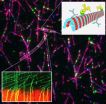
(Press-News.org) Neurodevelopmental disorders such as intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorders are marked by mutations that impair signaling between neurons. These mutations cause key brain circuits involved in learning and memory to develop too quickly, leading to long-lasting behavioral and cognitive deficits, according to a study published by Cell Press in the November 9th issue of the journal Cell. The findings could pave the way to new treatment strategies for severe forms of neurodevelopmental disorders.
"We have provided perhaps the first evidence that acceleration of certain neural milestones is just as disruptive as delay in the same milestones," says senior study author Gavin Rumbaugh of Scripps Florida. "These studies have far-reaching implications for how we will treat these severe forms of neurodevelopmental disorders."
Autism spectrum disorders are often accompanied by intellectual disability, and these disorders are linked to harmful mutations that affect proteins responsible for regulating the communication between neurons. A deficiency in one of these proteins, known as SynGAP, can lead to severe forms of these disorders, but it has not been clear how mutations affecting this protein alter the development of brain circuits and behavior.
To answer this question, Rumbaugh and his team inactivated one copy of the SYNGAP1 gene in mice to cause a deficiency in the protein. By two weeks of age, these mice showed a dramatic and premature increase in the communication between neurons in the hippocampus—a critical brain region for learning and memory. As a result, the mice were hyperactive, showed learning deficits, and were prone to seizures, similar to human patients.
These behavioral and cognitive abnormalities persisted even after the researchers restored normal levels of SynGAP in adult mice, suggesting that this protein exerts its effects on cognitive maturation only during a narrow developmental window. Thus, mutations that affect SYNGAP1 can cause neural networks to become miswired early in development and to resist repair during adulthood.
"Our results imply that very early intervention is essential in certain neurodevelopmental disorders, particularly for cognitive symptoms," Rumbaugh says. "We believe that certain pharmacological or genetic treatments initiated in this sensitive developmental window will greatly benefit our model mice, and hence could be translated into patients."
###Clement et al.: "Pathogenic SYNGAP1 mutations impair cognitive development by disrupting the maturation of dendritic spine synapses."
The right pace of neural development protects against autism and intellectual disability
2012-11-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fairy-wren babies need password for food
2012-11-08
AUDIO:
This is a fairy-wren incubation call.
Click here for more information.
It's always a good idea to listen to your mother, but that goes double for baby fairy-wrens even before they are hatched.
If those fairy-wren babies want to be fed, they need to have a password—a single unique note—taught to them by their mothers from outside the egg. The nestlings incorporate that password right into their begging calls, according to researchers who report their discovery online ...
Scientists uncover secrets of how intellect and behavior emerge during childhood
2012-11-08
JUPITER, FL – Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have shown that a single protein plays an oversized role in intellectual and behavioral development. The scientists found that mutations in a single gene, which is known to cause intellectual disability and increase the risk of developing autism spectrum disorder, severely disrupts the organization of developing brain circuits during early childhood. This study helps explain how genetic mutations can cause profound cognitive and behavioral problems.
The study was published in the ...
Meet Xenoceratops: Canada's newest horned dinosaur
2012-11-08
Ottawa, Canada (November 8, 2012) – Scientists have named a new species of horned dinosaur (ceratopsian) from Alberta, Canada. Xenoceratops foremostensis (Zee-NO-Sare-ah-tops) was identified from fossils originally collected in 1958. Approximately 20 feet long and weighing more than 2 tons, the newly identified plant-eating dinosaur represents the oldest known large-bodied horned dinosaur from Canada. Research describing the new species is published in the October 2012 issue of the Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences.
"Starting 80 million years ago, the large-bodied ...
UMass Amherst cell biologists identify new protein key to asymmetric cell division
2012-11-08
AMHERST, Mass. – Recently biologists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst led by Wei-lih Lee have identified a new molecular player in asymmetric cell division, a regulatory protein named She1 whose role in chromosome- and spindle positioning wasn't known before. Asymmetric cell division is important in the self-renewal of stem cells and because it ensures that daughter cells have different fates and functions.
When a fertilized egg develops in a fruit fly or a human being, the number of asymmetric cell divisions must be precisely balanced by symmetric cell divisions, ...
Scientists reveal key protein interactions involved in neurodegenerative disease
2012-11-08
JUPITER, FL, November 8, 2012 – Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have defined the molecular structure of an enzyme as it interacts with several proteins involved in outcomes that can influence neurodegenerative disease and insulin resistance. The enzymes in question, which play a critical role in nerve cell (neuron) survival, are among the most prized targets for drugs to treat brain disorders such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
The study was published online ahead of print ...
Unique spinal nerve cell activity discovery announced by University of Leicester biologists
2012-11-08
Scientists from the University of Leicester have hit upon unique forms of spinal nerve activity that shape output of nerve cell networks controlling motor behaviours.
The breakthrough in the Department of Biology at the University of Leicester is announced today (5pm GMT on Thursday Nov 8) in the journal Current Biology. The three- year study was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC).
Although the neural basis of motor control has been studied for over a century, the processes controlling maturation of locomotor behaviours – like ...
Rethinking body mass index for assessing cancer risk
2012-11-08
November 8, 2012 — (Bronx, NY) — A study by researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University suggests that body mass index (BMI)—the most commonly used weight-for-height formula for estimating fatness—may not be the best measure for estimating disease risk, and particularly the risk of certain types of cancer. The study was published today in the online edition of the American Journal of Epidemiology.
BMI is calculated by dividing a person's weight (in kilograms) by his or her height in meters squared, or W/H2. Most of the early studies that ...
Cells from skin create model of blinding eye disease
2012-11-08
MADISON — For the first time, Wisconsin researchers have taken skin from patients and, using induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology, turned them into a laboratory model for an inherited type of macular degeneration.
Dr. David Gamm, director of the UW's McPherson Eye Research Institute, said that while Best disease is relatively rare, having a patient-specific model of the eye disease, which destroys the macula of the retina, could lead to a greater understanding of more common eye disorders such as age-related macular degeneration.
"This model gives us a chance ...
Dream symbols could help in psychotherapy
2012-11-08
Dream images could provide insights into people's mental health problems and may help with their treatment, according to a psychology researcher from the University of Adelaide.
Dr Lance Storm, a Visiting Research Fellow with the University of Adelaide's School of Psychology, has been studying dream symbols (or "archetypes") and their meanings, as described by the famous psychologist and psychiatrist, Carl Jung.
In the early 1900s, Jung proposed that these archetypes were ancient images stemming from humans' collective unconscious. He believed that dream symbols carried ...
Injection is the best method for cutting ammonia emissions from slurry spreading on lands
2012-11-08
In order to contribute to the development of the primary sector and environmental care, the Basque Institute of Agricultural Research and Development, NEIKER-Tecnalia, has analysed various ways of spreading slurry on arable land to determine the most appropriate way of cutting the amount of ammonia that is released into the atmosphere.
The three methods studied were: the traditional splash plate or fan method, hanging pipes, or injection. The last one turned out to be the most environmentally friendly in terms of ammonia emissions (NH3), as it achieves a 93% cut in NH3 ...