(Press-News.org) Forty years after the last Apollo spacecraft launched, the science from those missions continues to shape our view of the moon. In one of the latest developments, readings from the Apollo 14 and 15 dust detectors have been restored by scientists with the National Space Science Data Center (NSSDC) at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
"This is the first look at the fully calibrated, digital dust data from the Apollo 14 and 15 missions," said David Williams, a Goddard scientist and data specialist at NSSDC, NASA's permanent archive for space science mission data.
The newly available data will make long-term analysis of the Apollo dust readings possible. Digital data from these two experiments were not archived before, and it's thought that roughly the last year-and-a-half of the data have never been studied.
The work was presented on December 6 at the American Geophysical Union meeting in San Francisco, as part of a session organized in honor of the 40th anniversary of the Apollo 17 launch. Also presented in this session was a similar effort to fill in gaps in the Apollo 15 and 17 heat-flow measurements, the only such measurements ever taken on the moon or any planetary body other than Earth.
The recovery of these data sets is part of the Lunar Data Project, an ongoing NSSDC effort, drawing on researchers at multiple institutions, to make the scientific data from Apollo available in modern formats.
The Lunar Dust Detectors that were placed on the lunar surface during Apollo 14 and 15 measured dust accumulation, temperature and damage caused by high-energy cosmic particles and the sun's ultraviolet radiation. The same kind of instrument had flown earlier on Apollo 11 and 12 (Later, Apollo 17 carried a different type of dust detector).
Restoring the data was a painstaking job of going through one data set and separating the raw detector counts from temperatures and "housekeeping" information that was collected to keep an eye on how healthy the Apollo instruments were. A second, less complete data set indicated how to convert the raw counts into usable measurements. But first, the second data set had to be converted from microfilm, which had been archived at NSSDC in the 1970s, and the two data sets had to reconciled because their time points didn't match up exactly. Most of this meticulous work was carried out by Marie McBride, an undergraduate from the Florida Institute of Technology in Melbourne who was working with Williams through a NASA internship.
Newer missions, such as NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), have continued to study lunar dust. "It's one of those questions that scientists keep coming back to," said McBride.
"Just last week, LRO did some important measurements seeking dust profiles in the lunar atmosphere," said Rich Vondrak, the LRO deputy project scientist at NASA Goddard. LRO has been orbiting the moon since June 2009, and the mission was recently extended through 2015.
And the main objective of NASA's Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE), scheduled to launch in 2013, is to characterize the moon's atmosphere and dust environment.
This offers another example of how profoundly influential the Apollo data continues to be, observed Noah Petro, a member of the LRO project science team at NASA Goddard. "A mission ends when it ends, but the science continues forever."
INFORMATION:
Apollo's lunar dust data being restored
2012-12-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
December 2012 Story Tips
2012-12-07
DISASTER RESPONSE – Limiting access . . .
Ensuring that only people who have legitimate business are allowed to enter areas hit by floods, hurricanes or other disasters is a big challenge, but Credentialing 2.0 offers a software solution. "Obviously, first responders, utility crews, tree cutters, disaster relief workers and members of the media have reasons to be on the scene, but there's no efficient way to control access," said Oak Ridge National Laboratory's David Resseguie, who leads the Credentialing 2.0 development team. The ORNL system helps officials to control ...
Combining two genome analysis approaches supports immune system contribution to autism
2012-12-07
Researchers using novel approaches and methodologies of identifying genes that contribute to the development of autism have found evidence that disturbances in several immune-system-related pathways contribute to development of autism spectrum disorders. The report published December 4 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE powerfully supports a role for the immune function in autism by integrating analysis of autism-associated DNA sequence variations with that of markers identified in studies of families affected by autism.
"Others have talked about immune function contributions ...
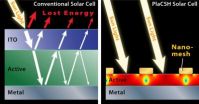
Tiny structure gives big boost to solar power
2012-12-07
Princeton researchers have found a simple and economic way to nearly triple the efficiency of organic solar cells, the cheap and flexible plastic devices that many scientists believe could be the future of solar power.
