(Press-News.org) Mobile telephone operators should verify the age of children and youngsters when they access multimedia services by having a record of users' dates of birth. This is one of the recommendations in a report by researchers from the Polytechnic University of Valencia (Spain), that also suggest content classifications for mobiles by age, like in the case of video games.
"Verification of age upon access to mobile phone services is not effective because the child can also falsify their age by checking a different box," as explained to SINC by María de Miguel Molina, lecturer at the Polytechnic University of Valencia.
"However, operators could be made aware of the age of their young users if their parents were to disclose such information when purchasing a mobile phone for their child. This information could then be registered," adds the researcher, who headed the study on mobile services aimed at children in Spain.
Published in the 'Quality & Quantity' journal, the report outlines that if this measure were adopted, access to adult sites or those not suitable for minors could be filtered or blocked. This would mean common regulations for operators.
The majority of companies currently operating in Spain have signed the self-regulation code of the Spanish Mobile Operators Association, AESAM, which supports "responsible access" to content. Even so, according to the study this does not suffice and it should be more specific when making reference to children.
The researchers have also recommended the creation of a classification scheme according to user age and service theme like the one currently in place for video games: the Pan European Game Information (PEGI), which recommends games for children and youngsters of 3, 7, 12, 16 and over 18 years.
Recommendations to the Government
The study was conducted using surveys sent to companies, government agencies and child protection associations. Its results suggest that the Spanish Government needs to work with families and schools to promote awareness campaigns on proper mobile phone usage.
In addition, emphasis was placed on the need to reach an agreement with operators so that they can get the opinion of parents and incorporate filtering services. These would include access and download bans on pornographic photographs and videos, SMS and MMS sending restrictions, internet purchasing restrictions and bans on participation in contests and competitions.
"Up until now we thought we could control youngsters' access to the internet on the household desktop by locating it in a visible place, for example, and ensuring that children use the internet properly. But, smartphones have opened up new doors," warns De Miguel, who also highlights the recent advance of mobile applications (apps) and, above all, the use of social networks like Tuenti and Facebook amongst minors.
"One of the main problems is that children under the age of 14 can easily gain access despite it being prohibited under Spanish legislation," outlines the researcher. "As a result, the only available resource would be the electronic ID card, but its short term implementation is a long way away."
In any case, if the youngster is older than 14 and provides their real identity, "the social network is then both legally and socially responsible to offer more than enough protection so that the user can enjoy the site without problems."
The researchers are now appealing to social networks to implement measures such as closed profiles by default, the use of passwords and clearer information, as well as teaching youngsters how to use social networking sites and protect their privacy.
INFORMATION:
References:
María De-Miguel-Molina, Mónica Martínez-Gómez, Blanca De-Miguel-Molina, Gabriela Ribes-Giner. "A quantitative study on mobile services aimed at children and self-regulation in Spain". Quality & Quantity 46 (6): 1795-1806, October 2012.
Proposals to record the age of youngsters when buying mobile phones
2012-11-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wolters Kluwer Health and International Association of Forensic Nurses partner to publish the Journal of Forensic Nursing
2012-11-20
New York, NY -- (November 20, 2012) – Wolters Kluwer Health and the International Association of Forensic Nurses (IAFN) are pleased to announce an agreement to publish Journal of Forensic Nursing, the official journal of IAFN. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW), part of Wolters Kluwer Health, will become the publisher for Journal of Forensic Nursing, beginning with the first Quarter 2013 issue.
The only journal dedicated exclusively to this emerging nursing specialty, the Journal of Forensic Nursing will continue on its quarterly publication schedule. In addition to ...
Researchers improve technology to detect hazardous chemicals
2012-11-20
Scientists at Imperial College London have developed a system to quickly detect trace amounts of chemicals like pollutants, explosives or illegal drugs.
The new system can pick out a single target molecule from 10 000 trillion water molecules within milliseconds, by trapping it on a self-assembling single layer of gold nanoparticles.
The team of scientists, all from the Department of Chemistry at Imperial, say this technology opens the way to develop devices that are compact, reusable and easy to assemble, and could have a range of uses including detecting illegal drugs, ...
