(Press-News.org) Lead scientist Professor Simon Cutting, from the School of Biological Sciences at Royal Holloway, has developed the jabs through the use of probiotic spores. He carried out fundamental studies into the biology of the bacterium Bacillus subtilis which attracted the attention of microbiologists due to its ability to form spores that can last millions of years before germinating under the appropriate environmental conditions.
Professor Cutting says: "The mechanisms by which this process occurs have fascinated microbiologists for decades making it one of the most intensively studied bacteria. Its simple life cycle and ease of use make it an ideal laboratory subject."
Professor Cutting discovered that the Bacillus spores act as ideal vehicles to carry antigens and promote an immune response. He explains: "Rather than requiring needle delivery, vaccines based on Bacillus spores can be delivered via a nasal spray, or as on oral liquid or capsule. Alternatively they can be administered via a small soluble film placed under the tongue, in a similar way to modern breath freshners. As spores are exceptionally stable, vaccines based on Bacillus do not require cold-chain storage alleviating a further issue with current vaccine approaches."
As well as eliminating the pain associated with needles, oral vaccines provide greater benefits including being safer to administer, especially in developing countries where HIV is rife, being inexpensive to produce and easier to store and reducing concerns of adverse reactions.
Professor Cutting has carried out pre-clinical evaluation of Bacillus-based vaccines for a number of diseases including Tuberculosis, influenza and tetanus but most recently he has been investigating the potential for use of the vaccines against a disease of particular relevance to the West - Clostridium difficile
"C. difficile, is a gastrointenstinal infection that is commonly picked up following hospital stays and causes around 50,000 infections and 4,000 deaths per year in the UK, mostly in elderly patients. Currently, there is no vaccine against the disease, and although several approaches are currently undergoing clinical trials, none are expected to provide full protection, and new solutions are urgently needed," says Professor Cutting.
He adds: "Bacillus based vaccines offer distinct advantages as unlike other approaches, oral delivery can cause a more specific immune response in the gastrointenstinal tract to fully eliminate C.difficile."
Professor Cutting has recently received private seed investment to form a company, Holloway Immunology, to develop the bacillus vaccine technology and concentrate on three lead vaccines for Tuberculosis, C. difficile infection and influenza (flu). The company is currently looking for investors to help fast track the implementation of these jabs and contribute to the transformation of vaccine delivery around the globe.
### END
Next-generation vaccines -- eliminating the use of needles
2012-10-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
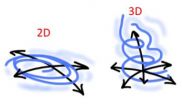
Turbulent flows in 2D can be calculated in new model
2012-10-23
Turbulent flows have challenged researchers for centuries. It is impossible to predict chaotic weather more than a week in advance. Wind resistance on a plane or a car cannot be calculated precisely, since it is determined by atmospheric turbulence. Now, however, researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute have succeeded in developing a statistical model that can replicate the chaotic flows and thereby provide a better understanding of the process. The research results are published in the scientific journal, Physics of Fluids.
"Without knowing the movements in detail, we ...
Quantum computing with recycled particles
2012-10-23
A research team from the University of Bristol's Centre for Quantum Photonics (CQP) have brought the reality of a quantum computer one step closer by experimentally demonstrating a technique for significantly reducing the physical resources required for quantum factoring.
The team have shown how it is possible to recycle the particles inside a quantum computer, so that quantum factoring can be achieved with only one third of the particles originally required. The research is published in the latest issue of Nature Photonics.
Using photons as the particles, the Bristol ...
A circuit diagram of the mouse brain
2012-10-23
This press release is available in German.
What happens in the brain when we see, hear, think and remember? To be able to answer questions like this, neuroscientists need information about how the millions of neurons in the brain are connected to each other. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg have taken a crucial step towards obtaining a complete circuit diagram of the brain of the mouse, a key model organism for the neurosciences. The research group working with Winfried Denk has developed a method for preparing the whole mouse ...
Lung mucus gel scaffold prevents nanoparticles from getting through
2012-10-23
Mucus coats our airways' internal surfaces. The viscous gel humidifies the lungs and prevents viruses and other small particles like diesel soot from entering the body unchecked. Previously unclear was the extent to which such nanoparticles are able to move through the lungs' mucus. Here, the research evidence was contradictory. Scientists could not explain why, in inhaled medication development, drug nanoparticles often simply got stuck in the mucus never making it to their target destination inside the lung cells.
Now, as part of a German Research Foundation (DFG)-funded ...
The complex association between moderate alcohol consumption and breast cancer
2012-10-23
An excellent review article from two scientists at the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism in the USA to be published in Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2012, describes the epidemiologic and basic scientific evidence linking alcohol consumption to the risk of breast cancer.
The authors point out deficiencies in the epidemiologic data, especially that the pattern of drinking (regular moderate versus binge drinking) has generally not been taken into consideration, important given that binge drinking is associated with much higher blood alcohol concentrations and acetaldehyde ...
TIM and TAM: 2 paths used by the Dengue virus to penetrate cells
2012-10-23
By demonstrating that it is possible to inhibit the viral infection in vitro by blocking the bonding between the virus and these receptors, the researchers have opened the way to a new antiviral strategy. These works were published on line in the review "Cell Host & Microbe" of October 18, 2012.
The Dengue virus circulates in four different forms (four serotypes). It is transmitted to humans by mosquitoes. It is a major public health problem. Two billion people throughout the world are exposed to the risk of infection and 50 million cases of Dengue fever are recorded by ...
19 species of ferns named for Lady Gaga
2012-10-23
DURHAM, N.C. -- Pop music megastar Lady Gaga is being honored with the name of a new genus of ferns found in Central and South America, Mexico, Arizona and Texas. A genus is a group of closely related species; in this case, 19 species of ferns will carry the name Gaga.
At one stage of its life, the new genus Gaga has somewhat fluid definitions of gender and bears a striking resemblance to one of Gaga's famous costumes. Members of the new genus also bear a distinct DNA sequence spelling GAGA.
Two of the species in the Gaga genus are new to science: Gaga germanotta from ...
Moffitt researchers study how patterns, timing of sunlight exposure contribute to skin cancers
2012-10-23
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center, the University of South Florida and the International Agency for Research on Cancer in France have studied the patterns and timing of sunlight exposure and how each is related to two nonmelanoma skin cancers – basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
This study, published in the open-access journal BioMed Central, is the first case-control study to simultaneously evaluate identical patterns and timing of sunlight exposure as they are related to basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas in the same U.S. population with high ...
Vanderbilt researchers find that diabetes drug could be effective in treating addiction
2012-10-23
Vanderbilt researchers are reporting today that a drug currently used to treat type 2 diabetes could be just as effective in treating addiction to drugs, including cocaine.
The findings, published online today as a Letter To The Editor in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, could have far-reaching implications for patients worldwide who suffer from addiction.
"What we have demonstrated is that a brain mechanism already known to be therapeutic for the treatment of diabetes also appears to be implicated in at least certain types of drug addiction," said Gregg Stanwood, ...
New American Chemical Society videos celebrate 25 years of National Chemistry Week
2012-10-23
WASHINGTON, Oct. 23, 2012 — The American Chemical Society (ACS) today released two new videos celebrating the 25th Anniversary of National Chemistry Week (NCW). The videos, from the world's largest scientific society, coincide with the start of this year's NCW, being observed in hundreds of communities around the country. Both videos are available now at www.BytesizeScience.com.
One video is a new episode of ACS' award-winning Bytesize Science series. It highlights research behind this year's NCW theme — nanotechnology. The second video is a retrospective on the history ...