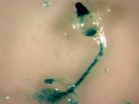
(Press-News.org) A 'cheater' mutation (chtB) in Dictyostelium discoideum, a free living slime mould able to co-operate as social organism when food is scarce, allows the cheater strain to exploit its social partner, finds a new study published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Evolutionary Biology. The mutation ensures that when mixed with 'normal' Dictyostelium more than the fair share of cheaters become spores, dispersing to a new environment, and avoiding dying as stalk cells.
Dictyostelium have an unusual life style. They generally live as individual amoeboid cells, eating bacteria in leaf litter and soil. However when they run out of food they form a multi-cellular 'slug' capable of travelling to a new environment. However if conditions are right they behave more like a fungus, producing a stalk and a fruiting body which releases spores. During this co-operative behaviour approximately 20% become stalk cells which are doomed to starvation but, after dispersal, the spores germinate into new amoeba.
The chtB strain is able to reduce the ability of normal Dictyostelium to form spores so that when mixed in equal numbers with wild type Dictyostelium 60% of the spores will be chtB. The chtB mutation appeared to be normal in all other respects and the mutation had no 'fitness cost' which might impede its behaviour or lifespan. In fact the mutation allowed chtB to divide faster in liquid medium.
Dr Lorenzo Santorelli from the University of Oxford who led this study, conducted at Baylor College of Medicine in the Shaulsky lab explained, "chtB cells inhibit the pre-spore gene cotB in their wild type partner. This appears to force the wild type Dictyostelium to become cells at the base of the stalk rather than stalk cells or spores. Cheaters are essentially parasites, but we could not find the expected fitness cost which usually prevents such cheaters from taking over."
INFORMATION:
Media Contact
Dr Hilary Glover
Scientific Press Officer, BioMed Central
Tel: +44 (0) 20 3192 2370
Mob: +44 (0) 778 698 1967
Email: hilary.glover@biomedcentral.com
Notes
1. A new social gene in Dictyostelium discoideum, chtB
Lorenzo A Santorelli, Adam Kuspa, Gad Shaulsky, David C Queller and Joan E Strassmann
BMC Evolutionary Biology (in press)
Please name the journal in any story you write. If you are writing for the web, please link to the article. All articles are available free of charge, according to BioMed Central's open access policy.
Article citation and URL available on request on the day of publication.
All images are to be credited to Lorenzo A Santorelli, Adam Kuspa, Gad Shaulsky, David C Queller and Joan E Strassmann.
2. BMC Evolutionary Biology is an open access, peer-reviewed journal that considers articles on all aspects of molecular and non-molecular evolution of all organisms, as well as phylogenetics and palaeontology.
3. BioMed Central is an STM (Science, Technology and Medicine) publisher which has pioneered the open access publishing model. All peer-reviewed research articles published by BioMed Central are made immediately and freely accessible online, and are licensed to allow redistribution and reuse. BioMed Central is part of Springer Science+Business Media, a leading global publisher in the STM sector. @BioMedCentral
Cheating slime mold gets the upper hand
2013-01-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Triple mix of blood pressure drugs and painkillers linked to kidney problems
2013-01-09
Patients who take a triple combination of blood pressure drugs and common painkillers are at an increased risk of serious kidney problems, especially at the start of treatment, finds a study published on bmj.com today.
Although the absolute risk for individuals is low, it is still something doctors and patients should be aware of, say the researchers.
Acute kidney injury (also known as kidney failure) is a major public health concern. It occurs in more than 20% of hospital inpatients and is associated with around half of all potentially preventable deaths in hospital. ...
Cancer screening unlikely to benefit patients with a short life expectancy
2013-01-09
Breast and colorectal cancer screening should be targeted towards patients with a life expectancy greater than 10 years: for any shorter life expectancy the harms are likely to outweigh the benefits, concludes a study published on bmj.com today.
The authors stress that their results "should not be used to deny screening for patients with limited life expectancy" but "should inform decision making which aims to account for patient preferences and values while maximising benefits and minimising risks."
Guidelines recommend screening healthy older patients because complications ...
