(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA - A team, led by senior author Morris J. Birnbaum, MD, PhD, the Willard and Rhoda Ware Professor of Medicine, with the Institute for Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, found that the diabetes drug metformin works in a different way than previously understood. Their research in mice found that metformin suppresses the liver hormone glucagon's ability to generate an important signaling molecule, pointing to new drug targets. The findings were published online this week in Nature.
For fifty years, one of the few classes of therapeutics effective in reducing the overactive glucose production associated with diabetes has been the biguanides, which includes metformin, the most frequently prescribed drug for type 2 diabetes. The inability of insulin to keep liver glucose output in check is a major factor in the high blood sugar of type 2 diabetes and other diseases of insulin resistance.
"Overall, metformin lowers blood glucose by decreasing liver production of glucose," says Birnbaum. "But we didn't really know how the drug accomplished that."
Imperfectly Understood
Despite metformin's success, its mechanism of action remained imperfectly understood. About a decade ago, researchers suggested that metformin reduces glucose synthesis by activating the enzyme AMPK. But this understanding was challenged by genetic experiments in 2010 by collaborators on the present Nature study. Coauthors Marc Foretz and Benoit Viollet from Inserm, CNRS, and Université Paris Descartes, Paris, found that the livers of mice without AMPK still responded to metformin, indicating that blood glucose levels were being controlled outside of the AMPK pathway.
Taking another look at how glucose is regulated normally, the team knew that when there is no food intake and glucose decreases, glucagon is secreted from the pancreas to signal the liver to produce glucose. They then asked if metformin works by stopping the glucagon cascade.
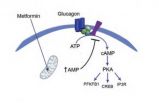
The Nature study describes a novel mechanism by which metformin antagonizes the action of glucagon, thus reducing fasting glucose levels. The team showed that metformin leads to the accumulation of AMP in mice, which inhibits an enzyme called adenylate cyclase, thereby reducing levels of cyclic AMP and protein kinase activity, eventually blocking glucagon-dependent glucose output from liver cells.
From this new understanding of metformin's action, Birnbaum and colleagues surmise that adenylate cyclase could be a new drug target by mimicking the way in which it is inhibited by metformin. This strategy would bypass metformin's affect on a cell's mitochondria to make energy, and possibility avoid the adverse side effects experienced by many people who take metformin, perhaps even working for those patients resistant to metformin.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors are Russell A. Miller and Qingwei Chu from Penn, and Jianxin Xie from Cell Signaling Technology, Mass.
This work was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (RO1 DK56886, PO1 DK49210, F32 DK079572); the Association pour l'Etude des Diabètes et des Maladies Métaboliques; the Programme National de Recherche sur le Diabète; and the Institut Benjamin Delessert.
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine is currently ranked #2 in U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $479.3 million awarded in the 2011 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; and Pennsylvania Hospital — the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Penn Medicine also includes additional patient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2011, Penn Medicine provided $854 million to benefit our community.
Most-used diabetes drug works in different way than previously thought
Findings could lead to diabetes treatments with less side effects
2013-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genetic mystery of Behcet's disease unfolds along the ancient Silk Road
2013-01-07
Researchers have identified four new regions on the human genome associated with Behcet's disease, a painful and potentially dangerous condition found predominantly in people with ancestors along the Silk Road. For nearly 2,000 years, traders used this 4,000-mile network linking the Far East with Europe to exchange goods, culture and, in the case of the Silk Road disease, genes. National Institutes of Health researchers and their Turkish and Japanese collaborators published their findings in the Jan. 6, 2013, advance online issue of Nature Genetics.
Named for the Turkish ...
From the Amazon rainforest to human body cells: Quantifying stability
2013-01-07
As they typically result from severe external perturbations, it is of vital interest how stable the most desirable state is. Surprisingly, this basic question has so far received little attention. Now scientists of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), in a paper published in Nature Physics, propose a new concept for quantifying stability.
"Up to now, science was able to say if a complex system is stable or not, but it wasn't able to properly say how stable it is," says Peter J. Menck, lead author of the paper. The proposed concept is the first to fill ...
