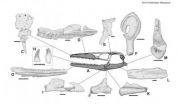
(Press-News.org) Prehistoric farming communities in Europe constructed water wells out of oak timbers, revealing that these first farmers were skilled carpenters long before metal was discovered or used for tools. The research published December 19 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Willy Tegel and colleagues from the University of Freiburg, Germany, contradicts the common belief that metal tools were required to make complex wooden structures.
The wooden water wells discovered in eastern Germany are over 7000 years old, and suggest that these early farmers had unexpectedly refined carpentry skills. "This early Neolithic craftsmanship now suggests that the first farmers were also the first carpenters", the study reports.
These first Central European farmers migrated from the Great Hungarian Plain approximately 7,500 years ago, and left an archeological trail of settlements, ceramics and stone tools across the fertile regions of the continent, a record named Linear Pottery Culture (LBK). However, much of the lifestyle of these early settlers is still a mystery, including the climate they lived in and technology or strategies they used to cope with their surroundings. According to the study, the oak timbers analyzed in this study are also a new archive of environmental data preserved in the tree rings, which could tell an accurate, year-by-year story of the times these early settlers lived in.
INFORMATION:
Citation: Tegel W, Elburg R, Hakelberg D, Stauble H, Buntgen U (2012) Early Neolithic Water Wells Reveal the World's Oldest Wood Architecture. PLOS ONE 7(12): e51374.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051374
Financial Disclosure: WT and DH received funding from the German Research Foundation, project #SP 437/16-1. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interest Statement: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
PLEASE LINK TO THE SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE IN ONLINE VERSIONS OF YOUR REPORT (URL goes live after the embargo ends): http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051374.
Human history preserved in tree rings of prehistoric wooden wells
First farming communities in Europe were skilled carpenters, made water wells out of wood
2012-12-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lizard tails detach at a biological 'dotted line'
2012-12-20
Like sheets of paper marked with perforated lines, gecko tails have unique structural marks that help them sever their tails to make a quick getaway. Though voluntarily shedding a body part in this manner is a well-known phenomenon, research published December 19 in the open access journal PLOS ONE reveals aspects of the process that may have applications for structural engineers making similar, quickly detachable structures.
VIDEO:
Bridging structures are not present between ...
Music with dinner: Whales sing during foraging season, not just while breeding
2012-12-20
Humpback whales might be expected to take their food seriously given their enormous size, but a new study shows that they may multi-task as they eat, singing mating or breeding songs as they forage in their Antarctic feeding grounds. The research, published December 19 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Alison Stimpert from the Naval Postgraduate School and colleagues, sheds new light on the whales' singing habits in different seasons, which are still a mystery.
Whales sing most frequently during the breeding season but are known to sing on other occasions, such as ...
First freshwater mosasaur discovered
2012-12-20
A new mosasaur species discovered in Hungary is the first known example of this group of scaled reptiles to have lived in freshwater river environments similar to modern freshwater dolphins, according to research published December 19 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Laszlo Makadi from the Hungarian Natural History Museum, Hungary and colleagues from the University of Alberta, Canada and MTA-ELTE Lendület Dinosaur Research Group, Hungary.
The species lived about 84 million years ago, the largest specimens reached about 20 feet in length, and belongs to a family ...
Transplanted neural stem cells treat ALS in mouse model
2012-12-20
LA JOLLA, Calif., December 19, 2012 – Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, is untreatable and fatal. Nerve cells in the spinal cord die, eventually taking away a person's ability to move or even breathe. A consortium of ALS researchers at multiple institutions, including Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute, Brigham and Women's Hospital, and the University of Massachusetts Medical School, tested transplanted neural stem cells as a treatment for the disease. In 11 independent studies, they found that transplanting neural stem cells ...
Unraveling the threads: Simplest cotton genome offers clues for fiber improvements
2012-12-20
From the stockings decorating mantles to the new outfits in display windows calling to shoppers, cotton is woven into the fabric of the holiday season. For bioenergy researchers, however, fiber composition matters more than color and texture as each cotton strand is composed of more than two dozen coils of cellulose, a target biomass for next-generation biofuels.
In the December 20, 2012 edition of Nature, an international consortium of researchers from 31 institutions including a team from the U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute (DOE JGI) present a high-quality ...
Occasional family meals enough to boost kids' fruit and veg intake
2012-12-20
Eating meals together as a family, even if only once or twice a week, increases children's daily fruit and vegetable intake to near the recommended 5 A Day, according to researchers at the University of Leeds.
The study of primary school-aged children, funded by the National Institute for Health Research Public Health Research (NIHR PHR) Programme, also suggests parental consumption of fruit and vegetables and cutting up portions of these foods boosted children's intake. It is published today in the British Medical Journal's Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Overall, ...
Stars reveal the secrets of looking young
2012-12-20
Globular clusters are spherical collections of stars, tightly bound to each other by their mutual gravity. Relics of the early years of the Universe, with ages of typically 12-13 billion years (the Big Bang took place 13.7 billion years ago), there are roughly 150 globular clusters in the Milky Way and they contain many of our galaxy's oldest stars.
But while the stars are old and the clusters formed in the distant past, astronomers using the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope and the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope have found that some of these clusters are still young at heart. ...
How to look young when you're not
2012-12-20
Globular clusters are spherical collections of stars, tightly bound to each other by their mutual gravity. Relics of the early years of the Universe, with ages of typically 12-13 billion years (the Big Bang took place 13.7 billion years ago), there are roughly 150 globular clusters in the Milky Way and they contain many of our galaxy's oldest stars.
But while the stars are old and the clusters formed in the distant past, astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope and the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope at the ESO La Silla Observatory have found that some of these ...
JILA physicists achieve elusive 'evaporative cooling' of molecules
2012-12-20
Achieving a goal considered nearly impossible, JILA physicists have chilled a gas of molecules to very low temperatures by adapting the familiar process by which a hot cup of coffee cools.
Evaporative cooling has long been used to cool atoms, at JILA and elsewhere, to extraordinarily low temperatures. The process was used at JILA in 1995 to create a then-new state of matter, the Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) of rubidium atoms. The latest demonstration, reported in the Dec. 20, 2012, issue of Nature,* marks the first time evaporative cooling has been achieved with molecules—two ...
Scientists develop technique to help prevent inherited disorders in humans
2012-12-20
NEW YORK, NY (December 19, 2012) – A joint team of scientists from The New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) Laboratory and Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) has developed a technique that may prevent the inheritance of mitochondrial diseases in children. The study is published online today in Nature.
Dieter Egli, PhD, and Daniel Paull, PhD, of the NYSCF Laboratory with Mark Sauer, MD, and Michio Hirano, MD, of CUMC demonstrated how the nucleus of a cell can be successfully
transferred between human egg cells. This landmark achievement carries significant implications ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
[Press-News.org] Human history preserved in tree rings of prehistoric wooden wellsFirst farming communities in Europe were skilled carpenters, made water wells out of wood