(Press-News.org) This colourful view of the globular star cluster NGC 6362 was captured by the Wide Field Imager attached to the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope at ESO's La Silla Observatory in Chile. This new picture, along with a new image of the central region from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, provide the best view of this little-known cluster ever obtained. Globular clusters are mainly composed of tens of thousands of very ancient stars, but they also contain some stars that look suspiciously young.
Globular star clusters are among the oldest objects in the Universe, and NGC 6362 cannot hide its age in this picture. The many yellowish stars in the cluster have already run through much of their lives and become red giant stars. But globular clusters are not static relics from the past -- some curious stellar activities are still going on in these dense star cities.
For instance, NGC 6362 is home to many blue stragglers -- old stars that really do succeed in passing for a younger age. All of the stars in a globular cluster formed from the same material at roughly the same time (typically, about 10 billion years ago for most globulars). Yet blue stragglers are bluer and more luminous -- and hence more massive -- than they should be after ten billion years of stellar evolution. Blue stars are hot and consume their fuel quickly, so if these stars had formed about ten billion years ago, then they should have fizzled out long ago. How did they survive?
Astronomers are keen to understand the secret of the youthful appearance of blue stragglers. Currently, there are two main theories: stars colliding and merging, and a transfer of material between two companion stars. The basic idea behind both of these options is that the stars were not born as big as we see them today, but that they received an injection of extra material at some point during their lifetimes and this then gave them a new lease of life.
Although less well known than some brighter globular clusters, NGC 6362 holds much that is of interest to astronomers and has been well studied over the years. It was selected as one of the 160 stellar fields for the Pre-FLAMES Survey -- a preliminary survey conducted between 1999 and 2002 using the 2.2-metre telescope at La Silla to find suitable stars for follow-up observations with the VLT's spectroscopic instrument FLAMES. The picture here comes from data collected as part of this survey.
The new image shows the entire cluster against a rich background of the carpet of stars in the Milky Way. The central parts of NGC 6362 have also been [studied in detail][1] by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. The Hubble view shows a much smaller area of sky in much greater detail. The two views -- one wide-angle and one zoomed in -- complement each other perfectly.
This brilliant ball of stars lies in the southern constellation of Ara (The Altar). It can be easily seen in a small telescope. It was first spotted in 1826 by the Scottish astronomer James Dunlop using a 22-centimetre telescope in Australia.
INFORMATION:
[1]: http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/potw1244a/ (studied in detail)
More information
The year 2012 marks the 50th anniversary of the founding of the European Southern Observatory (ESO). ESO is the foremost intergovernmental astronomy organisation in Europe and the world's most productive astronomical observatory. It is supported by 15 countries: Austria, Belgium, Brazil, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. ESO carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities enabling astronomers to make important scientific discoveries. ESO also plays a leading role in promoting and organising cooperation in astronomical research. ESO operates three unique world-class observing sites in Chile: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope, the world's most advanced visible-light astronomical observatory and two survey telescopes. VISTA works in the infrared and is the world's largest survey telescope and the VLT Survey Telescope is the largest telescope designed to exclusively survey the skies in visible light. ESO is the European partner of a revolutionary astronomical telescope ALMA, the largest astronomical project in existence. ESO is currently planning the 39-metre European Extremely Large optical/near-infrared Telescope, the E-ELT, which will become "the world's biggest eye on the sky".
Links
[Photos of the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope][1]
[Other photos taken with the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope][2]
[Photos of La Silla][3]
[1]: http://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/search/?adv=&subject_name=mpg
[2]: http://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/search/?adv=&facility=15
[3]: http://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/category/lasilla/
Contacts
Richard Hook
ESO, La Silla, Paranal, E-ELT and Survey Telescopes Public Information Officer
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6655
Cell: +49 151 1537 3591
Email: rhook@eso.org
Stars ancient and modern?
2012-10-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Higher risk of maternal complications/preterm deliveries for women undergoing multiple cesareans
2012-10-31
The risk of maternal complications and preterm deliveries is significantly higher for women undergoing their fifth or more caesarean section, finds a new study published today (31 October) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.
The study explored the incidence of UK women having Multiple Repeat Caesarean Sections (MRCS), defined as five or more, and the outcomes for them and their babies compared to women having their second to fourth caesarean section.
The researchers, from Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust and the University of Oxford ...
