(Press-News.org) CHICAGO – In a study that involved more than 16,000 Hispanic/Latino men and women living in the United States, the prevalence of major cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors was high and varied markedly across different background groups; and those born in the U.S. were more likely to report a history of coronary heart disease and stroke and to have multiple CVD risk factors, according to a study appearing in November 7 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on cardiovascular disease. The study is being released early online to coincide with the American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions.
In the last decades, the U.S. Hispanic and Latino population has increased dramatically, now comprising the nation's largest minority group. Cardiovascular diseases are leading causes of death among Hispanic/Latino individuals in the United States, and this relatively young ethnic group is at high risk of future CVD illness and death as it ages. "Risk for CVDs among Hispanic/Latino individuals has been reported to differ with acculturation and duration of residence in the United States," according to background information in the article. "Comprehensive data are limited regarding the prevalence of CVD risk factors in this population and relations of these traits to socioeconomic status (SES) and acculturation."
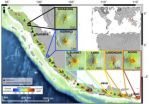
Martha L. Daviglus, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Illinois at Chicago and Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, and Gregory A. Talavera, M.D., M.P.H., of San Diego State University, and colleagues conducted a study to examine the prevalence of major CVD risk factors and CVD (coronary heart disease [CHD] and stroke) among U.S. Hispanic/Latino individuals of different backgrounds. The multicenter, population-based Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos included individuals of Cuban (n = 2,201), Dominican (n = 1,400), Mexican (n = 6,232), Puerto Rican (n = 2,590), Central American (n = 1,634), and South American backgrounds (n = 1,022), ages 18 to 74 years. The analyses involved 15,079 participants (5,979 men; 9,100 women) with complete data enrolled between March 2008 and June 2011. Seventy percent had lived in the United States for 10 or more years. The study included measurements of adverse CVD risk factors defined using national guidelines for hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol), hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and smoking. Prevalence of CHD and stroke were determined from self-reported data.
The researchers found that large proportions of participants (80 percent of men, 71 percent of women) had at least one risk factor. Overall, 31 percent of men had an adverse level of any 1 major risk factor only (most commonly hypercholesterolemia); 28 percent and 21 percent had any 2 only or 3 or more risk factors. Prevalence of 3 or more risk factors was highest among Puerto Rican men and lowest among South American men. Among women, 30 percent had 1 risk factor only (most commonly obesity); 23 percent and 17 percent had any 2 or 3 or more risk factors. Prevalence of 3 or more risk factors was highest among Puerto Rican women and lowest among South American women.
The prevalence of 3 or more risk factors was significantly higher with lower education or income. "In general, participants with lower income or education had higher rates of smoking, diabetes, obesity, and hypercholesterolemia. Compared with those who were less acculturated (i.e., were foreign-born or first-generation immigrants, had lived in the United States END
Study finds high prevalence of major cardiovascular disease risk factors among US Hispanic adults
2012-11-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Taking the 'pulse' of volcanoes using satellite images
2012-11-05
MIAMI – November 5, 2012 -- A new study by scientists at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science uses Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) data to investigate deformation prior to the eruption of active volcanoes in Indonesia's west Sunda arc. Led by geophysicist Estelle Chaussard and UM Professor Falk Amelung, the study uncovered evidence that several volcanoes did in fact 'inflate' prior to eruptions due to the rise of magma. The fact that such deformation could be detected by satellite is a major step forward in volcanology; ...
Hydro-fracking: Fact vs. fiction
2012-11-05
Boulder, CO, USA – In communities across the U.S., people are hearing more and more about a controversial oil and gas extraction technique called hydraulic fracturing – aka, hydro-fracking. Controversies pivot on some basic questions: Can hydro-fracking contaminate domestic wells? Does it cause earthquakes? How can we know? What can be done about these things if they are true? A wide range of researchers will address these and related critical questions at the GSA Annual Meeting this week.
"When people talk about contamination from hydraulic fracturing, for instance, ...
