(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Employees who are more satisfied with their pay report lower levels of work-family conflict, a study by a University of Illinois labor and employment relations professor shows.
A worker's actual salary is as important as pay satisfaction in determining a worker's happiness, according to the research by professor Amit Kramer.
"Pay, as you might expect, is a relative thing," Kramer said. "I think most people would agree that a certain level of pay that allows you to meet your needs is critical. However, beyond that level, relative pay becomes an issue and with it, perception of pay or pay satisfaction."
Kramer, who co-wrote the study with Devasheesh P. Bhave, of Concordia University, and Theresa M. Glomb, of the University of Minnesota, says once workers achieve this "sufficient" level of pay, they shift their reference point from what their actual pay allows them to do, to other social reference points such as how much their peers are paid.
"It becomes 'my pay' compared to others; 'my pay' compared to the effort I invest; 'my pay' compared to the things I give up and miss in life for the opportunity cost of working," he said. "Organizations believe that actual pay is the No. 1 incentive for employees. While this may be true for some employees, for others the social aspects of pay and the things they perceive to be sacrificing for pay are stronger or act as additional incentives and disincentives."
The effect of a pay raise on pay satisfaction only has a moderate relationship, Kramer says.
"I'm not sure that the effect of a pay raise lasts very long," he said. "It might have a short-term effect on pay satisfaction, but individuals are likely to regress to their initial pay satisfaction level over time. As an example, when employees change jobs, they
re-evaluate their pay and are more likely to change their pay satisfaction, not necessarily because they get a raise, but because of the social aspect of pay. And the way individuals evaluate their pay is by comparing their pay relative to their co-workers' pay, relative to the effort the put in, and relative to what they sacrifice in order to work."
According to the study, even highly compensated employees report high
work-family conflict because they, too, can perceive pay inequity among colleagues. So what can employers do – if anything – to increase pay satisfaction among employees?
A lot, Kramer says.
"If employees perceive work as a sacrifice they have to make, then the work environment itself is not ideal," he said. "If employers can understand the trade-offs employees perceive to be doing – sacrificing family for work, for example – then they can offer different work arrangements and policies that compensate for that. Flexible work arrangements, paid vacation days and compressed workweeks would be good examples of this. It also might be ideal to tailor policies and benefits based on different needs of employees, since each employee will perceive that they are making different trade-offs."
The only downside to such benefits is that they're expensive, and they usually can't be offered to all employees, Kramer says.
"Firms will usually only offer these type of working arrangements to workers who are expensive to recruit, retain and replace – the high-performing, star employees," he said.
With Americans among the world leaders in hours worked and worker productivity, Kramer says the research speaks to the need for more family-and
life-friendly policies in the workplace.
"In a time when the boundaries between work, life and family are so blurred with the increased use of technology that allows many employees to work everywhere, anytime, I think employers should consider offering flexible work arrangements to employees who can perform their work off-site and off-schedule," he said. "That type of a flexible policy that would allow all employees – not just those with families – to better balance work, family and life demands as they see fit."
Family demands can come from many different sources, all of which require different kinds of flexibility, Kramer says.
"Young children demand more emergency-type flexibility – for example, leaving work on short notice to pickup a sick child from daycare, or staying home with a sick child," he said. "Older children require more 'planned' flexibility – for example, a week of college visits – while elder parents, like young children, need more short-notice, emergency-type flexibility."
INFORMATION:
The study will be published in the Journal of Organizational Behavior.
Editor's note: To contact Amit Kramer, call 217-333-3118; email
Research: Pay satisfaction key driver of work-family conflict
2012-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Texas at Austin study measures methane emissions released from natural gas production
2012-10-30
A research team led by The University of Texas at Austin, and including engineering and environmental testing firms URS and Aerodyne Research, is conducting a major field study to measure methane emissions from natural gas production, about which little empirical data exist. With a goal of obtaining scientifically rigorous, representative data from multiple producing basins, the study brings together Environmental Defense Fund (EDF), the university and nine of the nation's leading natural gas producers: Anadarko Petroleum Corporation, BG Group plc, Chevron, Encana Oil & ...
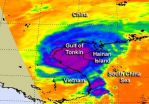
NASA sees Tropical Storm Son-Tinh fill the Gulf of Tonkin
2012-10-30
Tropical Storm Son-tinh made landfall in northern Vietnam is and is curving to the northeast to track over southern China. NASA's Aqua satellite revealed powerful thunderstorms around the storm's center before it made landfall and as it filled up the Gulf of Tonkin.