The researchers, led by electrical engineer Stephen Chou, were able to increase the efficiency 175 percent by using a nanostructured "sandwich" of metal and plastic that collects and traps light. Chou said the technology also should increase the efficiency of conventional inorganic solar collectors, such as standard silicon solar panels, although he cautioned ...
Valuable tool for predicting pain genes in people
2012-12-07
Scientists in Australia and Austria have described a "network map" of genes involved in pain perception, with remarkable similarity from fruit flies to people. The work should help identify new analgesic drugs.
Dr Greg Neely from the Garvan institute of Medical Research in Sydney and Professor Josef Penninger from the Austrian Academy of Sciences in Vienna had previously screened the 14,000 genes in the fly genome and identified 580 genes identified with heat perception. In the current study, using a database from the US National Centre for Biotechnology Information, ...
Severe acute kidney injuries rise rapidly nationwide
2012-12-07
Severe acute kidney injuries are becoming more common in the United States, rising 10 percent per year and doubling over the last decade, according to a retrospective study at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
The study, to be published online this week in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, analyzed information from a national database that monitors all causes of hospitalizations and used this data to estimate the total number of acute kidney injuries in the United States that were severe enough to require a patient to be placed on dialysis. ...
Fasting may benefit patients with epilepsy, Johns Hopkins Children's Center study suggests
2012-12-07
Children with persistent and drug-resistant seizures treated with the high-fat, low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet may get an added therapeutic benefit from periodic fasting, according to a small Johns Hopkins Children's Center study.
The results, published online Dec. 3 in the journal Epilepsy Research, suggest the ketogenic diet and fasting can work in tandem to reduce seizures but appear do so through different mechanisms -- a finding that challenges the longstanding assumption that the two share a common mechanism.
"Our findings suggest that fasting does not merely ...
Paradox of aging: The older we get, the better we feel?
2012-12-07
Presently, there are about 40 million Americans over the age of 65, with the fastest-growing segment of the population over 80 years old. Traditionally, aging has been viewed as a period of progressive decline in physical, cognitive and psychosocial functioning, and aging is viewed by many as the "number one public health problem" facing Americans today.
But this negative view of aging contrasts with results of a comprehensive study of 1,006 older adults in San Diego by researchers from the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Stanford University. ...
New IDSA guidelines aim to reduce death, disability, and cost of prosthetic joint infections
2012-12-07
[EMBARGOED FOR DEC. 7, 2012, ARLINGTON, Va.] – Of the one million people each year who get hips and knees replaced, as many as 20,000 will get an infection in the new joint, a number that is expected to skyrocket in the next 20 years. Multispecialty physician teams need to work together to reduce disability, death and costs associated with the ever-growing number of these prosthetic joint infections, note the first guidelines on the topic being released by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
"There are very few things that improve quality of life as much ...
Antibiotic-eating bug unearthed in soil
2012-12-07
It's well known how bacteria exposed to antibiotics for long periods will find ways to resist the drugs—by quickly pumping them out of their cells, for instance, or modifying the compounds so they're no longer toxic.
Now new research has uncovered another possible mechanism of antibiotic "resistance" in soil. In a paper published on Dec. 6 in the Journal of Environmental Quality, a group of Canadian and French scientists report on a soil bacterium that breaks down the common veterinary antibiotic, sulfamethazine, and uses it for growth.
Certain soil bacteria are already ...
Nicaragua Participates in the 2012 Outsource to LAC
2012-12-07
Nicaragua is currently participating in the Latin American and the Caribbean (LAC) Offshoring and Outsourcing Summit, held in Medellin Colombia from December 4th to the 6th, whose objective is to promote the development of the outsourcing and offshoring industry in the region and establish key contacts between international companies interested in seeking new outsourcing destinations.
The Nicaraguan delegation participating in the summit includes representatives from PRONicaragua, the official investment and export promotion agency of the Government of Nicaragua, and ...