BMJ raises concerns over the effectiveness of a costly and invasive procedure for melanoma
2013-01-09
A special report published by the BMJ today finds that thousands of melanoma patients around the world are undergoing an expensive and invasive procedure called sentinel node biopsy, despite a lack of clear evidence and concerns that it may do more harm than good.
Although not recommended for routine use in England, it has become the standard care for melanoma patients in several countries including the United States, where it was estimated to cost over $686m in 2012.
Melanoma is the fifth most common cancer in the UK, affecting one in 60 people. In the US it affects ...
Reduction in air pollution from wood stoves associated with significantly reduced risk of death
2013-01-09
Male deaths from all-causes, but particularly cardiovascular and respiratory disease, could be significantly reduced with a decrease in biomass smoke (smoke produced by domestic cooking and heating and woodland fires), a paper published today on bmj.com suggests.
The researchers say this could have significant impact on further interventions to reduce pollution from this source.
Although a large amount of research has been carried out on the adverse health effects of air pollution, no studies have reported reductions in deaths associated with interventions to reduce ...
First oral drug for spinal cord injury improves movement in mice, study shows
2013-01-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – An experimental oral drug given to mice after a spinal cord injury was effective at improving limb movement after the injury, a new study shows.
The compound efficiently crossed the blood-brain barrier, did not increase pain and showed no toxic effects to the animals.
"This is a first to have a drug that can be taken orally to produce functional improvement with no toxicity in a rodent model," said Sung Ok Yoon, associate professor of molecular & cellular biochemistry at Ohio State University and lead author of the study. "So far, in the spinal cord ...
Synthetic 'poop' can cure C. difficile infection, study finds
2013-01-09
A synthetic "poop" developed at the University of Guelph can cure nasty gastrointestinal infections caused by Clostridium difficile, a toxin-producing bacterium.
A study on the artificial stool was published today in the inaugural issue of Microbiome, a new peer-reviewed science journal.
The stool – a "super-probiotic" called RePOOPulate – was created by Guelph microbiologist Emma Allen-Vercoe to replace human fecal matter used in stool transplants, a known treatment for C. difficile.
She made the super-probiotic from purified intestinal bacterial cultures grown ...
Earth-size planets common in galaxy
2013-01-09
An analysis of the first three years of data from NASA's Kepler mission, which already has discovered thousands of potential exoplanets, contains good news for those searching for habitable worlds outside our solar system.
It shows that 17 percent of all sun-like stars have planets one to two times the diameter of Earth orbiting close to their host stars, according to a team of astronomers from the University of California, Berkeley, and the University of Hawaii at Manoa.
This estimate includes only planets that circle their stars within a distance of about one-quarter ...
'Tricorder' invention could put medical diagnosis and terrorism prevention in the palm of the hand
2013-01-09
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- The hand-held scanners, or tricorders, of the Star Trek movies and television series are one step closer to reality now that a University of Missouri engineering team has invented a compact source of X-rays and other forms of radiation. The radiation source, which is the size of a stick of gum, could be used to create inexpensive and portable X-ray scanners for use by doctors, as well as to fight terrorism and aid exploration on this planet and others.
"Currently, X-ray machines are huge and require tremendous amounts of electricity," said Scott Kovaleski, ...
'Universal' personality traits may not be universal after all
2013-01-09
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– For decades, consensus among psychologists has held that a group of five personality traits –– or slight variations of these five –– are a universal feature of human psychology. However, a study by anthropologists at UC Santa Barbara raises doubt about the veracity of that five-factor model (FFM) of personality structure as it relates to indigenous populations. Their findings appear in the current issue of the American Psychological Association's Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Studying the Tsimane, an isolated indigenous group ...
Counting the twists in a helical light beam
2013-01-09
Cambridge, Mass. - January 8, 2013 - At a time when communication networks are scrambling for ways to transmit more data over limited bandwidth, a type of twisted light wave is gaining new attention. Called an optical vortex or vortex beam, this complex beam resembles a corkscrew, with waves that rotate as they travel.
Now, applied physicists at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have created a new device that enables a conventional optical detector (which would normally only measure the light's intensity) to pick up on that rotation.
The ...