(Press-News.org) New York, NY (December 17, 2012) — Are you stressed? Results of a new meta-analysis of six studies involving nearly 120,000 people indicate that the answer to that question may help predict one's risk of incident coronary heart disease (CHD) or death from CHD. The study, led by Columbia University Medical Center researchers, was published in a recent issue of the American Journal of Cardiology.
The six studies included in the analysis were large prospective observational cohort studies in which participants were asked about their perceived stress (e.g., "How stressed do you feel?" or "How often are you stressed?"). Respondents scored either high or low; researchers then followed them for an average of 14 years to compare the number of heart attacks and CHD deaths between the two groups. Results demonstrate that high perceived stress is associated with a 27% increased risk for incident CHD (defined as a new diagnosis or hospitalization) or CHD mortality.
"While it is generally accepted that stress is related to heart disease, this is the first meta-analytic review of the association of perceived stress and incident CHD," said senior author Donald Edmondson, PhD, assistant professor of behavioral medicine at CUMC. "This is the most precise estimate of that relationship, and it gives credence to the widely held belief that general stress is related to heart health. In comparison with traditional cardiovascular risk factors, high stress provides a moderate increase in the risk of CHD – e.g., the equivalent of a 50 mg/dL increase in LDL cholesterol, a 2.7/1.4 mmHg increase in blood pressure or smoking five more cigarettes per day."
"These findings are significant because they are applicable to nearly everyone," said first author Safiya Richardson, MD, who collaborated with Dr. Edmondson on the paper while attending the Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons (she graduated in 2012 and is currently a resident at North Shore Long Island Jewish Health System in Manhasset, New York). "The key takeaway is that how people feel is important for their heart health, so anything they can do to reduce stress may improve their heart health in the future."
Coronary heart disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease, is a narrowing of the small blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. It is caused by a buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can lead to hardening of the arteries, or atherosclerosis. CHD is the leading cause of death in the United States for men and women; more than 385,000 people die each year from CHD.
The researchers did further analysis to try to learn what might underlie the association between stress and CHD. They found that while gender was not a significant factor, age was. The people in the studies were between the ages of 43–74 among older people, the relationship between stress and CHD was stronger.
"While we do not know for certain why there appears to be an association between age and the effect of perceived stress on CHD, we think that stress may be compounding over time. For example, someone who reports high perceived stress at age 60 may also have felt high stress at ages 40 and 50, as well." Dr. Edmondson also noted that older individuals tend to have worse CHD risk factors such as hypertension to begin with, and that stress may interact with those risk factors to produce CHD events.
"The next step is to conduct randomized trials to assess whether broad population-based measures to decrease stress are cost-effective. Further research should look at whether the stress that people report is about actual life circumstances (e.g., moving or caregiving), or about stable personality characteristics (e.g., type A vs. B), said Dr. Edmondson.
"We also need to ask why we found this association between stress and CHD, e.g., what biological components or mechanisms are involved, and what is the role of environment or lifestyle (e.g., diet, alcohol and drug use, exercise), and how best to moderate these factors to lower the risk of CHD," said Dr. Richardson.
###
The paper is titled, "Meta-Analysis of Perceived Stress and Its Association With Incident Coronary Heart Disease." The other contributors are Jonathan A. Shaffer, Louise Falzon, David Krupka and Karina W. Davidson, all from CUMC's Center for Behavioral Cardiovascular Health.
This research was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants HL-088117 and CA-156709. It was supported in part by Columbia University's Clinical and Translational Science Awards (CTSA) grant No. UL1RR024156 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences – National Center for Research Resources/NIH. Dr. Edmondson is supported by NIH grant KM1CA156709.
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
Columbia University Medical Center provides international leadership in basic, pre-clinical and clinical research; medical and health sciences education; and patient care. The medical center trains future leaders and includes the dedicated work of many physicians, scientists, public health professionals, dentists, and nurses at the College of Physicians and Surgeons, the Mailman School of Public Health, the College of Dental Medicine, the School of Nursing, the biomedical departments of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, and allied research centers and institutions. Established in 1767, Columbia's College of Physicians and Surgeons was the first institution in the United States to grant the MD degree and is among the country's most selective medical schools. Columbia University Medical Center is home to the largest medical research enterprise in New York City and State and one of the largest in the United States. www.cumc.columbia.edu.