Field geologists (finally) going digital
2012-11-05
Boulder, CO, USA – Not very long ago a professional geologist's field kit consisted of a Brunton compass, rock hammer, magnifying glass, and field notebook. No longer. In the field and in the labs and classrooms, studying Earth has undergone an explosive change in recent years, fueled by technological leaps in handheld digital devices, especially tablet computers and cameras.
Geologist Terry Pavlis' digital epiphany came almost 20 years ago when he was in a museum looking at a 19th-century geology exhibit that included a Brunton compass. "Holy moly!" he remembers thinking, ...
Learning a new sense
2012-11-05
Rats use a sense that humans don't: whisking. They move their facial whiskers back and forth about eight times a second to locate objects in their environment. Could humans acquire this sense? And if they can, what could understanding the process of adapting to new sensory input tell us about how humans normally sense? At the Weizmann Institute, researchers explored these questions by attaching plastic "whiskers" to the fingers of blindfolded volunteers and asking them to carry out a location task. The findings, which recently appeared in the Journal of Neuroscience, have ...
Cystic kidney growth curbed
2012-11-05
Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is one of the most common genetic disorders, affecting one in every 1,000 people and responsible for up to ten percent of patients on dialysis worldwide. The disease is characterized by the development of cysts that lead to progressive kidney failure and necessitate dialysis or a kidney transplant in most patients aged around fifty. Moreover, the persistent cyst growth causes high blood pressure and painful complications. Although we have known about the disease for over a century and its genetic basis for almost 20 years, ...
US Hispanics at high risk for cardiovascular disease
2012-11-05
Hispanics and Latinos living in the U.S. are highly likely to have several major cardiovascular disease risk factors, such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, and smoking, according to a new, large-scale study. Risks vary among the diverse Hispanic/Latino groups, but individuals who were born in the U.S. are more likely to have multiple risk factors.
The findings are reported in the Nov. 7 issue of JAMA.
Hispanic and Latino people now comprise the largest minority group in the U.S. Although this population is relatively young, cardiovascular ...
New findings on gene regulation and bone development
2012-11-05
The patients have single short fingers (metacarpals) and toes (metatarsals) and can be restricted in growth due to a shortened skeleton. This hereditary disease is called brachydactyly type E (Greek for short fingers). Three years ago Dr. Philipp G. Maass from the research group of Professor Friedrich C. Luft at the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), a joint cooperation between the Charité Medical Faculty and the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) in Berlin-Buch, has discovered an epigenetic mechanism, which, when dysregulated, causes this condition. ...
Grandfathers play a more prominent role
2012-11-05
Europeans spend much time with their grandchildren. And past 70, the grandfather takes the lead.
Norwegian sociologist Knud Knudsen sets great store by his grandchildren. In that respect, he is typical of the grandparents in Europe who are the subjects of his recent research.
"Europeans with grandchildren generally opt to spend a good deal of time with them," says 67-year-old Knudsen, who is professor of sociology at the University of Stavanger (UiS).
"And grandfathers appear to be more involved than before," he adds. In a new study, he found that grandmothers are ...
Prenatal testosterone levels influence later response to reward
2012-11-05
Philadelphia, PA, November 5, 2012 – New findings led by Dr. Michael Lombardo, Prof. Simon Baron-Cohen and colleagues at the University of Cambridge indicate that testosterone levels early in fetal development influence later sensitivity of brain regions related to reward processing and affect an individual's susceptibility to engage in behavior, that in extremes, are related to several neuropsychiatric conditions that asymmetrically affect one sex more than the other.
Although present at low levels in females, testosterone is one of the primary sex hormones that exerts ...
Inhibition of enzyme NOX4 prevents liver fibrosis
2012-11-05
Researchers at the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) have led a study published in PLoS One showing that the inhibition of a family member of NADPH oxidase enzyme, NOX4, plays an important role in liver fibrosis.
The researchers studied the function of a cytokine called transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) in the pathophysiology of the liver, which is one of the main research lines of the Biological Clues of the Invasive and Metastatic Phenotype research group at the IDIBELL, leaded by Isabel Fabregat.
This paper is related with the processes of ...