they hypothesized, test takers would have to retrieve information about why correct alternatives are correct and also about why incorrect alternatives are incorrect in order to be able to distinguish between the two. In two experiments, the researchers found that properly constructed multiple-choice tests can, in fact, trigger productive retrieval processes. They also found that multiple-choice tests had one potentially important advantage over tests in which only the question is presented. Both kinds of tests helped test takers remember the information they been tested on, but only the multiple-choice tests helped them recall information related to incorrect alternatives. These findings suggest that multiple-choice tests can be constructed in ways that exercise the very retrieval processes they have been accused of bypassing.
Corresponding author: Jeri L. Little – Washington University in St. Louis – jerilittle@gmail.com
Published in Psychological Science
Testing Enhances the Transfer of Learning
Many studies have shown that having to retrieve information during a test helps you remember that information later on. But most research on this "testing effect" has measured the ability to recall information in the form of a final test that's similar to the initial test. Much less is known about the whether testing might also promote the application – or transfer – of learning. In this article, psychological scientist Shana Carpenter reviews recent studies that have begun to address this issue, especially as it relates to the benefits of testing on our ability to transfer information across multiple contexts, test formats, and knowledge domains. The few studies on this topic have, so far, reported robust benefits of testing on the transfer of learning. Carpenter highlights the need for research that explores the potential of tests to promote not just the direct retention of information, but also the application of knowledge to new situations.
Corresponding author: Shana K. Carpenter – Iowa State University – shacarp@iastate.edu
Published in Current Directions in Psychological Science
Testing Can Strengthen Short-Term Memory for Cross-Language Information
Researchers know that repeated testing leads to better long-term memory for information than does repeated study, but they're unsure of why this is the case. Psychological scientist Peter Verkoeijen and his colleagues hypothesized that studying may strengthen the aspects of a memory trace that pertain to the way words look and sound, while testing may strengthen the aspects of a memory trace that have to do with the meaning of words. The researchers had Dutch-English bilingual participants learn several lists of words in Dutch. In some instances they were tested after an initial study period (test condition), and in others they were told to study the list again (restudy condition). Participants' memory for the words was then tested in Dutch or English. The main finding shows that participants in the test condition were better at recognizing the words they had been told to learn when they took the final test in English (across-language) but not when they took the final test in Dutch (within-language). These results suggests that using a test as a method of learning – strengthening the meaning of words – was useful for the participants when they weren't able to rely on the visual or phonological familiarity of words because the words were presented in different languages. The results lend support to the researchers' hypothesis that restudying and testing strengthen memory in different ways.
Corresponding author: Peter Verkoeijen – Erasmus University Rotterdam – verkoeijen@fsw.eur.nl
Published in Psychological Science
Active Retrieval Promotes Meaningful Learning
When researchers think about the retrieval of information from memory, they often focus on retrieval as a way to figure out what people have already learned. But psychological scientist Jeffrey Karpicke argues that retrieval processes play a central role in the active process of learning as it happens. Karpicke outlines the retrieval-based learning perspective and discusses the role of retrieval in learning, the means by which it can enhance learning over the long-term, and the ways in which it can help to promote meaningful learning.
Corresponding author: Jeffrey D. Karpicke – Purdue University – karpicke@purdue.edu
Published in Current Directions in Psychological Science
###
Please contact Anna Mikulak at 202-293-9300 or amikulak@psychologicalscience.org for more information.
Testing can be useful for students and teachers, promoting long-term learning
The right tests can promote long-term, transferable learning
2012-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mount Sinai researchers find mechanism of opiate addiction is completely different from other drugs
2012-10-06
Chronic morphine exposure has the opposite effect on the brain compared to cocaine in mice, providing new insight into the basis of opiate addiction, according to Mount Sinai School of Medicine researchers. They found that a protein called brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is increased in cocaine addiction, is inhibited in opioid addiction. The research is published in the October 5 issue of Science.
"Our study shows that BDNF responds completely differently with opioid administration compared to cocaine," said Ja Wook Koo, PhD, Postdoctoral Fellow in ...
Methadone reduces the risk of HIV transmission
2012-10-06
This press release is available in French.
Methadone reduces the risk of HIV transmission in people who inject drugs (PWID), as reported by an international team of researchers in a paper published today in the online edition of the British Medical Journal. This team included Dr. Julie Bruneau from the CHUM Research Centre (CRCHUM) and the Department of Family Medicine at the Université de Montréal.
"There is good evidence to suggest that opiate substitution therapies (OST) reduce drug-related mortality, morbidity and some of the injection risk behaviors among PWID. ...
NASA's Swift satellite discovers a new black hole in our galaxy
2012-10-06
WASHINGTON -- NASA's Swift satellite recently detected a rising tide of high-energy X-rays from a source toward the center of our Milky Way galaxy. The outburst, produced by a rare X-ray nova, announced the presence of a previously unknown stellar-mass black hole.
