(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, CA —) Portable, accurate, and highly sensitive devices that sniff out vapors from explosives and other substances could become as commonplace as smoke detectors in public places, thanks to researchers at University of California, Santa Barbara.
Researchers at UCSB, led by professors Carl Meinhart of mechanical engineering and Martin Moskovits of chemistry, have designed a detector that uses microfluidic nanotechnology to mimic the biological mechanism behind canine scent receptors. The device is both highly sensitive to trace amounts of certain vapor molecules, and able to tell a specific substance apart from similar molecules.
"Dogs are still the gold standard for scent detection of explosives. But like a person, a dog can have a good day or a bad day, get tired or distracted," said Meinhart. "We have developed a device with the same or better sensitivity as a dog's nose that feeds into a computer to report exactly what kind of molecule it's detecting." The key to their technology, explained Meinhart, is in the merging of principles from mechanical engineering and chemistry in a collaboration made possible by UCSB's Institute for Collaborative Biotechnologies.
Results published this month in Analytical Chemistry show that their device can detect airborne molecules of a chemical called 2,4-dinitrotoluene, the primary vapor emanating from TNT-based explosives. The human nose cannot detect such minute amounts of a substance, but "sniffer" dogs have long been used to track these types of molecules. Their technology is inspired by the biological design and microscale size of the canine olfactory mucus layer, which absorbs and then concentrates airborne molecules.
"The device is capable of real-time detection and identification of certain types of molecules at concentrations of 1 ppb or below. Its specificity and sensitivity are unparalleled," said Dr. Brian Piorek, former mechanical engineering doctoral student in Meinhart's laboratory and Chief Scientist at Santa Barbara-based SpectraFluidics, Inc. The technology has been patented and exclusively licensed to SpectraFluidics, a company that Piorek co-founded in 2008 with private investors.
"Our research project not only brings different disciplines together to develop something new, but it also creates jobs for the local community and hopefully benefits society in general," commented Meinhart.
VIDEO:
Inspired by the biology of canine scent receptors, UC Santa Barbara scientists develop a chip capable of quickly identifying trace amounts of vapor molecules.
Click here for more information.
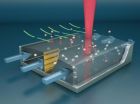
Packaged on a fingerprint-sized silicon microchip and fabricated at UCSB's state-of-the-art cleanroom facility, the underlying technology combines free-surface microfluidics and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to capture and identify molecules. A microscale channel of liquid absorbs and concentrates the molecules by up to six orders of magnitude. Once the vapor molecules are absorbed into the microchannel, they interact with nanoparticles that amplify their spectral signature when excited by laser light. A computer database of spectral signatures identifies what kind of molecule has been captured.
"The device consists of two parts," explained Moskovits. "There's a microchannel, which is like a tiny river that we use to trap the molecules and present them to the other part, a mini spectrometer powered by a laser that detects them. These microchannels are twenty times smaller than the thickness of a human hair."
"The technology could be used to detect a very wide variety of molecules," said Meinhart. "The applications could extend to certain disease diagnosis or narcotics detection, to name a few."
Moskovits added, "The paper we published focused on explosives, but it doesn't have to be explosives. It could detect molecules from someone's breath that may indicate disease, for example, or food that has spoiled."
The fundamental research was developed through an interdisciplinary collaboration between Professors Meinhart and Moskovits, and carried out by former doctoral researchers Dr. Piorek and Dr. Seung-Joon Lee. Their project was funded in part by UCSB's Institute for Collaborative Biotechnologies through the Army Research Office and DARPA.
INFORMATION:
The College of Engineering at University of California, Santa Barbara is recognized globally as a leader among the top tier of engineering education and research programs, and is renowned for a successful interdisciplinary approach to engineering research.
The Institute for Collaborative Biotechnologies at University of California, Santa Barbara is a uniquely interdisciplinary alliance of more than 150 researchers in academia, industry, and the U.S. Army that conducts unclassified, fundamental bio-inspired research in sensors, materials, biodiscovery, network science, and cognitive neuroscience. Led by the University of California, Santa Barbara, in collaboration with MIT, Caltech, the Army, and industry partners, the ICB transforms biological inspiration into technological innovation.
Nanotech device mimics dog's nose to detect explosives
Inspired by the biology of canine scent receptors, UC Santa Barbara scientists develop a chip capable of quickly identifying trace amounts of vapor molecules
2012-11-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nanomedicine breakthrough could improve chemotherapy for childhood cancer
2012-11-20
In a world-first, researchers from the Australian Centre for Nanomedicine at the University of New South Wales (UNSW) in Sydney have developed a nanoparticle that could improve the effectiveness of chemotherapy for neuroblastoma by a factor of five.
Neuroblastoma is an aggressive childhood cancer that often leaves survivors with lingering health problems due to the high doses of chemotherapy drugs required for treatment. Anything that can potentially reduce these doses is considered an important development.
The UNSW researchers developed a non-toxic nanoparticle ...
