(Press-News.org) Amphibians are the vertebrate group that is more likely to become roadkill in Catalonia, even more so than reptiles, mammals and birds. This is the case according to an international team of scientists who have concluded that highly protected areas are home to more cases of animal death on the roads.
Our network of roads is considered one of the main threats to fauna survival. Researchers at the universities of Barcelona (UB), Porto (Portugal) and Uppsala (Sweden) have studied the number of vertebrate deaths on 820 kilometres of road in North Eastern area of Spain and Portugal.
"The project consisted of analysing the impact of the road network on fauna, leading to numerous studies across the whole of Catalonia to record all specimens of roadkill found," as explained to SINC by Núria Garriga, researcher at the UB and lead author of the study headed by Gustavo A. Llorente, a scientist at the same university.
Field work was published in the 'Biodiversity and Conservation' journal and was carried out over four years on 41 secondary roads in Catalonia. Some 20 km of each road were inspected during summer and autumn. As Garriga points out, "there are few studies on an international level that have carried out such an extensive research and sampling."
Nature reserves like Parc Natural dels Aiguamolls de l'Empordà, Parc del Garraf, Parc Natural de la Zona Volcànica de la Garrotxa, Parc Natural de Sant Llorenç del Munt i l'Obac and Parc Natural del Montseny.
"We got in a slow moving car to collect data. When we spotted a dead animal we would stop, make a record and note down the species. We also took down other significant information like surrounding vegetation and the closest water points," outlines the researcher.
One of the main conclusions of the study was that amphibians are more likely to become roadkill and that roads within nature reserves and natural parks are home to the highest number of animal road deaths.
"This could be explained by the fact that protected areas frequently receive a high number of visitors, which in turn increases the flow of traffic in places that are teaming with wild life," ensures the researcher.
According to the experts, to decrease amphibian death we would have to build special passages for them in high-risk areas. These come in the form of tunnels under the road designed to allow the passage of animals.
The team is currently working to identify hotspots. They therefore inspected seven roads throughout an entire year to define the most dangerous areas and protect them.
References:
Núria Garriga, Xavier Santos, Albert Montori, Alex Richter-Boix, Marc Franch, Gustavo A. Llorente. "Are protected areas truly protected? The impact of road traffic on vertebrate fauna" Biodiversity and Conservation 21: 2761. DOI 10.1007/s10531-012-0332-0.
INFORMATION:
The majority of roadkill amongst vertebrates in Catalonia are in protected areas
2012-10-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New insights into membrane-assisted self-assembly
2012-10-24
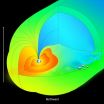
"In our current paper we present new computational results that explore how membranes may influence crucial biological processes", explains Richard Matthews, Lise-Meitner-Fellow at the University of Vienna and first author of the study. The focus of the investigation is the self-assembly of microscopic particles, the formation of structures or patterns without human intervention. More specifically, the effect of the interactions between membranes and proteins, which can influence the formation of ordered structures in cells, is considered.
Self-assembly has become a hot ...
Study: Flame retardant 'Firemaster 550' is an endocrine disruptor
2012-10-24
The flame-retardant mixture known as "Firemaster 550" is an endocrine disruptor that causes extreme weight gain, early onset of puberty and cardiovascular health effects in lab animals, according to a new study spearheaded by researchers from North Carolina State University and Duke University.
Firemaster 550 is made up of four principal component chemicals and is used in polyurethane foam in a wide variety of products, ranging from mattresses to infant nursing pillows. The flame-retardant mixture was developed by Chemtura Corp., and was first identified by the research ...
Voice prostheses can help patients regain their lost voice
2012-10-24
Help is on the way for people who suffer from vocal cord dysfunction. Researchers are developing methods that will contribute to manufacturing voice prostheses with improved affective features. For example, for little girls who have lost their voices, the improved artificial voice devices can produce age-appropriate voices, instead of the usual voice of an adult male. These advances in artificial voice production have been made possible by results achieved in a research project led by Professor Samuli Siltanen, results that are good news indeed for the approximately 30,000 ...
Unearthing a hidden dietary behavior
2012-10-24
Though it was identified as a disorder as early as the 14th century, pica, or the eating of non-food items, has for years believed to be all but non-existent in a few corners of the globe – a 2006 study that reviewed research on pica found just four regions – the South of South America, Japan, Korea and Madagascar –where the behavior had never been observed.
A new Harvard study, however, is showing that pica – and particularly geophagy, or the eating of soil or clay, is far more prevalent in Madagascar, and may be more prevalent worldwide, than researchers previously ...
Hypnosis helps hot flashes
2012-10-24
CLEVELAND, Ohio (October 24, 2012)—Hypnosis can help cut hot flashes by as much as 74%, shows a study supported by the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine. This is the first controlled, randomized study of the technique to manage hot flashes, which affect as much as 80% of women who go through menopause. The study was published online this month in Menopause, the journal of the North American Menopause Society.
Controlled, randomized studies may pit an active drug against an inactive placebo pill. But it's hard to find a placebo for mind-body techniques. ...
Brainwave training boosts network for cognitive control and affects mind-wandering
2012-10-24
A breakthrough study conducted in Canada has found that training of the well-known brainwave in humans, the alpha rhythm, enhances a brain network responsible for cognitive-control. The training technique, termed neurofeedback, is being considered as a promising new method for restoring brain function in mental disorders. Using several neuroimaging methods, a team of researchers at the Western University and the Lawson Health Research Institute have now uncovered that functional changes within a key brain network occur directly after a 30-minute session of noninvasive, ...
Earth's magnetosphere behaves like a sieve
2012-10-24
ESA's quartet of satellites studying Earth's magnetosphere, Cluster, has discovered that our protective magnetic bubble lets the solar wind in under a wider range of conditions than previously believed.
Earth's magnetic field is our planet's first line of defence against the bombardment of the solar wind. This stream of plasma is launched by the Sun and travels across the Solar System, carrying its own magnetic field with it.
Depending on how the solar wind's interplanetary magnetic field – IMF – is aligned with Earth's magnetic field, different phenomena can arise ...
An eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth
2012-10-24
This press release is available in German.
It all began with a harmless game of soccer among young men in northwestern Albania. After one of the players had been injured in a subsequent dispute, his team members shot a relative of the suspected attacker. Now the male members of the families involved in the blood feud do not dare leave their homes. Such vendettas and blood feuds occur in many societies, sometimes lasting for decades. The harm for the participants is enormous and lacks apparent benefit, as the participants often no longer remember what actually triggered ...
Lactation protein suppresses tumors and metastasis in breast cancer
2012-10-24
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- A protein that is necessary for lactation in mammals inhibits the critical cellular transition that is an early indicator of breast cancer and metastasis, according to research conducted at the University at Buffalo and Princeton University and highlighted as the cover paper in November issue of Nature Cell Biology.
"This is the first confirmed report that this protein, called Elf5, is a tumor suppressor in breast cancer," explains Satrajit Sinha, PhD, associate professor of biochemistry in the UB School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences and a corresponding ...
Hot flashes can come back after SSRI
2012-10-24
CLEVELAND, Ohio (October 24, 2012)—Hot flashes and night sweats can return after women stop using escitalopram—an antidepressant—to treat these menopause symptoms, according to a study published online this month in Menopause, the journal of the North American Menopause Society. This is typical of stopping hormone therapy as well.
Not every woman who took escitalopram in this National Institutes of Health-supported study had her symptoms come back, however. Symptoms returned for only about one third of the women. These women were more likely than others to have had insomnia, ...