(Press-News.org) COLUMBIA, Mo. -- In today's globalized economy, a large percentage of apparel products are multinational products as raw materials are produced, transported and assembled in different countries. However, consumers have little information about where and to what extent their apparel is produced domestically or overseas. Now, University of Missouri researchers have found that American consumers place a much higher value on apparel produced entirely in the US with US raw materials as opposed to products produced partially or entirely overseas. The value is so high, in fact, that MU experts worry it could be damaging to US apparel manufacturing businesses and the overall economy.
In a study published in Clothing and Textiles Research Journal, Jung Ha-Brookshire, an assistant professor in the textile and apparel management department in the College of Human Environmental Sciences at MU, surveyed American consumers to determine the value they place on apparel produced in different countries. She showed participants a cotton shirt, told them it was made in China, and said it sold for $40 in retail stores. She then showed them the same piece of clothing and told them it was made in the US with US cotton. The study participants valued the US cotton shirt at $57, which is more than 42 percent higher than the same shirt produced in China. Ha-Brookshire says this demonstrates a troubling trend for American consumers.
"Americans tend to severely overvalue apparel produced entirely in the US," Ha-Brookshire said. "This is concerning because if Americans place higher values on these US products, they perceive those products to be too expensive and are less likely to buy them, opting instead to buy similar Chinese-made products perceived to be more in their price range. To help US apparel businesses create and maintain domestic jobs, American consumers need to have a realistic understanding of the value of apparel made in the US."
One positive finding in Ha-Brookshire's study was that American consumers do value apparel made with US-grown cotton, even if the finished goods are manufactured overseas. When she showed the survey participants the same cotton shirt and told them it was made in China from US cotton, participants valued the shirt at $47, or 17 percent higher than a shirt with only a "Made in China" label. Ha-Brookshire says this increased value is not large enough to be prohibitive for consumers.
"US cotton growers can utilize these findings by better indicating what apparel is manufactured from their cotton," Ha-Brookshire said. "Currently, retailers are only required to indicate where the apparel was manufactured or sewn, but if consumers could see that apparel produced in China was made with US cotton, they would probably be more likely to purchase it."
Ha-Brookshire also will present her research in November at the Textile Product Labeling Summit at the University of Missouri. The summit will consist of discussions among national policy makers, researchers, consumer advocates and industry leaders about important topics regarding current textile product labeling practices and regulations. For more information about the summit, visit http://muconf.missouri.edu/textilelabeling/index.html.
### END
American consumers overvalue US-produced apparel, MU study finds
Consumer trend could be damaging to American apparel manufacturing businesses and US economy
2012-10-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study suggests new way to prevent recurrent ear infections
2012-10-31
Eliminating bacteria's DNA and boosting antimicrobial proteins that already exist may help prevent middle ear infections from reoccurring. These are the findings from a Nationwide Children's Hospital study that examined how an immune defense protein common in the middle ear interacts with a structure meant to protect a colony of bacteria.
The bacterium nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHI) causes a wide range of diseases of both the lower and upper airways, including middle ear infection. NTHI, like most other bacteria, can form a biofilm, a robust community of ...
Finding triggers of birth defects in an embryo heart
2012-10-31
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University have found a way to create three-dimensional maps of the stress that circulating blood places on the developing heart in an animal model – a key to understanding triggers of heart defects.
The team has begun testing the technology to uncover how alcohol, drugs and other factors set off events that result in defects found in newborn humans.
Passing blood cells drag on the endothelial cells that line the growing heart, a phenomenon called shear stress, which has been linked to changes in gene expression that results in defects, ...
Low-resistance connections facilitate multi-walled carbon nanotubes for interconnects
2012-10-31
Using a new method for precisely controlling the deposition of carbon, researchers have demonstrated a technique for connecting multi-walled carbon nanotubes to the metallic pads of integrated circuits without the high interface resistance produced by traditional fabrication techniques.