On Oct. 28 at 0553 UTC (2:53 a.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared imagery of Tropical Storm Son-tinh that showed a concentration of strong thunderstorms around the storm's center before it made landfall. Son-tinh was located over the Gulf ...
Early autism intervention improves brain responses to social cues
2012-10-30
An autism intervention program that emphasizes social interactions and is designed for children as young as 12 months has been found to improve cognitive skills and brain responses to faces, considered a building block for social skills. The researchers say that the study, which was completed at the University of Washington, is the first to demonstrate that an intensive behavioral intervention can change brain function in toddlers with autism spectrum disorders.
"So much of a toddler's learning involves social interaction, and early intervention that promotes attention ...
NASA examines Hurricane Sandy as it affects the eastern US
2012-10-30
On Monday, Oct. 29, Hurricane Sandy was ravaging the Mid-Atlantic with heavy rains and tropical storm force winds as it closed in for landfall. Earlier, NASA's CloudSat satellite passed over Hurricane Sandy and its radar dissected the storm get a profile or sideways look at the storm. NASA's Aqua satellite provided an infrared view of the cloud tops and NOAA's GOES-13 satellite showed the extent of the storm. The National Hurricane Center reported at 11 a.m. EDT on Oct. 29 that Hurricane Sandy is "expected to bring life-threatening storm surge and coastal hurricane winds ...
Higher-math skills entwined with lower-order magnitude sense
2012-10-30
The ability to learn complex, symbolic math is a uniquely human trait, but it is intricately connected to a primitive sense of magnitude that is shared by many animals, finds a study to be published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
"Our results clearly show that uniquely human branches of mathematics interface with an evolutionarily primitive general magnitude system," says lead author Stella Lourenco, a psychologist at Emory University. "We were able to show how variations in both advanced arithmetic and geometry skills specifically correlated ...
Transforming America by redirecting wasted health care dollars
2012-10-30
The respected national Institute of Medicine estimates that $750 billion is lost each year to wasteful or excessive health care spending. This sum includes excess administrative costs, inflated prices, unnecessary services and fraud — dollars that add no value to health and well-being.
If those wasteful costs could be corralled without sacrificing health care quality, how might that money be better spent?
In a study published in the current online edition of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, Frederick J. Zimmerman, professor and chair of the department ...
How silver turns people blue
2012-10-30
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Researchers from Brown University have shown for the first time how ingesting too much silver can cause argyria, a rare condition in which patients' skin turns a striking shade of grayish blue.
"It's the first conceptual model giving the whole picture of how one develops this condition," said Robert Hurt, professor of engineering at Brown and part of the research team. "What's interesting here is that the particles someone ingests aren't the particles that ultimately cause the disorder."
Scientists have known for years argyria had ...
Risk factors predict childhood obesity, researchers find
2012-10-30
High birth weight, rapid weight gain and having an overweight mother who smokes can all increase the risk of a baby becoming obese later in childhood, research by experts at The University of Nottingham has found.
The study, published in the latest edition of the journal Archives of Disease in Childhood, also discovered that children who were breastfed and were introduced to solid food later had a slightly reduced chance of becoming overweight.
The findings come following a systematic review and analysis of data from around 30 previous studies looking at the impact ...
BMJ editor urges Roche to fulfil promise to release Tamiflu trial data
2012-10-30
In an open letter to company director, Professor Sir John Bell, she says: "Billions of pounds of public money have been spent on [Tamiflu] and yet the evidence on its effectiveness and safety remains hidden from appropriate and necessary independent scrutiny."
The letter is published on the BMJ's website (bmj.com/tamiflu
) alongside correspondence by the Cochrane team with Roche, the US Centres for Disease Control (CDC) and the World Health Organisation (WHO), as part of an open data campaign aimed at persuading Roche to give doctors and patients access to the full data ...
More than good vibes: Researchers propose the science behind mindfulness
2012-10-30
BOSTON, MA—Achieving mindfulness through meditation has helped people maintain a healthy mind by quelling negative emotions and thoughts, such as desire, anger and anxiety, and encouraging more positive dispositions such as compassion, empathy and forgiveness. Those who have reaped the benefits of mindfulness know that it works. But how exactly does it work?
Researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) have proposed a new model that shifts how we think about mindfulness. Rather than describing mindfulness as a single dimension of cognition, the researchers demonstrate ...