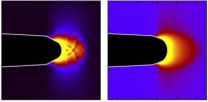
(Press-News.org) CHICAGO – People with Parkinson's disease benefit from exercise programs on stationary bicycles, with the greatest effect for those who pedal faster, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Functional connectivity magnetic resonance imaging (fcMRI) data showed that faster pedaling led to greater connectivity in brain areas associated with motor ability.
Parkinson's disease is a chronic, progressive disorder of the central nervous system. Early-stage symptoms like shaking and difficulty with walking eventually may progress to cognitive and behavioral problems such as dementia. An estimated 7 to 10 million people worldwide live with Parkinson's disease, according to the Parkinson's Disease Foundation, with most cases occurring after the age of 50.
As the disease progresses and the frequency of side effects increases, the therapeutic window begins to close. Deep brain stimulation is an effective therapy for late-stage Parkinson's disease, but is an invasive and costly procedure.
Exercise is thought to have beneficial effects on Parkinson's disease. Jay L. Alberts, Ph.D., neuroscientist at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute in Cleveland, saw this firsthand in 2003 when he rode a tandem bicycle across Iowa with a Parkinson's disease patient to raise awareness of the disease. The patient experienced improvements in her symptoms after the ride.
"The finding was serendipitous," Dr. Alberts recalled. "I was pedaling faster than her, which forced her to pedal faster. She had improvements in her upper extremity function, so we started to look at the possible mechanism behind this improved function."
As part of this inquiry, Dr. Alberts, researcher Chintan Shah, B.S., and their Cleveland Clinic colleagues, recently used fcMRI to study the effect of exercise on 26 Parkinson's disease patients.
"By measuring changes in blood oxygenation levels in the brain, fcMRI allows us to look at the functional connectivity between different brain regions," Shah said.
The patients underwent bicycle exercise sessions three times a week for eight weeks. Some patients exercised at a voluntary level and others underwent forced-rate exercise, pedaling at a speed above their voluntary rate. The researchers used a modified exercise bike to induce forced-rate activity.
"We developed an algorithm to control a motor on the bike and used a controller to sense the patient's rate of exertion and adjust the motor based on their input," Dr. Alberts said.
fcMRI was conducted before and after the eight weeks of exercise therapy and again as follow-up four weeks later. The research team calculated brain activation and connectivity levels from the fcMRI results and correlated the data with average pedaling rate. Results showed increases in task-related connectivity between the primary motor cortex and the posterior region of the brain's thalamus. Faster pedaling rate was the key factor related to these improvements, which were still evident at follow-up.
"The results show that forced-rate bicycle exercise is an effective, low-cost therapy for Parkinson's disease," Shah said.
Dr. Alberts noted that that while faster pedaling led to more significant results, not all Parkinson's patients need to do forced-rate exercise to see improvement.
"We're now looking at this phenomenon in patients with exercise bikes in their home," he said, "and other exercises like swimming and rowing on tandem machines may provide similar benefits."
###
Coauthors are Micheal D. Phillips, M.D. (principal investigator), Erik B. Beall, Ph.D., Anneke M.M. Frankemolle, B.S., Amanda Penko, M.A., and Mark J. Lowe, Ph.D.
Note: Copies of RSNA 2012 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press12 beginning Monday, Nov. 26.
RSNA is an association of more than 50,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists, promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill.
Editor's note: The data in these releases may differ from those in the published abstract and those actually presented at the meeting, as researchers continue to update their data right up until the meeting. To ensure you are using the most up-to-date information, please call the RSNA Newsroom at 1-312-949-3233.
For patient-friendly information on functional MRI, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
CHICAGO – Both very high and very low levels of physical activity can accelerate the degeneration of knee cartilage in middle-aged adults, according to a new study presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Nearly one in every two people in the U.S. may develop knee osteoarthritis by age 85, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. By 2030, an estimated 67 million Americans over the age of 18 are projected to have physician-diagnosed arthritis.
Researchers at the University of California in San Francisco ...
CHICAGO – An active lifestyle helps preserve gray matter in the brains of older adults and could reduce the burden of dementia and Alzheimer's disease (AD), according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Dementia exacts a staggering toll on society. More than 35 million people worldwide are living with the disease, according to the World Health Organization, and the prevalence is expected to double by 2030. AD is the most common cause of dementia and currently has no cure.
Cyrus Raji, M.D., Ph.D., radiology ...
CHICAGO – Using a special magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique to image patients with mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI), researchers have identified a biomarker that may predict which patients will do well over the long term, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
The results of the study showed that in some patients the brain may have changed to compensate for the damage caused by the injury.
"This finding has huge potential implications for preventing and repairing the damage that accompanies ...
CHICAGO – All patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) lose brain cells, which leads to a shrinking, or atrophy, of the brain. But the pattern of gray matter loss is significantly different in men and women, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
"We found that the extent and distribution of regional gray matter volume loss in the brain was strongly influenced by gender," said lead researcher Maria Vittoria Spampinato, M.D., associate professor of radiology at the Medical University of South Carolina ...
VIDEO:
Inflatable bouncers such as bounce houses, slides or obstacle courses are the new craze for kids' birthday parties and/or celebrations. While they appear to be a fun activity for a...
Click here for more information.
A new study by researchers at the Center for Injury Research and Policy of The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital examined pediatric injuries associated with inflatable bouncers, such as bounce houses and moonwalks. Researchers found ...
November 26, 2012 – (BRONX, NY) – Researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University and Montefiore Medical Center have found that a special magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique may be able to predict which patients who have experienced concussions will improve. The results, which were presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), suggest that, in some patients, the brain may change to compensate for the damage caused by the injury.
"This finding could lead to strategies for preventing and repairing ...
Metallic glass alloys (or liquid metals) are three times stronger than the best industrial steel, but can be molded into complex shapes with the same ease as plastic. These materials are highly resistant to scratching, denting, shattering and corrosion. So far, they have been used in a variety of products from golf clubs to aircraft components. And, some smartphone manufacturers are even looking to cast their next-generation phone cases out of it.
But despite their potential, the mechanical properties of these substances are still a scientific mystery. One lingering question ...
PULLMAN, Wash.—Scientists and business people have known for decades that certain scents—pine boughs at Christmas, baked cookies in a house for sale—can get customers in the buying spirit. Eric Spangenberg, a pioneer in the field and dean of the Washington State University College of Business, has been homing in on just what makes the most commercially inspiring odor.
Spangenberg and colleagues at WSU and in Switzerland recently found that a simple scent works best.
Writing in the Journal of Retailing, the researchers describe exposing hundreds of Swiss shoppers to simple ...
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- What types of public messages will most likely deter drug and alcohol abuse or dissuade people from engaging in risky behavior? Negatively framed messages may not be an effective way to reach those most in need of persuasion, suggests a new study in Psychology of Addictive Behaviors by researchers from Indiana University and Wayne State University.
"The findings are somewhat ironic because a whole lot of public service announcements say, 'Drugs are bad for you,' 'Just say no,' or 'This is your brain on drugs' with an image of an egg frying," said ...
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- An Indiana University study in the Journal of Child Neurology proposes an innovative treatment for developmental coordination disorder, a potentially debilitating neurological disorder in which the development of a child's fine or gross motor skills, or both, is impaired.
DCD strikes about one in 20 children, predominantly boys, and frequently occurs alongside ADHD, autism spectrum disorders and other better known conditions. Like ADHD, DCD has broad academic, social and emotional impact. It can severely affect reading, spelling and handwriting abilities; ...