Based on electron beam-induced deposition (EBID), the work is believed to be the first to connect multiple shells of a multi-walled carbon nanotube to metal terminals on a semiconducting substrate, which is relevant to integrated circuit fabrication. Using this three-dimensional fabrication ...
Bullying has long-term health consequences
2012-10-31
HUNTSVILLE, TX (10/30/12) -- Childhood bullying can lead to long term health consequences, including general and mental health issues, behavioral problems, eating disorders, smoking, alcohol use, and homelessness, a study by the Crime Victims' Institute at Sam Houston State University found.
"What is apparent from these results is that bullying victimization that occurs early in life may have significant and substantial consequences for those victims later in life," said Leana Bouffard, Director of the Crime Victims' Institute. "Thus, the adverse health consequences of ...
Metabolic syndrome makes a difference in hormone therapy risk
2012-10-31
CLEVELAND, Ohio (October 29, 2012)—A new analysis of the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) trials show that women who had metabolic syndrome before they started hormone therapy had a greatly increased risk of heart attack or dying of heart disease. Women who didn't have metabolic syndrome beforehand showed no increased risk. The study was published this month online in Menopause, the journal of the North American Menopause Society.
"Our findings emphasize the importance of assessing cardiovascular disease risk status when hormone therapy is considered for relief of menopausal ...
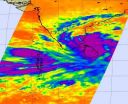
ASA infrared eye sees tropical cyclone Nilam soak Sri Lanka
2012-10-31
Tropical Storm 02B was renamed Tropical Cyclone Nilam when NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of the storm soaking Sri Lanka on its crawl to a landfall in southern India.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Tropical Cyclone Nilam on Oct. 29 at 2029 4:29 p.m. EDT. At the time of the AIRS image, the strongest storms with coldest cloud top temperatures were covering Sri Lanka and stretched into the open waters of the Northern Indian Ocean. Cloud top temperatures in those areas were ...
NASA satellites capture Hurricane Sandy's massive size
2012-10-31
NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image Sandy's massive circulation. Sandy covers 1.8 million square miles, from the Mid-Atlantic to the Ohio Valley, into Canada and New England.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image Sandy's massive circulation on October 29 at 18:20 UTC (2:20 p.m. EDT). Sandy covered 1.8 million square miles, from the Mid-Atlantic to the Ohio Valley, into Canada and New England. Sandy made landfall hours after the MODIS image was taken.
Sandy was still a hurricane ...
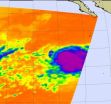
NASA sees Tropical Storm Rosa being born and powering up quickly
2012-10-31
The seventeenth tropical depression of the eastern Pacific Ocean hurricane season formed early on October 30 and quickly strengthened into Tropical Storm Rosa. Infrared data from NASA's Aqua satellite revealed strong convection in the storm's center, hinting at that intensification.
When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Depression 17E at 5:41 a.m. EDT (0951 UTC) on Tuesday, October 30, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument took an infrared picture of the storm. The AIRS data showed a large, circular area of very strong convection (rising air that ...
Women with lupus have a higher risk for preeclampsia
2012-10-31
New research reports that women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have a two-fold increase in risk of preeclampsia—a dangerous condition in which pregnant women develop high blood pressure (hypertension) and protein in their urine (proteinuria) after 20 weeks of gestation. According to the findings published in Arthritis Care & Research, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), use of Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) during pregnancy was rare in the study population, but women who did use these medications show a statistically non-significant ...
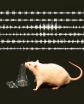
Animals learn to fine-tune their sniffs
2012-10-31
Animals use their noses to focus their sense of smell, much the same way that humans focus their eyes, new research at the University of Chicago shows.
A research team studying rats found that animals adjust their sense of smell through sniffing techniques that bring scents to receptors in different parts of the nose. The sniffing patterns changed according to what kind of substance the rats were attempting to detect.
The sense of smell is particularly important for many animals, as they need it to detect predators and to search out food. "Dogs, for instance, are quite ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
[Press-News.org] American consumers overvalue US-produced apparel, MU study findsConsumer trend could be damaging to American apparel manufacturing businesses and US economy