(Press-News.org) Someday, Oahu's Koolau and Waianae mountains will be reduced to nothing more than a flat, low-lying island like Midway.
But erosion isn't the biggest culprit. Instead, scientists say, the mountains of Oahu are actually dissolving from within.
"We tried to figure out how fast the island is going away and what the influence of climate is on that rate," said Brigham Young University geologist Steve Nelson. "More material is dissolving from those islands than what is being carried off through erosion."
The research pitted groundwater against stream water to see which removed more mineral material. Nelson and his BYU colleagues spent two months sampling both types of sources. In addition, ground and surface water estimates from the U.S. Geological Survey helped them calculate the total quantity of mass that disappeared from the island each year.
"All of the Hawaiian Islands are made of just one kind of rock," Nelson said. "The weathering rates are variable, too, because rainfall is so variable, so it's a great natural laboratory."
Forecasting the island's future also needs to account for plate tectonics. As Oahu is pushed northwest, the island actually rises in elevation at a slow but steady rate. You've heard of mountain climbing; this is a mountain that climbs.
According to the researchers' estimates, the net effect is that Oahu will continue to grow for as long as 1.5 million years. Beyond that, the force of groundwater will eventually triumph and the island will begin its descent to a low-lying topography.
Undergraduate student Brian Selck co-authored the study, which appears in the journal Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. Unfortunately for him, he joined the project only after the field work in Hawaii took place.
Instead, Selck performed the mineralogical analysis of soil samples in the lab back in Provo. The island's volcanic soil contained at least one surprise in weathered rock called saprolites.
"The main thing that surprised me on the way was the appearance of a large amount of quartz in a saprolite taken from a 1-meter depth," Selck said.
###After he graduates from BYU, Selck will pursue a career in hydrogeology. BYU geology professor David Tingey joins Nelson and Selck as a co-author on the new study.
Hawaiian Islands are dissolving, study says
2012-12-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
miR-205 can be responsible for breast cancer
2012-12-21
Over the past couple of years research into miRNAs has become increasingly diversified and attracted a great number of research articles across genetics and medicine. This should hardly come as a surprise to any scientist in the field, especially since it has become clear that miRNAs, a recently discovered class of non-coding RNAS, are represented in nearly all cellular functions and molecular pathways. A growing list of reports demonstrates that microRNAs play a critical role in cancer initiation and progression, and that miRNA alterations are ubiquitous in human cancers. ...
May the force be with the atomic probe
2012-12-21
Theoretical physicist Elad Eizner from Ben Gurion University, Israel, and colleagues created models to study the attractive forces affecting atoms located at a wide range of distances from a surface, in the hundreds of nanometers range. Their results, about to be published in EPJ D, show that these forces depend on electron diffusion, regardless of whether the surface is conducting or not. Ultimately, these findings could contribute to designing minimally invasive surface probes.
Bombarding a surface with atoms helps us understand the distribution of its electrons and ...
Carin Göring's remains identified by researchers at Uppsala University
2012-12-21
The putative remains of Carin Göring, wife of Nazi leader Herman Göring, were found in 1991 at a site close to where she had been buried. In a recently published article, Maria Allen, professor of forensic genetics at Uppsala University, Sweden, and her associates present evidence supporting that it is Carin Göring's remains that have been identified.
The Swedish Carin Göring was married to the well-known Nazi leader Herman Göring. When she died in 1931 she was buried in Stockholm, but three years later Herman Göring had her remains moved to his residence Karinhall outside ...
Fighting sleeping sickness with X-ray lasers
2012-12-21
This press release is available in German.
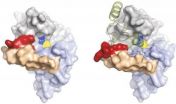
Using the world's most powerful X-ray free-electron laser, an international team of researchers, including scientists of the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg, has obtained new insight into the structure of a medicinally important protein that may serve as a blueprint for the development of drugs to fight sleeping sickness. Science magazine have chosen the experimental study as one of the top ten scientific breakthroughs of the year.
Sleeping sickness is caused by the unicellular organism Trypanosoma ...
New calculations solve an old problem with DNA
2012-12-21
In a recent publication, researchers achieved new accuracy in the ability to measure energy differences between states of molecules, thus predicting which states will be observed.
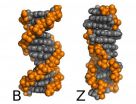
It has been known since the seventies that excessive salt causes DNA to reverse its twist, from a right-handed spiral to a left-handed one. DNA in the Z form is treated by our natural repair enzymes as damaged, and is therefore usually deleted from the cell. Deletion of genetic material can lead to cancer or to other problems, so the B-Z transition is no mere curiosity. However such is the ...
Ups and downs of biodiversity after mass extinction
2012-12-21
The climate after the largest mass extinction so far 252 million years ago was cool, later very warm and then cool again. Thanks to the cooler temperatures, the diversity of marine fauna ballooned, as paleontologists from the University of Zurich have reconstructed. The warmer climate, coupled with a high CO2 level in the atmosphere, initially gave rise to new, short-lived species. In the longer term, however, this climate change had an adverse effect on biodiversi-ty and caused species to become extinct.
Until now, it was always assumed that it took flora and fauna ...
Strength training improves vascular function in young black men
2012-12-21
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Six weeks of weight training can significantly improve blood markers of cardiovascular health in young African-American men, researchers report in the Journal of Human Hypertension.
The researchers measured blood markers associated with inflammation, immune response or the remodeling of arteries that normally occur after tissue damage, infection or other types of stress. They found that levels of two of these markers dropped significantly in African-American men but not in Caucasian men after six weeks of resistance training.
"This suggests that resistance ...
Physicists take photonic topological insulators to the next level
2012-12-21
AUSTIN, Texas—Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have designed a simulation that for the first time emulates key properties of electronic topological insulators.
Their simulation, which was described this week in Nature Materials, is part of a rapidly moving scientific race to understand and exploit the potential of topological insulators, which are a state of matter that was only discovered in the past decade. These insulators may enable dramatic advances in quantum computing and spintronics.
"The discovery of these materials, which are insulators in ...
Targeted gene silencing drugs are more than 500 times more effective with new delivery method
2012-12-21
New Rochelle, NY, December 20, 2012—Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are a potent new drug class that can silence a disease-causing gene, but delivering them to a target cell can be challenging. An innovative delivery approach that dramatically increases the efficacy of an siRNA drug targeted to the liver and has made it possible to test the drug in non-human primates is described in an article in Nucleic Acid Therapeutics, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers (http://www.liebertpub.com). The article is available on the Nucleic Acid Therapeutics ...
Researchers discover genetic basis for eczema, new avenue to therapies
2012-12-21
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers at Oregon State University today announced the discovery of an underlying genetic cause of atopic dermatitis, a type of eczema most common in infancy that also affects millions of adults around the world with dry, itchy and inflamed skin lesions.
The findings were just published in PLoS ONE, a professional journal, and may set the stage for new therapeutic approaches to this frustrating syndrome, which is difficult to treat and has no known cure. Eczema is also related to, and can sometimes cause asthma, a potentially deadly immune dysfunction.
Pharmaceutical ...