Paper highlights blood pressure risk in overweight children
2010-10-17
(Press-News.org) Sophia Antipolis, 15 October 2010: The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) welcomes the findings of a paper presented today at the American Heart Association's High Blood Pressure Research 2010 Scientific Sessions (HBPR 2010) held in Washington, DC, USA. The paper details research into the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and blood pressure in children. It concludes that an increase in BMI in already overweight children risks a far greater rise in blood pressure than would the same increase in BMI in normal-weight children.
Commenting on the paper, ESC spokesperson Professor José Ramón Gonzáles-Juanatey from the Hospital Clinico Universitario Santiago in Spain, said, "This study is relevant because it emphasises the relationship between BMI and blood pressure in children. It is very important for everyone, especially the general population, to understand the significant cardiovascular risk caused by childhood obesity, and the simple fact that weight reduction and exercise can have a major and positive impact."
Co-author of the paper is Doctor Wanzhu Tu of the Regenstrief Institute in Indianapolis. The research team tracked blood pressure, height and weight measurements from over 1,000 children for a period up to 10 years, and compared BMI to national charts adjusted for age, sex and height. Children with BMIs above the 85 percent point are considered overweight. Below this level, BMI effects on blood pressure appear fairly linear, but for those above the 85 percent point – and especially above the 90 percent point – the BMI effects are noticeably stronger.
Analysis indicated that the effect on both systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings of overweight children was over four times that of normal-weight children for whom BMI and blood pressure remained related but with weaker associations. The paper argues that even a modest reduction in BMI can result in a significant lowering of blood pressure in overweight children while, conversely, just a small increase could put them at much greater risk of higher blood pressure.
Professor Joep Perk of the School of Health and Caring Sciences at Linneaus University in Sweden, and Board Member of the European Association of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation (EACPR)1, says that the research is very interesting. "The obesity epidemic in children presents a major threat to future public health strategy," he notes, adding, "Overweight children usually grow into overweight adults with all the risks this carries of cardiovascular disease. The results of the study reinforces that we must maintain our focus on relevant campaigns to promote weight loss and control in all sections of society, but particularly amongst the young."
###
References
1The mission of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR) is to promote excellence in research, practice, education and policy in cardiovascular prevention and rehabilitation in Europe.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-10-17
ChoiceBatter's® transformation from a federal laboratory bench technology to a grocery shelf product is among topics that will be discussed here today by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) officials and other participants attending the 17th annual conference of the National Association of Seed and Venture Funds (NASVF).
ChoiceBatter®, the brand name for a line of low oil-uptake batters marketed by CrispTek, LLC, of Columbia, Md., is based on a rice-flour formulation created by Fred Shih and Kim Daigle, chemists with the Agricultural Research Service (ARS), USDA's principal ...
2010-10-17
Scientific data continue to indicate that higher intake of alcohol during pregnancy adversely affects the fetus, and could lead to very severe developmental or other problems in the child. However, most recent publications show little or no effects of occasional or light drinking by the mother during pregnancy. The studies also demonstrate how socio-economic, education, and other lifestyle factors of the mother may have large effects on the health of the fetus and child; these must be considered when evaluating the potential effects of alcohol during pregnancy.
A ...
2010-10-17
INDIANAPOLIS – Technologies for rapid detection of bacterial pathogens are crucial to maintaining a secure food supply.
Researchers from the School of Science at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis (IUPUI) and the Bindley Bioscience Center at Purdue University have developed a novel approach to automated detection and classification of harmful bacteria in food. The investigators have designed and implemented a sophisticated statistical approach that allows computers to improve their ability to detect the presence of bacterial contamination in tested samples. ...
2010-10-17
UPTON, NY - A new source of ions will soon be the starting point for the beams entering two major research facilities at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory - the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC - http://www.bnl.gov/rhic), where physicists are recreating conditions of the early universe to learn more about the forces that hold matter together, and the NASA Space Radiation Laboratory (NSRL: http://www.bnl.gov/medical/NASA/NSRL_description.asp), where scientists study the effects of space radiation to help find ways to protect astronauts. ...
2010-10-17
Alzheimer's disease is not the only type of dementia. Two particular forms are dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease dementia. In both forms, the diagnosis is of vital importance because the treatment for these dementias differs from that for Alzheimer's dementia, as Brit Mollenhauer and co-authors explain in the dementia theme issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2010; 107[39]: 684-91).
In more than 75% of patients, the memory impairments are due to Alzheimer's disease. In Lewy body dementia, which is accompanied by cognitive and/or ...
2010-10-17
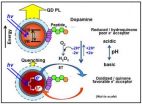
Scientists at the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) in conjunction with the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, Ca., recently reported a detailed study of the interactions of water soluble semi-conductor quantum dots (QDs) with the electro-active neuro-transmitter dopamine. These biocompatible QD-dopamine nano-assemblies may be used as the active component for sensors that are used to detect a wide variety of target analytes ranging from sugars to peroxides.
According to NRL's Dr. Michael Stewart, a member of the research team "The nature of the QD-dopamine ...
2010-10-17
The ordinary squid, Loligo pealii—best known until now as a kind of floating buffet for just about any fish in the sea—may be on the verge of becoming a scientific superstar, providing clues about the origin and evolution of the sense of hearing.
In a hangar-like research building at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), biologist T. Aran Mooney is exploring virtually uncharted waters: Can squid hear? Is their hearing sensitive enough to hear approaching predators? How do squid and other marine species rely on sound to interact, migrate, and communicate? Will ...
2010-10-17
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- We've all heard the adage that whatever doesn't kill us makes us stronger, but until now the preponderance of scientific evidence has offered little support for it.
However, a new national multi-year longitudinal study of the effects of adverse life events on mental health has found that adverse experiences do, in fact, appear to foster subsequent adaptability and resilience, with resulting advantages for mental health and well being.
The study, "Whatever Does Not Kill Us: Cumulative Lifetime Adversity, Vulnerability and Resilience," to be published in ...
2010-10-17
For the first time researchers have found out what effect multiple, rather than just single, foods with anti-inflammatory effects have on healthy individuals.
The results of a diet study show that bad cholesterol was reduced by 33 per cent, blood lipids by 14 per cent, blood pressure by 8 per cent and a risk marker for blood clots by 26 per cent. A marker of inflammation in the body was also greatly reduced, while memory and cognitive function were improved.
"The results have exceeded our expectations! I would like to claim that there has been no previous study ...
2010-10-17
An article published in the October issue of the Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden describes a new genus of tree of the Aptandraceae family, a group that is related to the sandalwoods (order Santalales). The genus, which has been given the name Hondurodendron, is endemic to Honduras and means "tree of Honduras."
In the article, "Hondurodendron, a New Monotypic Genus of Aptandraceae from Honduras," lead author Dr. Carmen Ulloa, associate curator at the Missouri Botanical Garden, and co-authors
Dr. Daniel L. Nickrent, Southern Illinois University-Carbondale, Dr. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Paper highlights blood pressure risk in overweight children