(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study of eight child prodigies suggests a possible link between these children's special skills and autism.
Of the eight prodigies studied, three had a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders. As a group, the prodigies also tended to have slightly elevated scores on a test of autistic traits, when compared to a control group.
In addition, half of the prodigies had a family member or a first- or second-degree relative with an autism diagnosis.
The fact that half of the families and three of the prodigies themselves were affected by autism is surprising because autism occurs in only one of 120 individuals, said Joanne Ruthsatz, lead author of the study and assistant professor of psychology at Ohio State University's Mansfield campus.
"The link between child prodigies and autism is strong in our study," Ruthsatz said. "Our findings suggest child prodigies have traits in common with autistic children, but something is preventing them from displaying the deficits we associate with the disorder."
The study also found that while child prodigies had elevated general intelligence scores, where they really excelled was in working memory - all of them scored above the 99th percentile on this trait.
Ruthsatz conducted the study with Jourdan Urbach of Yale University. Their results were published in a recent issue of the journal Intelligence.
For the study, the researchers identified eight child prodigies through the internet and television specials and by referral. The group included one art prodigy, one math prodigy, four musical prodigies and two who switched domains (one from music to gourmet cooking, and one from music to art). The study included six males and two females.
The researchers met with each prodigy individually over the course of two or three days. During that time, the prodigies completed the Stanford-Binet intelligence test, which included sub-tests on fluid reasoning, knowledge, quantitative reasoning, visual spatial abilities and working memory.
In addition, the researchers administered the Autism-Spectrum Quotient assessment, which scores the level of autistic traits. The prodigies' scores on the test were compared to a control group of 174 adults who were contacted randomly by mail.
Ruthsatz said the most striking data was that which identified autistic traits among the prodigies.
The prodigies showed a general elevation in autistic traits compared to the control group, but this elevation was on average even smaller than that seen in high-functioning autistic people diagnosed with Asperger's syndrome.
Autism is a developmental disability characterized by problems with communicating and socializing and a strong resistance to change. People with Asperger's are more likely than those with autism to have normal intelligence, but tend to have difficulties with social interaction.
The prodigies did score higher than the control group and the Asperger's group on one subsection of the autism assessment: attention to detail.
"These prodigies had an absolutely amazing memory for detail," she said. "They don't miss anything, which certainly helps them achieve the successes they have."
Ruthsatz said it was not the three prodigies who were diagnosed with autism who were driving this particular finding. In fact, the three autistic prodigies scored an average of 8 on attention to detail, compared to 8.5 for the entire group of prodigies.
On the intelligence test, the prodigies scored in the gifted range, but were not uniformly exceptional. While five of the eight prodigies scored in the 90th percentile or above on the IQ test, one scored at the 70th percentile and another at the 79th percentile.
But just as they did in the autism assessment, the prodigies stood out in one of the sub-tests of the intelligence test. In this case, the prodigies showed an exceptional working memory, with all of them scoring above the 99th percentile.
Working memory is the system in the brain that allows people to hold multiple pieces of information in mind for a short time in order to complete a task.
The findings paint a picture of what it takes to create a prodigy, Ruthsatz said.
"Overall, what we found is that prodigies have an elevated general intelligence and exceptional working memory, along with an elevated autism score, with exceptional attention to detail," Ruthsatz said.
These results suggest that prodigies share some striking similarities with autistic savants - people who have the developmental disabilities associated with autism combined with an extraordinary talent or knowledge that is well beyond average.
"But while autistic savants display many of the deficits commonly associated with autism, the child prodigies do not," Ruthsatz said. "The question is why."
The answer may be some genetic mutation that allows prodigies to have the extreme talent found in savants, but without the deficits seen in autism. But the answer will require more study, Ruthsatz said.
"Our findings suggest that prodigies may have some moderated form of autism that actually enables their extraordinary talent."
### Contact: Joanne Ruthsatz, Ruthsatz.4@osu.edu (It is best to reach Dr. Ruthsatz first by email.)
Written by Jeff Grabmeier, (614) 292-8457; Grabmeier.1@osu.edu
Link found between child prodigies and autism
2012-11-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study questions the relevance of SCIP benchmarks among CABG patients
2012-11-09
(Boston) – Cardiothoracic surgeons and endocrinologists from Boston Medical Center (BMC) have found that among patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, achieving Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) benchmarks for glycemic control may be irrelevant when perioperative continuous insulin infusion protocols are implemented. These findings appear on-line in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.
Currently, 40 percent of all patients undergoing CABG suffer from diabetes, and this number is quickly rising. Traditionally these patients ...
