(Press-News.org) CHICAGO – Researchers assessing the impact of revised guidelines for screening mammography issued by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found evidence that the new recommendations may lead to missed cancers and a decline in screening, according to two studies presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Routine screening mammography has traditionally been recommended by both the USPSTF and the American Cancer Society for all women over the age of 40. In 2009, the USPSTF issued controversial new guidelines recommending routine screening with mammography every two years for women 50 to 74 years old. In the studies being presented at RSNA 2012, researchers analyzed the impact of the new guidelines on women between the ages of 40 and 49 and the Medicare population.
"Recommendations on screening mammography are extremely important public policy and we wanted to contribute to that dialogue," said Elizabeth Arleo, M.D., assistant professor of radiology at New York – Presbyterian Hospital — Weill Cornell Medical College in New York City. "We get questions all day long from patients and referring physicians on the appropriateness of screening mammography. The inconsistent information is very confusing for everyone."
For her study, Dr. Arleo and a team of researchers analyzed data on screening mammography at New York – Presbyterian Hospital — Weill Cornell Medical College between 2007 and 2010. Over the four years, 43,351 screening exams were performed, which led to the detection of 205 breast cancers.
"Nearly 20 percent of cancers detected with screening mammography were found among women in their 40s, Dr. Arleo said. "It seems unacceptable to potentially miss nearly 20 percent of the breast cancers we are identifying. This, in our view, would represent a substantial degree of under-diagnosis."
Of the women screened in the study, 14,528, or 33.5 percent, were between the ages of 40 and 49. Of the 205 breast cancers detected, 39 (19 percent) were found in the 40-49 age group. Of those cancers, more than 50 percent (21 of 39) were invasive. Only three of the women between the ages of 40 and 49 diagnosed with cancer had a first-degree relative with pre-menopausal cancer.
"Our data favor the American Cancer Society recommendations of annual mammograms starting at age 40," Dr. Arleo said.
In the second study, a team of researchers analyzed data from The Medicare Part B Physician/Supplier Procedure Summary Master Files for 2005-2010. They calculated the following annual utilization rates for screening mammography per 1,000 female Medicare beneficiaries: 2005, 311.6; 2006, 312.4; 2007, 316.2; 2008, 320.1; 2009, 322.9; and 2010, 309.1.
From 2005 to 2009, the compound annual growth rate for screening mammography utilization was 0.9 percent, compared to a 4.3 percent decline in the utilization rate from 2009 to 2010.
"There was considerable controversy over the task force guidelines, but it was unclear how much they would influence women's choices about screening," said David C. Levin, M.D., professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Radiology at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital in Philadelphia. "We're not able to tell from the data whether this significant drop in utilization was a result of women deciding to wait another year to have their mammogram, or women over the age of 74 not having the exam. But, clearly, the new USPSTF guidelines have had an effect."
Dr. Levin said the drop in the mammography utilization rate is especially concerning, given that the 2009 rate of 322.9 per 1,000 women wasn't particularly high.
"We'll never see 1,000 out of 1,000 women getting a screening mammogram, but you'd like to see that number closer to 1,000, and certainly higher than 322," he said. "We need to continue to follow these numbers and to watch the breast cancer mortality statistics."
###
Coauthors of Dr. Arleo's research are Melissa B. Reichman, M.D., Ruth Rosenblatt, M.D., Kemi T. Babagbemi, M.D., and Brittany Zadek Dashevsky, M.D., Ph.D.
Coauthors of Dr. Levin's research are Andrea J. Frangos, M.P.H., Vijay M. Rao, M.D., Laurence Parker, Ph.D., and Richard Sharpe, M.D., M.B.A.
Note: Copies of RSNA 2012 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press12 beginning Monday, Nov. 26.
RSNA is an association of more than 50,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists, promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill.
Editor's note: The data in these releases may differ from those in the published abstract and those actually presented at the meeting, as researchers continue to update their data right up until the meeting. To ensure you are using the most up-to-date information, please call the RSNA Newsroom at 1-312-949-3233.
For patient-friendly information on mammography, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
New studies show effects of mammography guideline changes
2012-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify physiological evidence of 'chemo brain'
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – Chemotherapy can induce changes in the brain that may affect concentration and memory, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Using positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography (PET/CT), researchers were able to detect physiological evidence of chemo brain, a common side effect in patients undergoing chemotherapy for cancer treatment.
"The chemo brain phenomenon is described as 'mental fog' and 'loss of coping skills' by patients who receive chemotherapy," said Rachel ...
