(Press-News.org) Are you allergic to peanuts and worried there might be some in that cookie? Now you can find out using a rather unlikely source: your cell phone.
A team of researchers from the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science has developed a lightweight device called the iTube, which attaches to a common cell phone to detect allergens in food samples. The iTube attachment uses the cell phone's built-in camera, along with an accompanying smart-phone application that runs a test with the same high level of sensitivity a laboratory would.
Food allergies are an emerging public concern, affecting as many as 8 percent of young children and 2 percent of adults. Allergic reactions can be severe and even life-threatening. And while consumer-protection laws regulate the labeling of ingredients in pre-packaged foods, cross-contaminations can still occur during processing, manufacturing and transportation.
Although several products that detect allergens in foods are currently available, they are complex and require bulky equipment, making them ill-suited for use in public settings, according to the UCLA researchers.
The iTube was developed to address these issues, said Aydogan Ozcan, leader of the research team and a UCLA associate professor of electrical engineering and bioengineering. Weighing less than two ounces, the attachment analyzes a test tube–based allergen-concentration test known as a colorimetric assay.
To test for allergens, food samples are initially ground up and mixed in a test tube with hot water and an extraction solvent; this mixture is allowed to set for several minutes. Then, following a step-by-step procedure, the prepared sample is mixed with a series of other reactive testing liquids. The entire preparation takes roughly 20 minutes. When the sample is ready, it is measured optically for allergen concentration through the iTube platform, using the cell phone's camera and a smart application running on the phone.
The kit digitally converts raw images from the cell-phone camera into concentration measurements detected in the food samples. And beyond just a "yes" or "no" answer as to whether allergens are present, the test can also quantify how much of an allergen is in a sample, in parts per million.
The iTube platform can test for a variety of allergens, including peanuts, almonds, eggs, gluten and hazelnuts, Ozcan said.
The UCLA team successfully tested the iTube using commercially available cookies, analyzing the samples to determine if they had any harmful amount of peanuts, a potential allergen. Their research was recently published online in the peer-reviewed journal Lab on a Chip and will be featured in a forthcoming print issue of the journal.
Other authors of the research included graduate student and lead author Ahmet F. Coskun and undergraduate students Justin Wong, Delaram Khodadadi, Richie Nagi and Andrew Tey, all of whom are members of the Ozcan BioPhotonics Laboratory at UCLA. Ozcan is also a member of the California NanoSystems Institute at UCLA.
"We envision that this cell phone–based allergen testing platform could be very valuable, especially for parents, as well as for schools, restaurants and other public settings," Ozcan said. "Once successfully deployed in these settings, the big amount of data — as a function of both location and time — that this platform will continuously generate would indeed be priceless for consumers, food manufacturers, policymakers and researchers, among others."
Allergen-testing results of various food products, tagged with a time and location stamp, can be uploaded directly from cell phones to iTube servers to create a personalized testing archive, which could provide additional resources for allergic individuals around the world. A statistical allergy database, coupled with geographic information, could be useful for future food-related policies — for example in restaurants, food production and for consumer protection, the researchers said.
INFORMATION:
The Ozcan BioPhotonics Lab is funded by the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE), the Army Research Office Young Investigator Award, the National Science Foundation CAREER Award, the Office of Naval Research Young Investigator Award and the National Institutes of Health Director's New Innovator Award.
For more information on the Ozcan BioPhotonics Research Group, visit http://innovate.ee.ucla.edu and http://biogames.ee.ucla.edu.
The UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science, established in 1945, offers 28 academic and professional degree programs and has an enrollment of more than 5,000 students. The school's distinguished faculty are leading research to address many of the critical challenges of the 21st century, including renewable energy, clean water, health care, wireless sensing and networking, and cybersecurity. Ranked among the top 10 engineering schools at public universities nationwide, the school is home to nine multimillion-dollar interdisciplinary research centers in wireless sensor systems, wireless health, nanoelectronics, nanomedicine, renewable energy, customized computing, the smart grid, and the Internet, all funded by federal and private agencies and individual donors.
(www.engineer.ucla.edu | www.twitter.com/uclaengineering)
For more UCLA news, visit the UCLA Newsroom and follow us on Twitter @UCLAnewsroom.