Belatacept after a kidney transplant: Minor added benefit for certain patients
2012-11-09
Belatacept (trade name Nulojix®) has been approved since June 2011 to prevent a rejection reaction of the body to the donor organ (transplant) in adults who have received a kidney transplant. The Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) has examined the added benefit of the drug pursuant to the "Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products" (AMNOG).
The assessment showed an indication of a minor added benefit of belatacept in adults with transplants from donors who had been selected according to the so-called standard criteria. Serious side ...
Moffitt Cancer Center researchers identify novel metabolic programs driving aggressive brain tumors
2012-11-09
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center have identified metabolic signatures that may pave the way for personalized therapy in glioma, a type of tumor that starts in the brain.
The study appears online in the October issue of Cancer Research, a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research.
According to the authors, little has been known about the underlying metabolic alterations that may drive the growth of the most aggressive type of glioma, termed glioblastoma.
"For the first time, we have described global metabolomic signatures in glioma," said study ...
Considerable added benefit of ipilimumab in advanced melanoma
2012-11-09
The humanized antibody ipilimumab (trade name Yervoy®) has been approved since August 2011 for the treatment of adult patients with advanced melanoma (black skin cancer) who have already been treated. The term "advanced" means that the melanoma can no longer be removed by an operation or that metastases have formed. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) has examined the added benefit of the drug pursuant to the Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products (AMNOG). According to the findings, the drug offers major advantages with ...
University of Huddersfield physicist investigates the Big Bang particle
2012-11-09
Scientists at the University of Huddersfield are collaborating with experts at some of the world's leading research institutes in an attempt to unravel the mysteries of a particle that played a role in the creation of the universe.
The existence of neutrinos and anti-neutrinos – particles that are almost massless and which travel at light speed from one side of the earth to the other – was confirmed more than 50 years ago. Scientists believe that they were created at the Big Bang and might hold the key to the nature of the universe.
But they are light particles that ...
Vandetanib in thyroid cancer: No proof of added benefit
2012-11-09
Vandetanib (trade name Caprelsa®) has been approved in Germany since February 2012 for adult patients suffering from a particular form of aggressive thyroid cancer. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) has now examined the added benefit of the drug pursuant to the Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products (AMNOG). According to the findings, there is no proof of added benefit, because no data on patient-relevant outcomes for those patients for whom the drug is approved were presented by the drug manufacturer in its dossier. ...
UGR and Michael J. Fox Foundation take a step forward in the study of Parkinson's disease
2012-11-09
This press release is available in Spanish.
During the past year, the research group TIC 218 at the Department of Signal Theory, Telematics and Communications attached to the University of Granada and the Andalusian Information Technology and Communications Center (CITIC) has implemented the methods for the detection and diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, within the PPMI initiative of the Michael J. Fox foundation for the study of Parkinson's disease. In addition, other databases were used such as that of the Virgen de la Victoria Hospital, Málaga, Spain, and Virgen de ...
CHOP experts describe research in pediatric heart disease
2012-11-09
Physician-researchers from the Cardiac Center at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia presented new findings on pediatric cardiovascular disease at the American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2012 in Los Angeles. They described racial disparities in risk factors for sudden cardiac death, imaging modalities and novel approaches to assessing cardiac anomalies, ventricular assist device use, special considerations in syndromes in adult congenital heart disease, changes in immunosuppressive drugs after pediatric heart transplant, and many other topics.
Children's ...
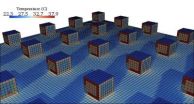
Cool pavements, warm buildings, rising electricity bills
2012-11-09
A push to replace old, heat-trapping paving materials with new, cooler materials could actually lead to higher electricity bills for surrounding buildings, engineers at the University of California, San Diego, have found. Researchers published their findings Oct. 29 in the new Journal of Urban Climate.
The new paving materials are designed to lower the overall temperature of the areas where they are used—something that the study, which was focused on local solar radiation and energy consumption, was not designed to measure.
The study sounds a note of caution at a time ...
Stem cell scientists discover potential way to expand cells for use with patients
2012-11-09
(TORONTO, Canada – Nov. 8, 2012) – Canadian and Italian stem cell researchers have discovered a new "master control gene" for human blood stem cells and found that manipulating its levels could potentially create a way to expand these cells for clinical use.
The findings, published today online ahead of print in Cell Stem Cell, usher in a new paradigm for the regulation of human blood stem cells, says co-principal investigator Dr. John Dick, who holds a Canada Research Chair in Stem Cell Biology and is a Senior Scientist at University Health Network's McEwen Centre for ...