Waste removal in worms reveals new mechanism to regulate calcium signaling
2013-01-04
(Press-News.org) Calcium is so much more than the mineral that makes our bones and teeth strong: It is a ubiquitous signaling molecule that provides crucial information inside of and between cells. Calcium is used to help our hearts beat regularly, our guts to function appropriately and even for fertilization to occur. It is also needed to help muscles and blood vessels contract, to secrete hormones and enzymes and to send messages throughout the nervous system.
In a study published in Current Biology, scientists from the University of Rochester Medical Center, Marquette University and Oberlin College discovered a new way in which calcium signaling may be controlled. Study authors say their findings define a mechanism for regulating calcium signaling that has never been recognized before and should be of great help to the thousands of scientists who study the extremely important role of calcium signaling in health and disease.
"It is hard to find a biological process that is not influenced by calcium signaling," said Keith Nehrke, Ph.D., study author and associate professor of Nephrology and Pharmacology & Physiology at the Medical Center. "In many cases, calcium signaling is absolutely central. The rise and fall of calcium is the molecular clock that times the execution of important processes like the regular and coordinated beating of our hearts."
Nehrke, along with lead study authors Allison L. Abbott, Ph.D., and Benedict J. Kemp, Ph.D., of Marquette University, made the finding while studying an unglamorous, yet scientifically ideal subject matter – worm poop.
Worms produce their own body weight in embryos every day, which requires immense caloric intake. However, as in all other animals, food is transformed into waste, which must be expelled from the body. As a result of their rapid nutrient intake, worms defecate a lot and fast – every 50 seconds. The fidelity of this biological rhythm is critical for good health and relies on a specific sequence of events: One can imagine what might happen if the bowels were to contract without a valve opening to let out the waste.
The rhythmic process is jumpstarted by a spike of calcium in cells in the end of the intestine. The initial spike triggers a wave of calcium through the remainder of the intestine, stimulating muscle contractions and forcing waste out of the worm's body. The team wondered what ensures that the wave always starts in the right place – the end of the intestine – as opposed to the middle or front?
"It's like dominos lined up in a row," said Erik Allman, Ph.D., a study author and graduate student in Nehrke's lab at the Medical Center. "We wanted to find out what provides the 'push' that topples that first domino and starts the sequence."
The team's analysis revealed that a molecule called a microRNA is required for the entire waste removal process to run smoothly. microRNA-786 is present in the two most posterior intestinal cells of worms and tags these cells as the pacemakers or leaders. These pacemakers dictate when and where the primary calcium spike occurs, activating the movement of waste through the worm's body. When the team removed microRNA-786 from worms the process went awry; the calcium wave started in the wrong place and the waste cycle was irregular and longer than normal.
"As a developmental biologist, I am interested in how cells become different from one another," said Abbott. "This microRNA acts to make the posterior cells different from their neighbors by changing the calcium signaling activity. This difference allows these cells to function as the pacemaker."
"What is really exciting here is that this particular microRNA appears to exert a subtle effect," added Nehrke. "Since calcium signaling is so ubiquitous, it is important to realize that fine tuning its output may be what helps to discriminate between its many biological functions. The next step is to find out if this specific microRNA has a similar effect on calcium signaling processes in people as it does in worms."
###
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation. Megan Mohnen from Marquette and Lois Immerman and Maureen Peters from Oberlin College also contributed to the research. END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2013-01-04
However, Francis Chaouloff, research director at Inserm's NeuroCentre Magendie (Inserm Joint Research Unit 862, Université Bordeaux Ségalen), Sarah Dubreucq, a PhD student and François Georges, a CNRS research leader at the Interdisciplinary Institute for Neuroscience (CNRS/Université Bordeaux Ségalen) have just discovered the key role played by a protein, the CB1 cannabinoid receptor, during physical exercise. In their mouse studies, the researchers demonstrated that the location of this receptor in a part of the brain associated with motivation and reward systems controls ...
2013-01-04
This press release is available in Spanish.
Vegetated drainage ditches can help capture pesticide and nutrient loads in field runoff, U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists report. These ditches—as common in the country as the fields they drain—give farmers a low-cost alternative for managing agricultural pollutants and protecting natural resources.