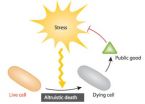
Engineered bacteria can make the ultimate sacrifice
2012-11-20
HEIDELBERG, 20 November 2012 – Scientists have engineered bacteria that are capable of sacrificing themselves for the good of the bacterial population. These altruistically inclined bacteria, which are described online in the journal Molecular Systems Biology, can be used to demonstrate the conditions where programmed cell death becomes a distinct advantage for the survival of the bacterial population.
"We have used a synthetic biology approach to explicitly measure and test the adaptive advantage of programmed bacterial cell death in Escherichia coli," said Lingchong ...
Impulsivity in first grade predicts problem gambling in late teen years for urban boys
2012-11-20
November 20, 2012 -- Results of a new study by researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health indicate that a developmental pattern of impulsiveness in young males is linked with gambling problems in late adolescence. Respondents considered to be in the high impulsivity track as early as first grade doubled the odds of meeting criteria for at-risk/problem gambling, and tripled the odds of meeting criteria for problem gambling. The study is the first to link a developmental pattern of impulsivity -- defined as a tendency to make rush decisions without ...
More than a machine
2012-11-20
Viruses can be elusive quarry. RNA viruses are particularly adept at defeating antiviral drugs because they are so inaccurate in making copies of themselves. With at least one error in every genome they copy, viral genomes are moving targets for antiviral drugs, creating resistant mutants as they multiply. In the best-known example of success against retroviruses, it takes multiple-drug cocktails to corner HIV and narrow its escape route.
Rather than target RNA viruses themselves, aiming at the host cells they invade could hold promise, but any such strategy would have ...
Call to establish 'Centers of Excellence' for pituitary diseases
2012-11-20
Philadelphia, Pa. (November 20, 2012) – The time has come to develop a pituitary "centers of excellence" (CoE) designation for hospitals with high-level surgical skills and other capabilities needed to provide state-of-the-art care for patients with pituitary tumors, according to an article in the November issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Recent advances in surgical and medical management—along with the high prevalence and impact ...
Why do meningiomas grow during pregnancy?
2012-11-20
Philadelphia, Pa. (November 16. 2012) – Meningiomas are a common type of benign brain tumor that sometimes grows dramatically in pregnant women. A new study suggests that this sudden tumor growth likely results from "hemodynamic changes" associated with pregnancy, reports the November issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The study also identifies some key characteristics associated with rapid growth of meningiomas in pregnant women. ...
Embattled childhoods may be the real trauma for soldiers with PTSD
2012-11-20
New research on posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in soldiers challenges popular assumptions about the origins and trajectory of PTSD, providing evidence that traumatic experiences in childhood - not combat - may predict which soldiers develop the disorder.
Psychological scientist Dorthe Berntsen of Aarhus University in Denmark and a team of Danish and American researchers wanted to understand why some soldiers develop PTSD but others don't. They also wanted to develop a clearer understanding of how the symptoms of the disorder progress.
"Most studies on PTSD in ...
Rice unveils super-efficient solar-energy technology
2012-11-20
HOUSTON -- (Nov. 19, 2012) -- Rice University scientists have unveiled a revolutionary new technology that uses nanoparticles to convert solar energy directly into steam. The new "solar steam" method from Rice's Laboratory for Nanophotonics (LANP) is so effective it can even produce steam from icy cold water.
Details of the solar steam method were published online today in ACS Nano. The technology has an overall energy efficiency of 24 percent. Photovoltaic solar panels, by comparison, typically have an overall energy efficiency around 15 percent. However, the inventors ...
Network's 'it takes a village' approach improves dementia care and informs research, study shows
2012-11-20
INDIANAPOLIS -- The approach of the Indianapolis Discovery Network for Dementia -- with contributions from family members, community advocates, health care systems and researchers -- improves dementia care and informs dementia research, according to a new study by researchers from the Regenstrief Institute and the Indiana University Center for Aging Research.
"Collaborative dementia care -- sensitive to local needs and concerns -- combines human interaction of all those involved plus technology. Regular face-to-face meetings of caregivers, clinicians and researchers provide ...