(Press-News.org) Overnight on October 4-5, 2012, a mass of energetic particles from the atmosphere of the Sun were flung out into space, a phenomenon known as a coronal mass ejection. Three days later, the storm from the Sun stirred up the magnetic field around Earth and produced gorgeous displays of northern lights. NASA satellites track such storms from their origin to their crossing of interplanetary space to their arrival in the atmosphere of Earth.
Using the "day-night band" (DNB) of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite acquired this view of the aurora borealis early on the morning of October 8, 2012. The northern lights stretch across Canada's Quebec and Ontario provinces in the image, and are part of the auroral oval that expanded to middle latitudes because of a geomagnetic storm.
The DNB sensor detects dim light signals such as auroras, airglow, gas flares, city lights, and reflected moonlight. In the case of the image above, the sensor detected the visible light emissions as energetic particles rained down from Earth's magnetosphere and into the gases of the upper atmosphere. The images are similar to those collected by the Operational Linescan System flown on U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites for the past three decades.
Auroras typically occur when solar flares and coronal mass ejections—or even an active solar wind stream—disturb and distort the magnetosphere, the cocoon of space protected by Earth's magnetic field. The collision of solar particles and pressure into our planet's magnetosphere accelerates particles trapped in the space around Earth (such as in the radiation belts). Those particles are sent crashing down into Earth's upper atmosphere—at altitudes of 100 to 400 kilometers (60 to 250 miles)—where they excite oxygen and nitrogen molecules and release photons of light. The results are rays, sheets, and curtains of dancing light in the sky.
Auroras are a beautiful expression of the connection between Sun and Earth, but not all of the connections are benign. Auroras are connected to geomagnetic storms, which can distort radio communications (particularly high frequencies), disrupt electric power systems on the ground, and give slight but detectable doses of radiation to flight crews and passengers on high-latitude airplane flights and on spacecraft.
The advantage of images like those from VIIRS and DMSP is resolution, according to space physicist Patrick Newell of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. "You can see very fine detail in the aurora because of the low altitude and the high resolution of the camera," he said. Most aurora scientists prefer to use images from missions dedicated to aurora studies (such as Polar, IMAGE, and ground-based imagers), which can offer many more images of a storm (rather than one per orbit) and can allow researchers to calculate the energy moving through the atmosphere. There are no science satellites flying right now that provide such a view, though astronauts regularly photograph and film auroras from the International Space Station.
INFORMATION:
Suomi NPP satellite sees auroras over North America
2012-10-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
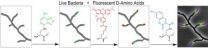
Filming bacterial life in multicolor as a new diagnostic and antibiotic discovery tool
2012-10-11
An international team of scientists led by Indiana University chemist Michael S. VanNieuwenhze and biologist Yves Brun has discovered a revolutionary new method for coloring the cell wall of bacterial cells to determine how they grow, in turn providing a new, much-needed tool for the development of new antibiotics.
Discovery of the new method is expected to broadly impact both basic and applied research tied to understanding, controlling or preventing bacterial cell growth in specific environments, said the two scientists in IU Bloomington's College of Arts and Sciences. ...
Choreography of submerged whale lunges revealed
2012-10-11
Returning briefly to the surface for great lungfuls of air, the underwater lifestyles of whales had been a complete mystery until a small group of pioneers from various global institutions – including Malene Simon, Mark Johnson and Peter Madsen – began attaching data-logging tags to these enigmatic creatures. Knowing that Jeremy Goldbogen and colleagues had successful tagged blue, fin and humpback whales to reveal how they lunge through giant shoals of krill, Simon and her colleagues headed off to Greenland where they tagged five humpback whales to discover how the animals ...
Soft-shelled turtles urinate through mouth
2012-10-11
Chinese soft-shelled turtles are exquisitely adapted to their aquatic lifestyle, sitting contentedly on the bottom of brackish muddy swamps or snorkelling at the surface to breath. According to Y. K. Ip from the National University of Singapore, they even immerse their heads in puddles when their swampy homes dry up: which intrigued Ip and his colleagues. Why do these air-breathing turtles submerge their heads when they mainly depend on their lungs to breathe and are unlikely to breathe in water? Given that some fish excrete waste nitrogen as urea – in addition to ammonia ...
