(Press-News.org) This press release is available in German.
Waves do not spread in a disordered medium if there is less than one wavelength between two defects. Physicists from the universities of Zurich and Constance have now proved Nobel Prize winner Philip W. Anderson's theory directly for the first time using the diffusion of light in a cloudy medium.
Light cannot spread in a straight line in a cloudy medium like milk because the many droplets of fat divert the light as defects. If the disorder – the concentration of defects – exceeds a certain level, the waves are no longer able to spread in a cloudy medium at all. Philip. W. Anderson was the first to describe this transition to a localized wave in 1958, which is why it is also referred to as Anderson localization. Until now, however, Anderson localization had never been observed. For the first time, physicists from the universities of Zurich and Constance have now demonstrated the Anderson localization of light directly in an experiment. As their article published in the science journal Nature Photonics reveals, the Anderson localization of light only occurs in much cloudier media than milk – in other words, only if there is only about one wavelength between two defects.
Light propagation followed closely to a billionth of a second
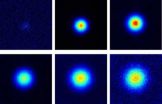
For their study, the team examined the diffusion of light in a very strongly scattering medium. "In order to make the diffusion of the light and thus Anderson localization visible, pictures had to be taken at an interval of less than a billionth of a second," says Christof Aegerter, explaining the technical challenges of the project. Based on these high-resolution images, the researchers were able to show that in the case of Anderson localization light is no longer able to spread any further in the medium after around four billionths of a second (or nanoseconds).
Until now, it was very difficult to calculate certain characteristics of localized states, such as how large the critical concentration of the defects is. "Thanks to our experimental data, the theory will gain new impetus and be able to be refined further," Aegerter is convinced.
The Anderson localization of waves is a general phenomenon that occurs in all waves with a heavy scattering and is also of practical importance: It describes, among other things, the transition between a conductor and an isolator.
INFORMATION:
Shedding light on Anderson localization
2012-12-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Small wasps to control a big pest?
2012-12-20
With the purpose of developing new biological methods to control one of the major pests affecting the southwest Europe pine stands, a joint collaboration leaded by the Instituto Nacional de Investigação Agrária e Veterinária, Portugal (R. Petersen-Silva, P. Naves, E. Sousa), together with the Universidad de Barcelona, Spain (J. Pujade-Villar) and a member of the Museum and Institute of Zoology from the Polish Academy of Sciences, Poland, (S. Belokobylskij) initiated a research to detect the parasitoid guild of the Pine Wood Nematode (PWN) vector, Monochamus galloprovincialis ...
Sync to grow
2012-12-20
From a single-cell egg to a fully functional body: as embryos develop and grow, they must form organs that are in proportion to the overall size of the embryo. The exact mechanism underlying this fundamental characteristic, called scaling, is still unclear. However, a team of researchers from EMBL Heidelberg is now one step closer to understanding it. They have discovered that scaling of the future vertebrae in a mouse embryo is controlled by how the expression of some specific genes oscillates, in a coordinated way, between neighbouring cells. Published today in Nature, ...
Silver sheds light on superconductor secrets
2012-12-20
The first report on the chemical substitution, or doping, using silver atoms, for a new class of superconductor that was only discovered this year, is about to be published in EPJ B. Chinese scientists from Institute of Solid State Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, discovered that the superconductivity is intrinsic rather than created by impurities in this material with a sandwich-style layered structure made of bismuth oxysulphide (Bi4O4S3).
Superconductors with a transition temperature (TC) above the boiling temperature of liquid nitrogen (77 kelvins or −196 ...
Gene expression improves the definition of a breast cancer subtype
2012-12-20
The study conducted by the Vall d'Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO) in conjunction with the GEICAM cooperative group and other American and Canadian researchers has led to a change in the definition of hormone-sensitive breast tumours.
Barcelona, 20 December 2012. Gene expression in breast cancer provides valuable biological information for better determining the diagnosis, treatment, risk of relapse and survival rate. However, the most common form of characterizing breast cancer is by histopathological techniques. This study, headed by Dr Aleix Prat, Head of the Translational ...
2 problems in chemical catalysis solved
2012-12-20
The research group of Professor Petri Pihko at the Department of Chemistry and the NanoScience Center of the University of Jyväskylä has solved two acute problems in chemical catalysis. The research has been funded by the Academy of Finland.
In the first project, the researchers designed a novel intramolecularly assisted catalyst for the synthesis of beta amino acids. Previously published catalysts work only with aromatic side chains in the imines, but the new catalyst designed at Jyväskylä does not have this limitation. The new method might find uses in the synthesis ...
Stroke drug kills bacteria that cause ulcers and tuberculosis
2012-12-20
Bethesda, MD—A drug currently being used to treat ischemic strokes may prove to be a significant advance in the treatment of tuberculosis and ulcers. In a new research report appearing online in The FASEB Journal, a compound called ebselen effectively inhibits the thioredoxin reductase system in a wide variety of bacteria, including Helicobacter pylori which causes gastric ulcers and Mycobacterium tuberculosis which causes tuberculosis. Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase proteins are essential for bacteria to make new DNA, and protect them against oxidative stress caused ...
UGA research offers new targets for stroke treatments
2012-12-20
Athens, Ga. – New research from the University of Georgia identifies the mechanisms responsible for regenerating blood vessels in the brain.
Looking for ways to improve outcomes for stroke patients, researchers led by the UGA College of Pharmacy assistant dean for clinical programs Susan Fagan used candesartan, a commonly prescribed medication for lowering blood pressure, to identify specific growth factors in the brain responsible for recovery after a stroke.
The results were published online Dec. 4 in the Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Although ...
Virtual reality and robotics in neurosurgery -- promise and challenges
2012-12-20
Philadelphia, Pa. (December 20, 2012) – Robotic technologies have the potential to help neurosurgeons perform precise, technically demanding operations, together with virtual reality environments to help them navigate through the brain, according to a special supplement to Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"Virtual Reality (VR) and robotics are two rapidly expanding fields with growing application within neurosurgery," according to an introductory ...
The paths of photons are random -- but coordinated
2012-12-20
Researchers at the Niels Bohr Institute have demonstrated that photons (light particles) emitted from light sources embedded in a complex and disordered structure are able to mutually coordinate their paths through the medium. This is a consequence of the photons' wave properties, which give rise to the interaction between different possible routes. The results are published in the scientific journal, Physical Review Letters.
The real world is complex and messy. The research field of photonics, which explores and exploits light, is no exception, and in, for example, biological ...
Italian wolves prefer pork to venison
2012-12-20
Some European wolves have a distinct preference for wild boar over other prey, according to new research.
Scientists from Durham University, UK, in collaboration with the University of Sassari in Italy, found that the diet of wolves was consistently dominated by the consumption of wild boar which accounted for about two thirds of total prey biomass, with roe deer accounting for around a third.
The study analysed the remains of prey items in almost 2000 samples of wolf dung over a nine year period and revealed that an increase in roe deer in the wolf diet only occurred ...