Agricultural Research Service (ARS) ecologist Matt Moore at the agency's National Sedimentation Laboratory in Oxford, Miss., and his colleagues conducted the research. ARS is USDA's chief intramural scientific ...
2013-01-04
This press release is available in German.
What is normal to most people in winter has so far been impossible in physics: a minus temperature. On the Celsius scale minus temperatures are only surprising in summer. On the absolute temperature scale, which is used by physicists and is also called the Kelvin scale, it is not possible to go below zero – at least not in the sense of getting colder than zero kelvin. According to the physical meaning of temperature, the temperature of a gas is determined by the chaotic movement of its particles – the colder the gas, the slower ...
2013-01-04
New research from Western University provides brain imaging evidence that students well-versed in very basic single digit arithmetic (5+2=7 or 7-3=4) are better equipped to score higher on the Preliminary Scholastic Aptitude Test (PSAT), an examination sat by millions of students in the United States each year in preparation for college admission tests.
In findings published today in The Journal of Neuroscience research led by Daniel Ansari, Associate Professor in Western's Department of Psychology and a principal investigator at the Brain and Mind Institute, showed by ...
2013-01-04
The U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) recently selected Southwest Research Institute to provide the flight low-rate crosslink wireless communications platform for the System F6 Program.
The System F6 Program, which is envisioned to culminate in an on-orbit demonstration in 2015–2016, is designed to validate a new space mission concept in which a cluster of smaller, wirelessly connected spacecraft replaces the typical single spacecraft carrying numerous instruments and payloads. This "fractionated" architecture enhances survivability, responsiveness ...
2013-01-04
BOSTON – Genomic research is widely expected to transform medicine, but progress has been slower than expected. While critics argue that the genomics "promise" has been broken – and that money might be better spent elsewhere -- proponents say the deliberate pace underscores the complexity of the relationship between medicine and disease and, indeed, argues for more funding.
But thus far, these competing narratives have been based mostly on anecdotes. Ramy Arnaout, MD, DPhil, a founding member of the Genomic Medicine Initiative at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), ...
2013-01-04
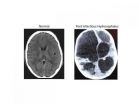
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- The amount of rainfall affects the number of infant infections leading to hydrocephalus in Uganda, according to a team of researchers who are the first to demonstrate that these brain infections are linked to climate.
Hydrocephalus -- literally "water on the brain" -- is characterized by the build-up of the fluid that is normally within and surrounding the brain, leading to brain swelling. The swelling will cause brain damage or death if not treated. Even if treated, there is only a one-third chance of a child maintaining a normal life after post-infectious ...
2013-01-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Norfolk Southern Railway No. 999 is the first all-electric, battery-powered locomotive in the United States. But when one of the thousand lead-acid batteries that power it dies, the locomotive shuts down. To combat this problem, a team of Penn State researchers is developing more cost-effective ways to prolong battery life.
The experimental locomotive's batteries, just like automotive batteries, are rechargeable until they eventually die. A leading cause of damage and death in lead-acid batteries is sulfation, a degradation of the battery caused ...
2013-01-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Experience working for a particular hospital matters when it comes to the performance of radiologists who work for outsourcing teleradiology companies, according to a team of researchers, whose finding could have important implications, given the growing use of telemedicine.
"More than half of all hospitals now use teleradiology services," said Jonathan Clark, assistant professor of health policy and administration, Penn State. "Hospitals send their X-rays, CT scans, MRIs and other images to outsourcing companies who then forward the images to ...
2013-01-04
SAN DIEGO – Genetic sequencing technology is altering the way cancer is diagnosed and treated, but traditional specimen handling methods threaten to slow that progress.
That's the message delivered this week in a column appearing in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) by Scripps Clinic physicians Eric Topol, Kelly Bethel and Laura Goetz.
Dr. Topol is a cardiologist who serves as chief academic officer of Scripps Health and director of the Scripps Translational Science Institute (STSI), leading Scripps' genomic medicine research efforts. Dr. Bethel ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Waste removal in worms reveals new mechanism to regulate calcium signaling