A new approach to assessing future sea level rise from ice sheets
2013-01-07
The study, published today in Nature Climate Change, is the first of its kind on ice sheet melting to use structured expert elicitation (EE) together with an approach which mathematically pools experts' opinions. EE is already used in a number of other scientific fields such as forecasting volcanic eruptions.
The ice sheets covering Antarctica and Greenland contain about 99.5 per cent of the Earth's glacier ice which would raise global sea level by some 63m if it were to melt completely. The ice sheets are the largest potential source of future sea level rise – and ...
The pain puzzle: Uncovering how morphine increases pain in some people
2013-01-07
Quebec City & Toronto, January 6, 2013—For individuals with agonizing pain, it is a cruel blow when the gold-standard medication actually causes more pain. Adults and children whose pain gets worse when treated with morphine may be closer to a solution, based on research published in the January 6 on-line edition of Nature Neuroscience.
"Our research identifies a molecular pathway by which morphine can increase pain, and suggests potential new ways to make morphine effective for more patients," says senior author Dr. Yves De Koninck, Professor at Université Laval in ...
New study defines the long-sought structure of a protein necessary for cell-cell interaction
2013-01-07
JUPITER, FL, January 6, 2012 – Scientists know that cells in all higher organisms cells need to bind to each other for the development, architecture, maintenance and function of tissues. Mysteries have remained, however, about exactly how cells manage this feat.
Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have now solved part of this puzzle by defining the structure of a protein known as α-catenin, which is essential to this process.
The work was published online ahead of print on January 6, 2012, by the journal Nature Structural ...
Joslin researchers identify important factor in fat storage and energy metabolism
2013-01-07
BOSTON – January 8, 2013 -- As part of their ongoing research on the physiologic factors that contribute to the development of obesity, Joslin Diabetes Center scientists have identified a cell cycle transcriptional co-regulator – TRIP-Br2 – that plays a major role in energy metabolism and fat storage. This finding has the potential to lead to new treatments for obesity. The study is being published today ahead of print by Nature Medicine.
Transcriptional co-regulators manage the expression of DNA, either by activating or suppressing the expression of genes. TRIP-Br2 ...
Astrophysicists find wide binary stars wreak havoc in planetary systems
2013-01-07
VIDEO:
This movie shows two simulations of planetary system disruption by galactic disturbances to wide binary stars. On the left is a zoomed-out view showing the orbit of a hypothetical 0.1...
Click here for more information.
TORONTO, ON – An international team of astrophysicists has shown that planetary systems with very distant binary stars are particularly susceptible to violent disruptions, more so than if they had stellar companions with tighter orbits around them.
Unlike ...
Study reveals ordinary glass's extraordinary properties
2013-01-07
Technologically valuable ultrastable glasses can be produced in days or hours with properties corresponding to those that have been aged for thousands of years, computational and laboratory studies have confirmed.
Aging makes for higher quality glassy materials because they have slowly evolved toward a more stable molecular condition. This evolution can take thousands or millions of years, but manufacturers must work faster. Armed with a better understanding of how glasses age and evolve, researchers at the universities of Chicago and Wisconsin-Madison raise the possibility ...
Counting the cost of mercury pollution
2013-01-07
Cleaning up mercury pollution and reducing prenatal exposure to the neurotoxin methylmercury (MeHg) could save the European Union €10,000 million per year, finds a new study published in BioMed Central's open access journal Environmental Health. New estimates suggest that between 1.5 and 2 million children in the EU are born each year with MeHg exposures above the safe limit of 0.58µg/g and 200,000 above the WHO recommended maximum of 2.5µg/g.
While some mercury occurs naturally in the environment for example from volcanic eruptions or forest fires, most is generated ...
A new phase in reading photons
2013-01-07
"That's not what I meant": human communication is fraught with misinterpretation. Written out in longhand, words and letters can be misread. A telegraph clerk can mistake a dot for a dash. Noise will always be with us, but at least a new JQI (*) device has established a new standard for reading quantum information with a minimum of uncertainty.
Success has come by viewing light pulses not with a single passive detector with but an adaptive network of detectors with feedback. The work on JQI's new, more assured photonic protocol was led by Francisco Becerra ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] Most-used diabetes drug works in different way than previously thoughtFindings could lead to diabetes treatments with less side effects