(Press-News.org) CINCINNATI—People living near a former uranium ore processing facility in Ohio are experiencing a higher than average rate of lupus, according a new study conducted by scientists at the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center.
Lupus is a chronic inflammatory disease that can affect the skin, joints, kidneys, lungs, nervous system and other organs of the body. The underlying causes of lupus are unknown, but it is usually more common in women of child-bearing age.
For this new study, a collaborative team of UC and Cincinnati Children's researchers wanted to compare lupus rates between people who were exposed to uranium and those who were not in an effort to explain the high number of lupus cases reported in a Cincinnati community.
Extensive review of medical records and serum antibody analysis to verify the cases, concluded that people who were exposed to higher levels of uranium, based on their living proximity to a former uranium ore processing plant, had lupus rates four times higher than the average population.
"Former studies have suggested that people with lupus may be more sensitive to radiation and that both genetics and environmental exposures play a role in disease development. Our study shows a strong correlation between uranium exposure, a radioactive substance, and an increased lupus rate that merits further investigation," says Pai-Yue Lu, MD, a pediatric rheumatology fellow at Cincinnati Children's and lead researcher for the study.
"With more research in this area, we may gain additional insight on the types of environmental factors that contribute to lupus development and the mechanisms by which they work," Lu adds. "There could be other effects of uranium and related exposures that could contribute to or help explain our findings."
Lu is presenting this finding and its potential implication at the American College of Rheumatology Annual Scientific Meeting Monday, Nov. 12, in Washington, D.C. She completed the project as part of her master's degree in clinical and translational science training at UC.
The Cincinnati-based team's research is based on nearly two decades of data collected through the Fernald Medical Monitoring Program, the United States' first and largest legally mandated comprehensive medical monitoring program. The program was established in 1990 after a federal investigation revealed that National Lead of Ohio's Feed Materials Production Center in the Hamilton County, Ohio, community of Fernald, was emitting dangerous levels of uranium dust and gases into the surrounding communities.
"The availability of this cohort and carefully collected data and biospecimens provides a great setting to ask research questions," says Susan Pinney, PhD, UC professor of environmental health and principal investigator of the Fernald study.
Almost 10,000 community residents enrolled in the Fernald Medical Monitoring Program. Community residents were classified into several exposure groups: high exposure, moderate exposure, low exposure and no exposure. (Uranium plant workers were not part of this study.)
"Typical U.S. incidence rates for lupus are 1.8 to 7.6 cases per 100,000. Among the 25 confirmed lupus cases we identified through the Fernald community cohort, 12 were in the high exposure group, eight with moderate exposure and five in the low exposure group," says Lu.
###Research was supported by a pilot grant from a Center for Environmental Genetics, a National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences-funded program to support core facilities and technologies needed to conduct innovative research that focuses on how environmental agents interact with genetic and epigenetic factors to influence disease risk and outcome. Shuk-mei Ho, PhD, Jacob A. Schmidlapp Chair and Professor of Environmental Health, serves as principal investigator of the CEG grant.
Uranium exposure linked to increased lupus rate
2012-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Less of a shock
2012-11-14
Implantable defibrillators currently on the market apply between 600 and 900 volts to the heart, almost 10 times the voltage from an electric outlet, says Ajit H. Janardhan, MD, PhD, a cardiac electrophysiology fellow at the Washington University's School of Medicine.
After being shocked, he says, some patients get post-traumatic stress disorder. Patients may even go so far as to ask their physicians to remove the defibrillator, even though they understand that the device has saved their lives.
The huge shocks are not only unbearably painful, they damage the heart muscle ...
The road to language learning is iconic
2012-11-14
Languages are highly complex systems and yet most children seem to acquire language easily, even in the absence of formal instruction. New research on young children's use of British Sign Language (BSL) sheds light on one of the mechanisms - iconicity - that may endow children with this amazing ability.
For spoken and written language, the arbitrary relationship between a word's form – how it sounds or how it looks on paper – and its meaning is a particularly challenging feature of language acquisition. But one of the first things people notice about sign languages is ...