Techniques used to infer pathways of protein evolution found unreliable
2012-10-11
A key assumption that biologists have relied on widely over the past quarter-century in studying the evolution of protein molecules is "highly questionable," according to an article published in the November issue of BioScience.
The article, by Shozo Yokoyama, a vision researcher at Emory University, summarizes experimental work that involved creating and measuring the properties of dozens of reconstructed ancestral versions of visual pigments found in the eyes of vertebrates, including humans, as well as deliberately altered variants. Yokoyama concludes that the studies ...
How food marketers can help consumers eat better while improving their bottom line!
2012-10-11
Food marketers are masters at getting people to crave and consume the foods that they promote. In this study authors Dr. Brian Wansink, co-director of the Cornell University Center for Behavioral Economics in Child Nutrition and Professor of Marketing and Dr. Pierre Chandon, professor of Marketing at the leading French graduate school of business, INSEAD challenge popular assumptions that link food marketing and obesity. Their findings presented last weekend at the Association for Consumer Research Conference in Vancouver, Canada point to ways in which smart food marketers ...
Prospective Alzheimer's drug builds new brain cell connections
2012-10-11
PULLMAN, Wash.—Washington State University researchers have developed a new drug candidate that dramatically improves the cognitive function of rats with Alzheimer's-like mental impairment.
Their compound, which is intended to repair brain damage that has already occurred, is a significant departure from current Alzheimer's treatments, which either slow the process of cell death or inhibit cholinesterase, an enzyme believed to break down a key neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory development.
Such drugs, says Joe Harding, a professor in WSU's College of Veterinary ...
The Marshmallow Study revisited
2012-10-11
For the past four decades, the "marshmallow test" has served as a classic experimental measure of children's self-control: will a preschooler eat one of the fluffy white confections now or hold out for two later?
Now a new study demonstrates that being able to delay gratification is influenced as much by the environment as by innate ability. Children who experienced reliable interactions immediately before the marshmallow task waited on average four times longer—12 versus three minutes—than youngsters in similar but unreliable situations.
"Our results definitely ...
Michelle Salater, CEO of Sumer, LLC, to Host New Podcast Show for Entrepreneurs to Hear Business Confessions
2012-10-11
Michelle Salater will host an extension of her business blog, Copy Doodle, in a new radio show that will focus on helping businesses grow and become more profitable.
Business Confessional Talk Radio: Where Entrepreneurs Gather and Experts Tell All is featured on the Entrepreneur Podcast Network, a platform that condenses advice, information, and inspiration into one space.
Geared toward an audience of entrepreneurs in different stages of their businesses, this show will invite innovative and successful business owners to answer questions and discuss the recipe for ...
Promising Pop Newcomer Courtney Rau Releases "Thanks, But No Thanks" On ITunes
2012-10-11
This new singer is continuing to make impressive music that showcases her keen sense of sound and style and natural talent. Following the successes of her previous single, Courtney has now released her highly anticipated single "Thanks, But No Thanks" on iTunes.
An energetic tune with an empowering tone, Courtney's latest release, "Thanks, But No Thanks," charges the listener, leaving them wanting more. It has a melody that makes it an easy one to play again and again, enlivening and uplifting with its catchy beat and great sense of energy. Now available ...
Lighthouse for the Blind-Saint Louis Wins Contract to Provide Disaster Response Emergency Supplies to U.S. Navy
2012-10-11
The Lighthouse for the Blind-St. Louis, a not-for-profit manufacturing and packaging organization with a dedicated social service mission, has been awarded a contract to provide supplies for use by U.S. Navy Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear and Explosives (CBRNE) disaster response groups.
Under the contract awarded by the federal AbilityOne program, the Lighthouse will utilize employees who are blind in fulfillment operations to pack orders for many types of personal protective equipment and ship these essential supplies to more than 65 U.S. Navy sites around ...