(Press-News.org) Research has shown a decrease in levels of the isotope nitrogen-15 in core samples from Greenland ice starting around the time of the Industrial Revolution. The decrease has been attributed to a corresponding increase in nitrates associated with the burning of fossil fuels.
However, new University of Washington research suggests that the decline in nitrogen-15 is more directly related to increased acidity in the atmosphere.
The increased acidity can be traced to sulfur dioxide, which in the atmosphere is transformed to sulfuric acid, said Lei Geng, a UW research associate in atmospheric sciences. Following the Industrial Revolution, sulfur dioxide emissions increased steadily because of coal burning.
"It changes the chemical properties of the lower troposphere, where we live, and that can have a lot of consequences," Geng said. He presents his findings Friday (Dec. 7) at the fall meeting of the American Geophysical Union in San Francisco.
The gradual buildup of acidity in the atmosphere over a century got a boost around 1950 with a sharp increase in nitrogen-oxygen compounds, referred to as NOx, mainly produced in high-temperature combustion such as occurs in coal-fired power plants and motor vehicle engines. NOx is easily converted to nitric acid in the atmosphere, further increasing the acidity.
NOx carries a chemical signature – the abundance of nitrogen-15, one of two nitrogen isotopes – which changes depending on the source. That means it is possible to distinguish NOx that came from a forest fire from NOx produced as a result of lightning, soil emissions, car exhaust and power plant emissions. The level of nitrogen-15 can be measured in nitrates that formed from NOx and were deposited in ice sheets such as those in Greenland.
Current evidence indicates NOx from coal-fired power plant and motor vehicle emissions likely carries more nitrogen-15 than NOx produced by natural sources, so nitrogen-15 levels in deposited nitrate could be expected to go up. However, those levels actually went down in the late 1800s, following the Industrial Revolution, Geng said. That's because increasing sulfuric acid levels in the atmosphere triggered chemical and physical processes that allowed less nitrogen-15 to remain in vaporized nitrate, which can be carried to remote places such as Greenland.
The growing acidity in the atmosphere was occurring decades before acid rain was recognized as a threat, particularly in industrial areas of North America.
Core samples from Greenland ice sheets reflect a correlation between nitrogen-15 levels and atmospheric acidity, Geng said. Data he studied came primarily from a core that is part of combined research between UW and South Dakota State University, funded by the National Science Foundation.
Geng noted that the core reflects a decline in signals for both NOx and sulfur dioxide emissions in the 1930s, during the Great Depression. The signals increased again following the Depression until the early 1970s, when Western nations experienced an economic downturn and an oil shortage. Shortly after that, the Clean Air Act in the United States began to have an impact on vehicle and power plant emissions.
"We've seen a huge drop in sulfate concentrations since the late 1970s," Geng said. "By 2005, concentrations had dropped to levels similar to the late 1800s."
Ice core data show nitrate levels have stabilized during that time, he said, because while emission levels from individual vehicles might have decreased substantially, the number of vehicles has increased significantly.
INFORMATION:
For more information, contact Geng at 206-543-4596 or leigeng@uw.edu.
Greenland ice sheet carries evidence of increased atmospheric acidity
2012-12-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA casts infrared eye on Southern Indian Ocean's Tropical Cyclone Claudia
2012-12-08
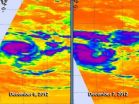
The third tropical cyclone in the Southern Indian Ocean has been renamed Tropical Cyclone Claudia as NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead.The AIRS instrument on Aqua captured infrared imagery of Claudia over two days that showed the western quadrant is most powerful part of the cyclone.
Aqua flew over Tropical Cyclone Claudia on Dec. 6 at 1959 UTC (2:59 p.m. EST/U.S.) and Dec. 7 at 0811 UTC (3:11 a.m. EST/U.S.). The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument analyzes storms in infrared light, and revealed the temperatures of clouds and sea surface around the storm. ...
NASA infrared data shows Typhoon Bopha re-strengthened in South China Sea
2012-12-08
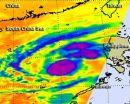
The deadly typhoon that caused almost 300 deaths in the southern Philippines is making a loop in the South China Sea, and infrared NASA satellite data indicated that Bopha re-intensified.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Bopha on Dec. 6 at 1811 UTC (1:11 p.m. EST, U.S.) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard captured an infrared look at the storm. The infrared data revealed where the coldest, highest cloud tops were. The coldest cloud tops indicate the strongest storms with the heaviest rain, and AIRS data revealed they surrounded the center of ...