State of Nuevo León first to benefit from improved nationwide air quality information system
2012-11-14
This press release is available in Spanish and French.
Monterrey, 13 November 2012—Today, the Nuevo León state ministry of sustainable development, with support from the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), launched a revamped air quality information management system in Monterrey, Mexico, using AirNow-International.
This CEC initiative, developed in coordination with Canadian, Mexican and US government agencies, is laying the foundation for improved ways to inform citizens around the country about air quality in their communities with real-time data that ...
NASA sees sun emit a mid-level flare
2012-11-14
On Nov. 13, 2012, the sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 9:04 p.m. EST.
Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where Global Positioning System (GPS) and communications signals travel. This disrupts the radio signals for as long as the flare is ongoing, anywhere from minutes to hours.
This flare is classified as an M6 flare. M-class flares are the weakest flares ...
Hinode to support ground-based eclipse observations
2012-11-14
On Nov. 13, 2012, certain parts of Earth will experience a total solar eclipse, which, like all eclipses, will only be visible when you are aligned in a straight line with the moon and the sun. In this case the eclipse will only be seen from a narrow corridor in the southern hemisphere that is mostly over the ocean but also cuts across the northern tip of Australia. The JAXA/NASA Hinode mission will experience a partial eclipse of the sun near the same time as the observers in Australia. Hinode will coordinate its observations with those from the ground, before, during, ...
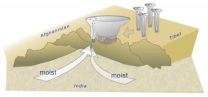
Roots of deadly 2010 India flood identified; Findings could improve warnings
2012-11-14
On the night of Aug. 5, 2010, as residents slept, water began rushing through Leh, an Indian town in a high desert valley in the Himalayas.
Average total rainfall in the area for August is about a half-inch. During this 24-hour period more than 8 inches fell, causing severe damage and leaving 193 dead, hundreds missing and thousands homeless.
"Flash flooding events don't happen often but when they do they are some of the scariest, most dangerous and quickest natural disasters that can happen," said Kristen Rasmussen, a University of Washington graduate student in ...
Increasing efficiency of wireless networks
2012-11-14
RIVERSIDE, Calif. (www.ucr.edu) — Two professors at the University of California, Riverside Bourns College of Engineering have developed a new method that doubles the efficiency of wireless networks and could have a large impact on the mobile Internet and wireless industries.
Efficiency of wireless networks is key because there is a limited amount of spectrum to transmit voice, text and Internet services, such as streaming video and music. And when spectrum does become available it can fetch billions of dollars at auction.
The "spectrum crunch" is quickly being accelerated ...
Migraine-associated brain changes not related to impaired cognition
2012-11-14
Women with migraines did not appear to experience a decline in cognitive ability over time compared to those who didn't have them, according to a nine-year follow up study funded by the National Institutes of Health.
The study also showed that women with migraine had a higher likelihood of having brain changes that appeared as bright spots on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a type of imaging commonly used to evaluate tissues of the body.
"The fact that there is no evidence of cognitive loss among these women is good news," said Linda Porter, Ph.D., pain health science ...
First-of-its-kind program improves outcomes for seniors admitted for trauma
2012-11-14
TORONTO, Nov. 13, 2012—A first-of-its-kind program at St. Michael's Hospital lowers risk of delirium in elderly patients admitted for trauma and decreases the likelihood they will be discharged to a long-term care facility.
The Geriatric Trauma Consultation Service is a program where every patient over 60 admitted to the trauma service is seen by a member of the geriatric team within 72 hours.
This is a big change from previous practice, where only 4 per cent of elderly patients admitted to trauma were seen by a geriatric team member during their stay in hospital.
"Older ...
Scientists question the designation of some emerging diseases
2012-11-14
The Ebola, Marburg and Lassa viruses are commonly referred to as emerging diseases, but leading scientists say these life-threatening viruses have been around for centuries.
In a perspective in the Nov. 9 issue of the journal Science, researchers including a professor at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) say it would be more appropriate to refer to these viruses as emerging diagnoses.
"The infectious agents were identified around the middle of the 20th century but that does not mean that they were new," said Joseph McCormick, M.D., ...