Rituximab shows promise for clinical problems tied to antiphospholipid antibodies
2012-11-20
Rituximab, a drug used to treat cancer and arthritis, may help patients with antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs) who suffer from aPL-related clinical problems that do not respond to anticoagulation, such as cardiac disease and kidney disease, according to a new study by rheumatology researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery. The study appears online ahead of print, in the journal Arthritis and Rheumatism.
"This is the first study to systematically analyze rituximab in aPL-positive patients. Rituximab may have a role in treating a subgroup of aPL patients," said Doruk ...
VTT: A low-carbon Finland is a great challenge, but an achievable one
2012-11-20
VTT specialists have assessed Finland's chances of achieving the 80% greenhouse gas emission reduction targets. The EU's goal for 2050 is to reduce emissions by at least 80% from the level of 1990.
The goal is a tough one for Finland, but possible to achieve as long as all sectors that produce or consume energy take part. On top of this, all greenhouse gas emissions must be reduced. Finland requires new technological solutions for industrial activity, for the transport of people, goods and services, and for housing and working methods. If clean forms of energy and the ...
Europe must not lose momentum in marine biodiversity research
2012-11-20
A new Marine Board Future Science Brief presents a roadmap for marine biodiversity science in Europe and warns against complacency.
The ocean provides 95% of the habitable space on Earth and harbours a vast diversity of life. Biodiversity underpins the health of the oceans and their productive ecosystems which are essential for human well-being and prosperity. But marine life is under significant threat from climate change and from increasing human impacts including pollution, overfishing and ocean acidification. Marine biodiversity research and its role in supporting ...
Gastric bypass surgery: Follow up as directed to lose more
2012-11-20
Gastric bypass patients who attended five follow-up office visits in two years as recommended by their surgeons lost nearly twice as much weight (113 lbs. vs. 57 lbs.) as patients who attended only two follow-up visits, according to a University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing study in Obesity Surgery.
The global epidemic of overweight and obese people is estimated to include 1.7 billion individuals, with two-thirds of those living in the U.S. Measurement of body mass index (BMI), a calculation of height and weight, classifies obesity. Patients with severe obesity ...
Sweat glands play major role in healing human wounds, U-M research shows
2012-11-20
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Turns out the same glands that make you sweat are responsible for another job vital to your health: they help heal wounds.
Human skin is rich with millions of eccrine sweat glands that help your body cool down after a trip to the gym or on a warm day. These same glands, new University of Michigan Health System research shows, also happen to play a key role in providing cells for recovering skin wounds – such as scrapes, burns and ulcers.
The findings were released online ahead of print in the American Journal of Pathology.
"Skin ulcers – including ...
King's Water Research Group co-convenes global conference on food and water security
2012-11-20
A team of experts from King's College London have played a major role in delivering an international conference on food and water security in Qatar this week. The Food Security in Dry Lands (FSDL) conference has been organised in the run up to the forthcoming UN climate meeting (COP18) later this month, where 'climate-smart' agriculture is expected to be a key focus.
The King's Water Research Group have contributed to the new Doha Declaration, which states that by 2022, participating countries -Qatar, Kenya, Tanzania, Chad, Egypt, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Nigeria, ...
Discovery of molecular pathway of Alzheimer's disease reveals new drug targets
2012-11-20
The discovery of the molecular pathway that drives the changes seen in the brains of Alzheimer's patients is reported today, revealing new targets for drug discovery that could be exploited to combat the disease. The study gives the most detailed understanding yet of the complex processes leading to Alzheimer's.
Alzheimer's disease is associated with plaques made up of deposits of a molecule called amyloid between brain cells, which leads to the formation of tangles of twisted fibres made from a molecule called tau, found inside the brain cells. This causes the death ...
Frequency of alcohol consumption and cardiovascular risk factors
2012-11-20
Critique 096: Frequency of alcohol consumption and cardiovascular risk factors: implications for drinking guidelines 20 November 2012
Read the full critique here: http://www.bu.edu/alcohol-forum/critique-096-frequency-of-alcohol-consumption-and-cardiovascular-risk-factors-implications-for-drinking-guidelines-20-november-2012/
The purpose of this paper was to examine whether drinkers who consume lower-risk amounts on more frequent occasions have favourable risk factor profiles compared with those who drink more per occasion but less frequently. The authors also discuss ...
Dance boosts young girls' mental health
2012-11-20
Young girls can dance their way to better mental health. Symptoms like depression, stress, fatigue, and headaches are alleviated with regular dancing. This is shown in a study run by Anna Duberg, a physical therapist at Örebro University Hospital and a doctoral candidate at Örebro University in Sweden. Regular dance training can thereby be regarded as a strategy for preventing and treating low spirits and depression. Dance also brings enhanced self-esteem and a greater capacity to deal with everyday problems.
The dance study included 112 Swedish girls 13 to 19 years ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
[Press-News.org] Nanotech device mimics dog's nose to detect explosivesInspired by the biology of canine scent receptors, UC Santa Barbara scientists develop a chip capable of quickly identifying trace amounts of vapor molecules