2013 will be a good year, NJIT biz professor forecasts at Chicago Fed Board
2012-12-08
Economic growth will rise to 3 percent in 2013 and 2014, while unemployment will drop to 7.3 percent by December of 2013, NJIT Leir Research Professor William V. Rapp, PhD, http://www.njit.edu/news/experts/rapp.php, told economists and others last week at the annual outlook symposium, http://www.chicagofed.org/webpages/events/eos_series.cfm, sponsored by the Chicago Federal Reserve Bank.
The first Henry J. Leir Professor of International Trade and Business in the NJIT School of Management, Rapp was invited to participate in the annual event which draws the nation's ...
Another muscular dystrophy mystery solved; MU scientists inch closer to a therapy for patients
2012-12-08
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Approximately 250,000 people in the United States suffer from muscular dystrophy, which occurs when damaged muscle tissue is replaced with fibrous, bony or fatty tissue and loses function. Three years ago, University of Missouri scientists found a molecular compound that is vital to curing the disease, but they didn't know how to make the compound bind to the muscle cells. In a new study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academies of Science, MU School of Medicine scientists Yi Lai and Dongsheng Duan have discovered the missing pieces to this ...
Long-distance solute transport in trees improved by intercellular pathways in living woody tissues
2012-12-08
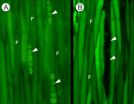
As large organisms, trees face some remarkable challenges, particularly regarding long-distance transport and communication. In addition to moving water and nutrients from their roots to their leaves, they must also integrate cell-to-cell communication over large areas. Furthermore, in order to function as a single, cohesive organism they must be able to effectively and efficiently send vital substances—such as DNA regulating signals—long distances along a network of cells, sieve-tubes, and vessels.
But how effective is this cell-to-cell communication and how far can ...
Massive crevasses and bendable ice affect stability of Antarctic ice shelf, CU research team finds
2012-12-08
Gaping crevasses that penetrate upward from the bottom of the largest remaining ice shelf on the Antarctic Peninsula make it more susceptible to collapse, according to University of Colorado Boulder researchers who spent the last four Southern Hemisphere summers studying the massive floating sheet of ice that covers an area twice the size of Massachusetts.
But the scientists also found that ribbons running through the Larsen C Ice Shelf – made up of a mixture of ice types that, together, are more prone to bending than breaking – make the shelf more resilient than it otherwise ...
Wildfires light up western Australia
2012-12-08
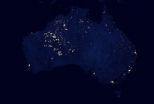
Careful observers of the new "Black Marble" images of Earth at night released this week by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration have noticed bright areas in the western part of Australia that are largely uninhabited. Why is this area so lit up, many have asked?
Away from the cities, much of the night light observed by the NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite in these images comes from wildfires. In the bright areas of western Australia, there are no nearby cities or industrial sites but, scientists have confirmed, there were fires in the area when Suomi ...
Storenvy Revamps With All-New Design, Social Shopping Experience For 25K Independent Storefronts
2012-12-08
Storenvy, the popular online store builder that's home to over 25,000 independent storefronts, today launches a socially-curated shopping platform for browsing items from the stores it powers, as well as a full brand redesign. The new platform will change the way people discover and buy products from the world's creative businesses.
"Right now, there isn't a go-to place on the web to buy from independent creative businesses, like industrial designers, fashion boutiques, clothing companies, nonprofits or musicians," founder and CEO Jon Crawford says. "Amazon ...
The Jumeirah Essex House Rated Best Hotel in New York
2012-12-08
In a recently published overview of Ten Top Hotels in New York, the 5 Star JW Marriott Essex House New York has been rated as the best hotel in Manhattan by the international hotel booking site http://whichhotel4me.com/.
A luxury hotel in Midtown Manhattan the JW Marriott Essex House New York is renowned for its excellent rooms, superb dining and world class customer service. Featuring panoramic park views and a range of top notch facilities including a swimming pool, business centre with secretarial service and meeting rooms, the hotel is close to all Manhattan's major ...
Nicholas Dracopoli, VP at Janssen to Keynote at GTC's Biomarker Summit, San Francisco, March 20-22
2012-12-08
Nicholas Dracopoli, Vice President and Head of Oncology Biomarkers at Janssen R&D will give a plenary keynote presentation entitled "Why So Few Companion Diagnostics? The Difficulty of Translating Biological Data into Predictive Biomarkers" at GTC's Biomarker Summit 2013, taking place in San Francisco, CA on March 20-22, 2013.
Translating complex genomic data into widely used clinical tests has been much slower than anticipated. FDA-approved diagnostic tests have only been approved to predict response to therapy for nine oncology drugs a decade after the ...