"Bright X-ray novae are so rare that they're essentially once-a-mission events and this is the first one Swift has seen," said Neil Gehrels, the mission's principal investigator, at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "This is really something we've been waiting for."
An X-ray nova is a short-lived ...
Sun spits out a coronal mass ejection
2012-10-06
At 11:24 p.m. EDT on Oct. 4, 2012, the sun unleashed a coronal mass ejection (CME). Not to be confused with a solar flare, which is a burst of light and radiation, CMEs are a phenomenon that can send solar particles into space and can reach Earth one to three days later. Experimental NASA research models show the CME to be traveling at about 400 miles per second.
When Earth-directed, CMEs can affect electronic systems in satellites and on Earth. CMEs of this speed, however, have not generally caused major effects in the past. Further updates will be provided if needed.INFORMATION:
NOAA's ...
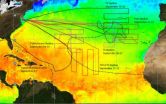
NASA's HS3 mission thoroughly investigates long-lived Hurricane Nadine
2012-10-06
NASA's Hurricane and Severe Storm Sentinel or HS3 scientists had a fascinating tropical cyclone to study in long-lived Hurricane Nadine. NASA's Global Hawk aircraft has investigated Nadine five times during the storm's lifetime.
NASA's Global Hawk also circled around the eastern side of Hurricane Leslie when it initially flew from NASA's Dryden Research Flight Center, Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. to the HS3 base at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. on Sept. 6-7, 2012.
Nadine has been a great tropical cyclone to study because it has lived so long ...
Getting NASA's SDO into focus
2012-10-06
From Sept. 6 to Sept. 29, 2012, NASA's Solar Dynamic Observatory (SDO) moved into its semi-annual eclipse season, a time when Earth blocks the telescope's view of the sun for a period of time each day. Scientists choose orbits for solar telescopes to minimize eclipses as much as possible, but they are a fact of life -– one that comes with a period of fuzzy imagery directly after the eclipse.
The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) on SDO observes the sun through a glass window. The window can change shape in response to temperature changes, and does so dramatically ...
NASA sees very strong wind shear battering Tropical Storm Gaemi
2012-10-06
It is easy to see the effect of the strong northeasterly wind shear battering Tropical Storm Gaemi in satellite imagery from NASA. Visible imagery on Oct. 5 shows a large oval-shaped area of showers and thunderstorms associated with the storm, southwest of the exposed center of circulation.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Gaemi as it was approaching Vietnam on Oct. 5, 2012 at 0550 UTC (1:50 a.m. EDT). A true-color image of the storm was captured by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument and shows bulk of showers and thunderstorms ...
BUSM study investigates genetic variants' role in increasing Parkinson's disease risk
2012-10-06
(Boston) – Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) investigators have led the first genome-wide evaluation of genetic variants associated with Parkinson's disease (PD). The study, which is published online in PLOS ONE, points to the involvement of specific genes and alterations in their expression as influencing the risk for developing PD.
Jeanne Latourelle, DSc, assistant professor of neurology at BUSM, served as the study's lead author and Richard H. Myers, PhD, professor of neurology at BUSM, served as the study's principal investigator and senior author.
A ...
The Largest Electric Power Expo of China Unveils in Beijing Smart Grid Technology in the Spotlight
2012-10-06
With the rapid development of industrialization and urbanization in China, the demand for electricity continues to grow, according to a report by State Grid Corporation of China. Exploring and utilizing renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency are significant to the energy supply, energy structure adjustment and energy-saving in China. Being the No. 1 Electric Power Expo in China, The 14th International Exhibition on Electric Power Equipment and Technology, The 7th International Exhibition on Electrical Equipment and 2012 International Exhibition on Electric Power ...
Puja Sapra, Director, Oncology Research Unit at Pfizer Will Give a Featured Presentation at the 5th ImmunoTherapeutics & ImmunoMonitoring Conference (Jan 31 - Feb 1, 2013 in San Diego)
2012-10-06
Puja Sapra, Director, Oncology Research Unit at Pfizer Will Give a Featured Presentation on "Design Considerations For Development of an Optimal Antibody-Drug Conjugate" at the 5th ImmunoTherapeutics & ImmunoMonitoring Conference (Jan 31 - Feb 1, 2013 in San Diego)
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) represent a promising therapeutic modality for the clinical management of cancer. Dr. Puja Sapra will use case studies to elaborate on the multifaceted optimization required to yield a viable clinical candidate ADC. ADCs employing different mechanism of action ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
[Press-News.org] Testing can be useful for students and teachers, promoting long-term learningThe right tests can promote long-term, transferable learning