Stereotactic radiosurgery shows promise for kidney cancer
2012-10-31
CLEVELAND – A first-of-its-kind clinical trial conducted at University Hospitals (UH) Case Medical Center Seidman Cancer Center has shown encouraging results for the use of stereotactic radiosurgery to treat kidney cancer. This non-invasive treatment technique may represent a potential new non-surgical option for patients with this deadly disease who have limited treatment options.
Rod Ellis, MD, lead author of the study along with Lee Ponsky, MD, who is the Principal Investigator, presented results of a Phase 1 clinical trial in 20 patients with localized primary renal ...
Privately owned genetic databases may hinder diagnosis and bar the way to the arrival of personalized medicine
2012-10-31
In response to the on-line publication by the European Journal of Human Genetics today (Wednesday) of an article by US researchers led by Dr. Robert Cook-Degan, a former member of the US Office of Technology Assessment, showing that Myriad Genetics, providers of the BRCA1/2 genetic test in the US, has amassed vast quantities of clinical data without sharing it, Professor Martina Cornel, chair of the European Society of Human Genetics' Professional and Public Policy committee, said:
"We are very concerned that such important data is being withheld from those who most need ...
Obese dogs at risk of health condition experienced by humans
2012-10-31
Veterinary scientists at the University of Liverpool have found that, like humans, obese dogs can experience metabolic syndrome, a condition that describes multiple health issues that occur in the body at the same time.
The condition occurs when a number of health problems, such as increased blood glucose and increased cholesterol levels, develop together, with the potential to increase the risk of other diseases, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Although canine obesity is known to cause insulin resistance, mild hypertension, and high blood cholesterol ...
Health inequalities could be reduced by more effective health care, says new study
2012-10-31
Wide differences in death rates from disease still persist throughout England – but effective healthcare can help to reduce these inequalities, a new study has discovered.
Researchers from the University of Leicester led a two-year project funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) into why differences in death rates from diseases like heart disease, strokes, lung disease and cancers still persist.
They found that age and poverty were among the biggest factors that accounted for the differences – but they also discovered that effective delivery of healthcare ...
Navy oceanographers delve deeper in wave data to improve forecasts
2012-10-31
WASHINGTON--Around the globe, mariners and navies alike have long observed and included weather and sea states in navigational planning when plotting course or developing military strategy. And although forecasting had become an integral function by the start of the 20th century, these predictions were often crude and qualitative.
For the U.S. Navy, the years 1941 through 1946 provided an unusual stimulus to ocean wave research, according to pioneer World War II oceanographer Charles Bates. During this brief five-year period, theory, observation, and prediction of sea, ...
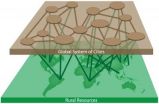
Sustainable cities must look beyond city limits
2012-10-31
City leaders aspiring to transform their cities into models of sustainability must look beyond city limits and include in their calculation the global flow of goods and materials into their realm, argue researchers in the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences journal Ambio.
Many cities are now developing sustainable strategies to reduce pollution and congestion, improve the quality of life of their citizens, and respond to growing concern about human impact on climate and the environment. But sustainable city initiatives often ignore the environmental footprint from imported ...
New metric to track prosthetic arm progress
2012-10-31
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Amputees with a new prosthetic arm must learn how to use their device to perform everyday tasks that were once second nature. Taking off a shirt becomes a conscious, multistep effort: grasp the shirt, lift the shirt over the head, pull arms through the sleeves, place the shirt on the table, let go of the shirt.
In the best cases of treatment, patients work with teams of doctors, prosthetists, and therapists to learn how their new limbs can help them regain function and quality of life. But clinicians have had few tools to assess ...
New hope for survivors of stroke and traumatic brain injury
2012-10-31
A new ground-breaking study about to be published in the Adis journal CNS Drugs provides clinical evidence that, for the first time, chronic neurological dysfunction from stroke or traumatic brain injury can rapidly improve following a single dose of a drug that targets brain inflammation, even years after the stroke or traumatic event.
The observational study¹ of 629 patients, conducted over the course of nearly two years, documents a diverse range of positive effects, including statistically significant rapid clinical improvement in motor impairment, spasticity, cognition, ...
Graphene mini-lab
2012-10-31
A team of physicists from Europe and South Africa showed that electrons moving randomly in graphene can mimic the dynamics of particles such as cosmic rays, despite travelling at a fraction of their speed, in a paper about to be published in EPJ B.
Andrey Pototsky and colleagues made use of their knowledge of graphene, which is made of a carbon layer, one atom thick, and packed in a honeycomb lattice pattern. In such material the interaction of electrons with atoms changes the effective mass of the electrons. As a result, the energy of electrons in graphene becomes similar ...