A new look at wetting models: Continuum analysis
2012-11-27
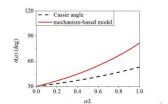
The wetting model is a classical problem in surface science and biomimetic science. Professor LIU Jianlin and his collaborators from China University of Petroleum, Wuhan University and Fourth Military Medical University approached this old and classical problem from a new direction. They stressed that it is the triple contact line and not the contact area of the droplet/solid interface that determines the macroscopic contact angle. The proposed continuum model, termed the mechanism-based model, can illustrate the contact line pinning effect at some wedges or phase interfaces ...
Gene that causes tumor disorder linked to increased breast cancer risk
2012-11-27
New Johns Hopkins research showing a more than four-fold increase in the incidence of breast cancer in women with neurofibromatosis-1 (NF1) adds to growing evidence that women with this rare genetic disorder may benefit from early breast cancer screening with mammograms beginning at age 40, and manual breast exams as early as adolescence.
In a small study of 126 women with NF1 at the Johns Hopkins Comprehensive Neurofibromatosis Center, the Johns Hopkins scientists identified four cases of breast cancer. The study showed a four-fold increased risk for breast cancer in ...
Researchers find chemical 'switches' for neurodegenerative diseases
2012-11-27
By using a model, researchers at the University of Montreal have identified and "switched off" a chemical chain that causes neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and dementia. The findings could one day be of particular therapeutic benefit to Huntington's disease patients. "We've identified a new way to protect neurons that express mutant huntingtin proteins," explained Dr. Alex Parker of the University of Montreal's Department of Pathology and Cell Biology and its affiliated CRCHUM Research Centre. A cardinal feature of ...
Four Steps to Protect Your Finances During a Divorce
2012-11-27
Four Steps to Protect Your Finances During a Divorce
Divorce is not only emotionally draining, but it also can be financially draining if you do not carefully plan your finances. With the current divorce rate in America sitting at 40 to 50 percent, divorce is a prevalent issue for many people. When going through a divorce, you can avoid financial turmoil by following a few simple planning tips.
Assess the Impact of Divorce on Your Financial Goals
Project future expenses that the divorce will create as well as any future expenses to which you will now contribute ...
Bankruptcy Can Help New Jersey Homeowners Avoid Foreclosure
2012-11-27
Bankruptcy Can Help New Jersey Homeowners Avoid Foreclosure
New Jersey second quarter foreclosure statistics were recently released. At first glance, the results appear encouraging. The overall number of New Jersey foreclosure sales decreased from last year by 40 percent. During the second quarter, one out of 11 New Jersey home sales involved a foreclosed property, in contrast to one in four nationwide.
However rosy the numbers look, experts say that the apparent statistical decrease in mortgage foreclosures is likely not due to a decrease in the actual number of ...
Michigan's "Super Drunk" Law: Higher BAC, More Penalties
2012-11-27
Michigan's "Super Drunk" Law: Higher BAC, More Penalties
Many drivers convicted of driving while intoxicated have a high blood alcohol concentration. Even just a few drinks in an hour can put a driver over the legal limit to drive, which is .08 percent in all 50 states. However, a significant number of drunk driving convictions stem from incidents where a driver is more than twice the legal limit to drive.
In an attempt to target such high BAC drivers, Michigan adopted a so-called "Super Drunk" law, which increases the fines and penalties associated ...
Spinal Cord Injury Research Continuing
2012-11-27
Spinal Cord Injury Research Continuing
Spinal cord research has made strides in recent years, good news to the 5.6 million paralyzed people currently living in America and the 12,000 new people hospitalized for spinal cord injury (SCI) every year. However, progress is being made in fits and starts, and new research continues to battle this devastating injury.
Promising New Research
Neuroscience 2012, the annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience, offered a variety of potential future solutions to SCI, from reducing pain in the injured patient to actually curing ...
New Study Shows Bedsores Linked to Patient Fatalities
2012-11-27
New study shows bedsores linked to patient fatalities
When we come to the conclusion that we must turn over the care of a loved one to a nursing home, it is common for that difficult decision to be accompanied by fears about his or her continued well-being. One of the dangers associated with nursing home care is the development of bedsores, also referred to as pressure ulcers. Recently, a new study revealed that the consequences of these injuries can be far more serious than previously understood.
Bedsores occur when the tissue and skin on an individual are injured, ...
Respond Intelligently to Debt Collector Harassment
2012-11-27
Respond Intelligently to Debt Collector Harassment
Each year, millions of Americans find themselves in significant debt. Too often, debt brings with it not only constant worry about bills and finances, but also harassing phone calls from unscrupulous bill collectors. Fortunately, consumers do have rights and there are some basic steps people can take to protect themselves from creditor harassment.
Make a Plan
If debt collectors begin making harassing phone calls to your home, it is important to come up with a plan on how to address them. Designate one person in ...