END
[EMBARGOED FOR DEC. 13, 2012] A new study suggests that human papillomavirus (HPV) infection in women at or after menopause may represent an infection acquired years ago, and that HPV infections may exist below limits of detection after one to two years, similar to other viruses, such as varicella zoster, which can cause shingles. The study, published in The Journal of Infectious Diseases and available online, highlights the need for additional research to better understand HPV infections and the role of HPV persistence and reactivation, particularly in women of the baby ...
An international team of scientists studying the elusive nocturnal primate the slow loris in the jungles of Borneo have discovered an entirely new species. The team's analysis of the primate's distinctive facial fur markings, published in the American Journal of Primatology, reveals the existence of one entirely new species, while two of species, previously considered as possible sub-species, are being officially recognized as unique.
"Technological advances have improved our knowledge about the diversity of several nocturnal mammals," said Rachel Munds from the University ...
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C., – Dec. 13, 2012 – Investigators at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center have concluded research on a new postmenopausal hormone therapy that shows promise as an effective treatment for menopausal symptoms and the prevention of osteoporosis without increasing the risk for heart disease or breast cancer.
Traditional forms of hormone therapy (HT) provide the benefits of symptom relief, prevention of osteoporosis and prevention of atherosclerosis, but increase the risk of uterine cancer (with estrogens alone) or breast cancer (with combined estrogens and ...
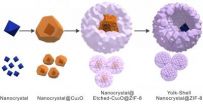
CHESTNUT HILL, MA (Dec. 13, 2012) – A chemical nanostructure developed by Boston College researchers behaves much like the pores of the skin, serving as a precise control for a typically stubborn method of catalysis that is the workhorse of industrial chemistry.
Scientists have been trying to develop so-called yolk-shell catalysts as a means of imparting greater selectivity on heterogeneous catalysis, a process used in most industrial chemistry, including the manufacture of fine chemicals, petrochemicals and agrochemicals.
Boston College Assistant Professor of Chemistry ...
A recent lawsuit highlights the rights of workers when faced with a recent disability. In Boyton Beach, Fla., a man is suing his employer after being fired three days after revealing he was approved to be on the waiting list to undergo a kidney transplant. He had been employed for 10 years in his role as a night shift manager, making $72,000 a year.
The employee did not want to quit and claims that he could have worked 40 hours a week. A doctor recommended self-cleaning dialysis, which the lawsuit claimed the employee could do over his lunch break and would not require ...
A Texas company that underpaid mentally disabled workers for decades recently received several million-dollar judgments against them for violating the Americans With Disabilities Act of 1990, the Fair Labor Standards Act and several state labor laws for its treatment of its disabled employees.
Hill Country Farms, d.b.a. Henry's Turkey Service, illegally paid disabled workers a total of 41 cents per hour to eviscerate turkeys at an Iowa plant. The workers' rate of pay did not change in 30 years. Some of the workers had been working at the plant since the 1970s. The company ...
Dealing with the death of a loved one is hard enough without having to handle the court appearances, legal duties and other details of administering to the final wishes of family and friends regarding their estates and burials. A comprehensive, up-to-date estate plan can avoid many inheritance disputes and complications, helping to ease the transition. Unfortunately, many people die without a proper estate plan, even if they managed to create a will. Even if an estate plan is legally valid and clear, simply by its nature, handling estate and inheritance matters can be complicated ...
After divorce, many people would like nothing more than to never see their ex-spouses again. However, those who had children while married do not have that option. They have to learn to redefine their relationships with their former spouses so they can continue to raise their children together after divorce. People can follow some simple steps to make co-parenting more successful.
Focus on the Child
One thing that successful co-parents have in common is that they put their children first. They are able to set the issues they have with their ex-spouses aside in order ...
One of the many ways that Americans celebrate their holidays is by setting off fireworks. In the Hoosier State, it's no different. With New Years Eve almost here, it is important to make yourself aware of the laws surrounding fireworks, so you can have a safe holiday season and minimize the possibility of a fireworks personal injury claim.
Indiana fireworks law
Indiana counties have some ability to adopt ordinances that regulate the days and hours that consumer fireworks can be discharged. However, any ordinance adopted cannot restrict the use of fireworks during ...
In the past, people in their 50s, 60s or 70s were seeing an attorney to create a will or other estate plan. Now, a growing number of people in this age group are seeking an attorney because they want to get a divorce after decades of marriage. According to a Bowling Green State University Study, divorce among those aged 46 to 64 has increased by more than 50 percent in the past two years and this has greatly contributed to the divorce rate in the country.
Divorce stabilizing among other age groups
The Bowling Green study showed that divorce rates in the country are ...