(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. — A new study analyzing the previous math standards of each state provides strong support for adoption of common standards, which U.S. students desperately need to keep pace with their counterparts around the globe, a Michigan State University scholar argues.
Forty-six states are implementing the Common Core math and reading standards, which nonetheless have come under fire recently by some researchers and would-be politicians.
But William Schmidt, MSU Distinguished Professor of statistics and education, said the Common Core is a world-class set of standards. In his study, published in the journal Educational Researcher, Schmidt found that states whose previous standards were most similar to the Common Core performed better on a national math test in 2009.
"We can't yet prove anything about the Common Core standards because they're just now being implemented, but if we look back we find that those states that were closest to the Common Core on average did better on the 2009 NAEP test (National Assessment of Educational Progress)," Schmidt said.
"This is another strong piece of evidence that we are moving in the right direction."
The study also found that some states previously had Common Core-worthy criteria – such as requiring eighth-graders to understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem – but essentially let the students and teachers off the hook by having low proficiency standards. Michigan, for example, had high standards but low proficiency guidelines – students could pass the standard math test by scoring less than 40 percent.
Common Core addresses that deficiency with a set of standard proficiency guidelines slated to go into effect with the 2014-15 school year, Schmidt said.
Schmidt's research refutes a Brookings Institute study that suggested Common Core will have no effect on student performance. But that study, Schmidt said, relied on opinion-based ratings whereas his is a statistical analysis relying on coded-based data.
Some political candidates in Michigan and elsewhere around the nation have criticized the Common Core as federal meddling into state education matters – despite the fact that the Common Core was developed by a coalition of state leaders including the governors.
Beyond the ideological attacks, Schmidt said the Common Core represents a great opportunity for U.S. students to become competitive in the global economy.
"This is probably the best chance we've had to improve America's mathematics education in 50 years if not more," Schmidt said. "We finally have standards that are comparable to what the top-achieving countries have. It would be foolish for Michigan or any other state to pull back now."
INFORMATION:
Study supports move toward common math standards
2012-11-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Waste management -- good marketing
2012-11-05
This press release is available in Spanish.
Spanish legislation on waste management changed in July last year. Until then, the consumer was responsible for the disposal of products. According to Mr Unai Tamayo, economist at the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU), the new laws "foment the construction of closed systems, such as in taverns: the container being taken out and subsequently returned. Moreover, when a manufacturer launches a product on to the market, once consumed, the packaging is considered waste, and the responsibility for this now falls on the manufacturer ...
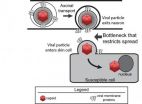
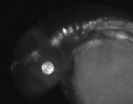
Princeton researchers identify unexpected bottleneck in the spread of herpes simplex virus
2012-11-05
VIDEO:
Princeton University research suggests that a common strain of herpes virus causes cold sores with only one or two viral particles, resulting in a bottleneck in which the infection is...
Click here for more information.
New research suggests that just one or two individual herpes virus particles attack a skin cell in the first stage of an outbreak, resulting in a bottleneck in which the infection may be vulnerable to medical treatment.
Unlike most viruses that ...
New research suggests standardized booster seat laws could save lives of children
2012-11-05
Boston, Mass, Nov. 5, 2012— A new study by researchers in Boston Children's Hospital's Division of Emergency Medicine indicates that a nationwide standard on booster seat laws for children 4 feet 9 inches and shorter, or up to 8 years old, would save lives. The findings were published online Nov. 5, 2012, in the journal Pediatrics.
Boston Children's researchers reviewed data from Fatality Analytic Reporting System, analyzing child deaths in motor vehicle accidents, looking specifically at whether the crash and resulting deaths or injuries took place in a state with or ...
Computers 'taught' to ID regulating gene sequences
2012-11-05
Johns Hopkins researchers have succeeded in teaching computers how to identify commonalities in DNA sequences known to regulate gene activity, and to then use those commonalities to predict other regulatory regions throughout the genome. The tool is expected to help scientists better understand disease risk and cell development.
The work was reported in two recent papers in Genome Research, published online on July 3 and Sept. 27.
"Our goal is to understand how regulatory information is encrypted and to learn which sequence variations contribute to medical risks," says ...
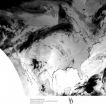
Superstorm animation
2012-11-05
A computer animation produced by University of Delaware researchers shows the explosive development of Hurricane Sandy, the superstorm and its unusual track. View the animation on the University's UDaily website at http://www.udel.edu/udaily/2013/nov/animation110212.html
Matt Shatley, computer research specialist in UD's College of Earth, Ocean, and Environment (CEOE), assembled the animation by digitally stitching together about 800 infrared images taken by GOES, the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, which keeps a continuous eye on the continental United ...
Japanese family members less likely than others to give CPR for cardiac arrest
2012-11-05
Family members didn't give CPR for cardiac arrests as often as passers-by or friends in a Japanese study presented at the American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2012.
Cardiac arrest is the sudden loss of heart function, typically resulting from an abnormal heart rhythm that causes the heart to quiver erratically and stop pumping blood. According to the American Heart Association, effective bystander CPR provided immediately after sudden cardiac arrest can double or triple a victim's chance of survival.
In a review of 547,218 cardiac arrests occurring in 2005-09, ...
New device could allow your heartbeat to power pacemaker
2012-11-05
An experimental device converted energy from a beating heart to provide enough electricity to power a pacemaker, in a study presented at the American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2012.
The findings suggest that patients could power their pacemakers — eliminating the need for replacements when batteries are spent.
In a preliminary study, researchers tested an energy-harvesting device that uses piezoelectricity — electrical charge generated from motion. The approach is a promising technological solution for pacemakers, because they require only small amounts ...
Heart disease map of England highlights growing social inequality in older ages
2012-11-05
A study estimating the death rate from heart and circulatory disease in each electoral ward in England has found that despite considerable improvements since the 1980s, the difference between the wealthiest and poorest communities has widened for people over 65.
Mortality from heart and circulatory disease – the leading cause of death in the UK – declined in most places between 1982 and 2006, but for men and women aged 65 or older, the decline was smaller in the most deprived communities, resulting in a wider gap between rich and poor.
The authors, from Imperial College ...
Smallholder farmers need improved stake in Nile's development
2012-11-05
ADDIS ABABA (5 NOVEMBER 2012)—A new book finds that the Nile river, together with its associated tributaries and rainfall, could provide 11 countries—including a new country, South Sudan, and the drought-plagued countries of the Horn of Africa—with enough water to support a vibrant agriculture sector, but that the poor in the region who rely on the river for their food and incomes risk missing out on these benefits without effective and inclusive water management policies.
The Nile River Basin: Water, Agriculture, Governance and Livelihoods, published by the CGIAR Challenge ...
Cardiac bypass surgery superior to non-surgical procedure for adults with diabetes and heart disease
2012-11-05
Adults with diabetes and multi-vessel coronary heart disease who underwent cardiac bypass surgery had better overall heart-related outcomes than those who underwent an artery-opening procedure to improve blood flow to the heart muscle, according to the results from an international study. The research was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), part of the National Institutes of Health.
The study compared the effectiveness of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery with a non-surgical procedure known as percutaneous coronary intervention ...