(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – As U.S. health care goes high tech, spurred by $20 billion in federal stimulus incentives, the widespread adoption of electronic medical records and related digital technologies is predicted to reduce errors and lower costs – but it is also likely to significantly boost musculoskeletal injuries among doctors and nurses, concludes a Cornell University ergonomics professor in two new papers.
The repetitive strain injuries, he said, will stem from poor office layouts and improper use of computer devices.
"Many hospitals are investing heavily in new technology with almost no consideration for principles of ergonomics design for computer workplaces," said Alan Hedge, professor of human factors and ergonomics in Cornell's College of Human Ecology's Department of Design and Environmental Analysis. "We saw a similar pattern starting in the 1980s when commercial workplaces computerized, and there was an explosion of musculoskeletal injuries for more than a decade afterward."
For a paper published in the Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society 56th Annual Meeting, held Oct. 22-26 in Boston, Hedge and James asked 179 physicians about the frequency and severity of their musculoskeletal discomfort, computer use in their clinic, knowledge of ergonomics and typing skills. The most commonly reported repetitive strain injuries were neck, shoulder and upper and lower back pain -- with a majority of female doctors and more than 40 percent of male doctors reporting such ailments on at least a weekly basis. About 40 percent of women and 30 percent of men reported right wrist injuries at a similar frequency. (Study: https://cornell.box.com/Hedge).
"These rates are alarming. When more than 40 percent of employees are complaining about regular problems, that's a sign something needs to be done to address it," said Hedge. "In a lot of hospitals and medical offices, workplace safety focuses on preventing slips, trips and falls and on patient handling, but the effects of computer use on the human body are neglected."
The gender differences, the authors write, appear to be in part because women reported spending about an hour longer on the computer per day than men.
In a second study of 180 physicians and 63 nurse practitioners and physician assistants in the same health system, published in a new volume, "Advances in Human Aspects of Healthcare" (CRC Press), more than 90 percent of respondents reported using a desktop computer at work. On average, they spent more than five hours per day using computers.
Fifty-six percent of doctors and 71 percent of nurse practitioners and physician assistants said their computer use at work had increased in the past year; 22 percent of doctors and 19 percent of nurse practitioners and physician assistants reported less time in face-to-face interactions with patients. Only about 5 percent of participants reported an "expert knowledge" of ergonomics, and more than two-thirds said they had no input in the planning or design of their computer or clinical workstation.
"We can't assume that just because people are doctors or work in health care that they know about ergonomics," Hedge said. "With so many potential negative effects for doctors and patients, it is critical that the implementation of new technology is considered from a design and ergonomics perspective."
###
Contact Syl Kacapyr for information about Cornell's TV and radio studios.
END
How effective is the German mammography screening program? This is the question examined by Oliver Heidinger of the Epidemiological Cancer Registry North Rhine–Westphalia and his co-authors in the first study on this subject in Germany, in Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2012; 109(46): 781-7).
To answer it, the authors have used the interval cancer rate as an indicator. Interval cancers are tumors found more or less by chance between two screenings. In approximately 880 000 women from North Rhine–Westphalia who had taken part in mammography screening ...
Philadelphia, Pa. (December 3, 2012) – A new technology called the Pipeline embolization device (PED) shows encouraging results in patients with certain types of difficult-to-treat brain aneurysms, reports the December issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Data collected since the PED was approved for marketing show generally good results in "real world" clinical practice. However, the report raises concerns about fatal bleeding and other ...
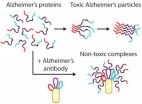
Troy, N.Y. – Antibodies developed by researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute are unusually effective at preventing the formation of toxic protein particles linked to Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, as well as Type 2 diabetes, according to a new study.
The onset of these devastating diseases is associated with the inappropriate clumping of proteins into particles that are harmful to cells in the brain (Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease) and pancreas (Type 2 diabetes). Antibodies, which are commonly used by the immune system to target foreign ...
ROSEMONT, Ill.—Extreme heat or cold can cause dangerous and potentially fatal side effects in athletes. A literature review appearing in the December 2012 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (JAAOS) provides an overview of the risk factors, signs and symptoms, and management of various conditions related to excessive heat and cold exposure.
"Both extreme heat and cold can be challenging for athletes during training and competition," said lead study author Benjamin Noonan, MD, MS. "One role of the team physician is to educate coaches and ...
Using deceptive behavioral patterns of squirrels and birds, researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have developed robots that are able to deceive each other. The research is funded by the Office of Naval Research and is led by Professor Ronald Arkin, who suggests the applications could be implemented by the military in the future. The research is highlighted in the November/December 2012 edition of IEEE Intelligent Systems.
Arkin and his team learned by reviewing biological research results that squirrels gather acorns and store them in specific locations. ...
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Dec. 3, 2012 – College football and basketball games may provide more than a way for students to show school spirit – they could help prevent the flu.
According to a new study by researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center, colleges and universities should implement new or improved influenza vaccine strategies, such as giving flu shots at sporting events or during campus-wide, day-long campaigns, to increase the number of their students who get the annual flu vaccine.
In the early online edition of the December issue of the Journal of American ...
Reston, Va. (December 3, 2012) – In the management of gliomas—or tumors that originate in the brain—precise assessment of tumor grade and the proliferative activity of cells plays a major role in determining the most appropriate treatment and predicting overall survival. Research published in the December issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (JNM) highlights the potential of imaging with 3'-deoxy-3'-F-18-fluorothymidine (F-18-FLT) positron emission tomography (PET) to noninvasively and accurately provide tumor-specific details to guide management of patients with gliomas.
Gliomas ...
University of Illinois researchers have developed a model that uses neonatal piglets for studying infant brain development and its effect on learning and memory. To determine if the model is nutrient-sensitive, they have done some research on the effects of iron-deficient diets.
"Iron deficiency is a major problem worldwide," said Rodney Johnson, professor of animal sciences and director of the Division of Nutritional Sciences. "Infants who experience iron deficiency during the first 6 to 12 months of age can have irreversible developmental delays in cognition."
He ...
This press release is available in Spanish.Outfitting soldiers with clothing that effectively repels or kills insects is one of the strategies U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists are using to help protect U.S. military personnel deployed overseas against disease-transmitting mosquitoes and sand flies.
As part of the Deployed War-Fighter Protection Research Program, scientists at the Agricultural Research Service (ARS) Center for Medical, Agricultural, and Veterinary Entomology (CMAVE) in Gainesville, Fla., and other ARS laboratories are collaborating with ...
ANN ARBOR—New research from the University of Michigan School of Public Health found BPA, or bisphenol A, in fetal liver tissue, demonstrating that there is considerable exposure to the chemical during pregnancy.
Researchers also found a proportionately higher concentration of free BPA—as opposed to the conjugated forms modified by the body for elimination—further showing that in fetuses the ability to eliminate the chemical from the body is not the same as in adults.
"The general message from our research is that people have to be cognizant of the fact that the adult ...