WASHINGTON, December 17, 2012 — With the holiday season a high-risk period for packing on unwanted pounds, the American Chemical Society (ACS) today posted a new video that may lend perspective on this year's battle of the bulge. Produced by the world's largest scientific society, it explains the science behind the calorie counts and other information on those Nutrition Facts Labels on food packages. Available at www.BytesizeScience.com, the video tells the story of how scientists first determined the calorie content of food in the 1800s, and how scientists determine fat, ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A new series of studies in mouse models by Mayo Clinic researchers uncovered that the aging process is characterized by high rates of whole-chromosome losses and gains in various organs, including heart, muscle, kidney and eye, and demonstrate that reducing these rates slows age-related tissue deterioration and promotes a healthier life span. The findings appear in today's online issue of Nature Cell Biology.
"We've known for some time that reduced levels of BubR1 are a hallmark of aging and correspond to age-related conditions, including muscle weakness, ...
Scientists from the Structural Computational Biology Group at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), led by Alfonso Valencia, together with French and American researchers, have published recently two articles in the journal Nucleic Acid Research (NAR) that introduce two new databases for studying the human genome.
Living eukaryote beings are capable of generating several proteins from the information contained in a single gene. This special characteristic exists partly thanks to the alternative splicing process that selectively joins some exons (the regions ...
A leading international expert on autism at the University of Leicester has been involved in contributing to a major new study of global health.
Professor Terry Brugha, of the Department of Health Sciences, is co-author of two papers in The Lancet's special issue on the Global Burden of Disease.
Because of his work on Autism Epidemiology, which was used to develop one new element of these global data syntheses, Professor Brugha was a co-author at the University of Leicester on two of the reports.
He said: "The most pressing issue to come out of the Global Burden of ...
More than one in every ten schoolchildren suffers from a transient tic disorder, and 1% have a particular type of tic disorder known as Tourette syndrome. In this issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, Andrea G. Ludolph of the Universitätsklinikum Ulm and her coauthors report on the available modes of diagnosis and treatment for these disorders (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2012; 109(48): 821).
Tic disorders usually take a benign course; in about 90% of patients, the tics regress spontaneously in adolescence. Specific treatment is indicated only if the tics are severe or cause ...
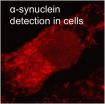
HOUSTON – (Dec. 17, 2012) – Rice University scientists have discovered a new way to look inside living cells and see the insoluble fibrillar deposits associated with Parkinson's disease.
The combined talents of two Rice laboratories – one that studies the misfolded proteins that cause neurodegenerative diseases and another that specializes in photoluminescent probes – led to the spectroscopic technique that could become a valuable tool for scientists and pharmaceutical companies.
The research by the Rice labs of Angel Martí and LauraSegatori appeared online this month ...
CLEVELAND -- Researchers at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine have identified a molecule linked to more aggressive forms of breast cancer – a discovery that could point the way to potential cures.
Until this study, the ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecule called miR-181a had never before been tied to breast cancer metastasis. But when scientists found elevated levels of the molecule in late-stage breast cancer tissues, they in turn tested an inhibitor in mouse models. The approach not only prevented metastasis, but also extended the animals' lives.
"Overall, ...
(Edmonton) Make no mistake, Alex Clark and Lionel Messi were not separated at birth.
Both might be stars in their own right, but Clark, associate dean of research in the Faculty of Nursing at the University of Alberta, realizes he's not about to woo stadiums of crazed soccer fans like FC Barcelona's all-time top scorer.
"It would probably take you about five seconds of watching Lionel Messi move the ball to work out who is the more talented soccer player; however, a lot of health research would see us as very similar," says Clark, noting they're both male, under 5-foot-11, ...
Daejeon, Republic of Korea, December 17th, 2012—Cell phones are getting ever smarter today, savvy enough to tell you where to go and what to buy in shopping centers or department stores. Although still in nascent stages, indoor positioning and navigation using mobile phones will be arriving anytime soon.
People widely rely on the Global Positioning System (GPS) for location information, but unlike outdoor environments, GPS does not work well in indoor spaces or urban canyons with streets cutting through dense blocks of high-rise buildings and structures. GPS requires ...
There is no difference between proton radiotherapy (PRT) and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) when comparing the toxicity among Medicare beneficiary patients with prostate cancer at 12 months post-treatment according to a study published December 14 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
IMRT is the standard form of radiotherapy for the treatment of prostate cancer, accounting for more than 80% of all treatments. Alternative treatments for radiotherapy have emerged, with the most notable being PRT. PRT treatment has surfaced partly due Medicare reimbursement, ...