Immunotherapy reduces allergic patients' sensitivity to peanuts
Placing peanut protein under a patient’s tongue helps dampen allergic reactions
2013-01-11
(Press-News.org) Of all foods, peanuts are the most frequent cause of life-threatening and fatal allergic reactions. New research at National Jewish Health provides additional support for a strategy to reduce the severity of reactions to peanut— repeatedly consuming small amounts of the very food that causes those reactions in the first place, a practice called immunotherapy.
The new research, published in the January 2013 issue of The Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology, shows that 70 percent of peanut-allergic patients who consumed daily doses of peanut protein in liquid drops could safely consume 10 times as much peanut protein as they had before the therapy. One patient's serious reaction, however, highlighted the care that must be taken to keep patients safe.
"Immunotherapy continues to show promise for treating food allergies," said lead author David Fleischer, MD, associate professor of pediatrics at National Jewish Health. "But it is not yet ready for widespread use; there is a fine line between safely desensitizing patients and causing serious allergic reactions. We are still working to discover where that line is and how to select patients who would most likely benefit."
Immunotherapy, in the form of allergy shots, has been used for more than a century to reduce patients' allergic reactions, mostly to pollen. Patients are injected with gradually increasing amounts of protein until they reach a "maintenance level," which they continue for two to five years. The current trial delivers immunotherapy through drops containing peanut protein placed under the tongue.
Somehow this small, but repeated exposure changes the way that the immune system 'sees' the protein—from mistakenly considering it a dangerous invader to accurately recognizing it as a harmless piece of the environment. Scientists do not understand exactly how this occurs. In recent years, there has been renewed interest in understanding and exploring new methods of immunotherapy for a variety of immune disorders.
In the current trial, researchers reported interim results of a study that enrolled 40 teenage and adult patients with moderate, but not severe, reactions to peanuts. They divided them evenly into groups receiving either peanut protein or a placebo. The participants took the drops daily at home, coming into National Jewish Health and other academic medical centers for increased doses. Patients will continue immunotherapy for approximately three years.
After 44 weeks, 70 percent of the participants receiving peanut immunotherapy increased the average amount of peanut protein they could safely consume from 3.5 milligrams to 496 milligrams. After 68 weeks, responders were desensitized further, safely consuming, on average, 996 milligrams of peanut protein. That level of desensitization could help protect against an accidental ingestion, which averages about 100 milligrams. One peanut contains on average about 250 milligrams of peanut protein.
"We are hopeful that continued immunotherapy will help more patients become less sensitive to peanuts," said Dr. Fleischer.
Even at relatively low doses, participants frequently experienced some symptoms, most commonly itching in the mouth and throat. One patient developed very itchy red skin and more serious symptoms in the mouth after a daily dose at home. The patient required an antihistamine, an epinephrine injection and close observation at one of the research centers.
"This is an experimental treatment, promising, but with potentially serious side effects," said Dr. Fleischer. "Some physicians are treating their peanut-allergic patients with immunotherapy outside of carefully controlled and observed trials. I don't think that approach is safe until we better understand how much protein to deliver, through what method, and to which patients."
###
The multicenter study was supported by the NIH's National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and conducted by the Consortium of Food Allergy Research (CoFAR) at clinical sites in Baltimore; Chapel Hill, N.C.; Denver; Little Rock, Ark.; and New York City. CoFAR investigators David Fleischer, MD, associate professor of pediatrics at National Jewish Health in Denver, and A. Wesley Burks, MD, chair of the Department of Pediatrics at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, led the trial.
National Jewish Health is known worldwide for treatment of patients with respiratory, cardiac, immune and related disorders, and for groundbreaking medical research. Founded in 1899 as a nonprofit hospital, National Jewish Health remains the only facility in the world dedicated exclusively to these disorders. U.S. News & World Report has ranked National Jewish the #1 respiratory hospital in the nation for 15 consecutive years.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A cloudy mystery
2013-01-11
PASADENA, Calif.—It's the mystery of the curiously dense cloud. And astronomers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) are on the case.
Near the crowded galactic center, where billowing clouds of gas and dust cloak a supermassive black hole three million times as massive as the sun—a black hole whose gravity is strong enough to grip stars that are whipping around it at thousands of kilometers per second—one particular cloud has baffled astronomers. Indeed, the cloud, dubbed G0.253+0.016, defies the rules of star formation.
In infrared images of the galactic ...
Unemployment benefits not sought by jobless
2013-01-11
Montreal, January 9, 2013 – Employment insurance is a vital safety net for the unemployed across North America, yet some take advantage of the system. Recent headlines have made much of a recent report from the U.S. Department of Labor that 11 per cent of all unemployment benefits were overpaid between 2009-11. But new research from Concordia University proves that uncollected benefits represent a much larger dollar figure than overpayments.
In a study commissioned by the St. Louis Federal Reserve Bank, Concordia economics professor David Fuller examines the U.S. unemployment ...
3-D biomimetic scaffolds support regeneration of complex tissues from stem cells
2013-01-11
New Rochelle, NY, January 10, 2013—Stem cells can be grown on biocompatible scaffolds to form complex tissues such as bone, cartilage, and muscle for repair and regeneration of damaged or diseased tissue. However, to function properly, the cells must often grow in a specific pattern or alignment. An innovative method for creating a stretched polymer scaffold that can support complex tissue architectures is described in an article in Tissue Engineering, Part C, Methods, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available on the Tissue ...
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Narelle approaching Western Australia coast
2013-01-11
NASA's Aqua satellite looked at Cyclone Narelle in visible and infrared light to understand the behavior of the storm. NASA's MODIS and AIRS instruments provided those data, respectively, and they showed that Narelle is gaining strength as it approaches the northern coast of Western Australia.
Watches and Warnings are posted for the western coast of Western Australia over the next several days as Narelle continues to move on a southerly track, where it is expected to remain at sea, but parallel the coast.
Current Australian warnings include: a Cyclone Warning is in ...
Surgical technique spots cancer invasion with fluorescence
2013-01-11
One of the greatest challenges faced by cancer surgeons is to know exactly which tissue to remove, or not, while the patient is under anesthesia. A team of surgeons and scientists at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have developed a new technique that will allow surgeons to identify during surgery which lymph nodes are cancerous so that healthy tissue can be saved. The findings will be published in the January 15 print edition of Cancer Research.
"This research is significant because it shows real-time intraoperative detection of cancer metastases ...
Scripps Florida scientists uncover potential drug target to block cell death in Parkinson's disease
2013-01-11
JUPITER, FL, January 10, 2013 – Oxidative stress is a primary villain in a host of diseases that range from cancer and heart failure to Alzheimer's disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Parkinson's disease. Now, scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have found that blocking the interaction of a critical enzyme may counteract the destruction of neurons associated with these neurodegenerative diseases, suggesting a potential new target for drug development.
These findings appear in the January 11, 2013 edition of The Journal of ...
NASA's robotic refueling demo set to jumpstart expanded capabilities in space
2013-01-11
In mid-January, NASA will take the next step in advancing robotic satellite-servicing technologies as it tests the Robotic Refueling Mission, or RRM aboard the International Space Station. The investigation may one day substantially impact the many satellites that deliver products Americans rely upon daily, such as weather reports, cell phones and television news.
During five days of operations, controllers from NASA and the Canadian Space Agency will use the space station's remotely operated Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, robot to simulate robotic ...
Study finds poorer outcomes for obese patients treated for lumbar disc herniation
2013-01-11
Rosemont, Ill. – While obese patients are more likely to have surgical treatment for lumbar disc herniation – a slipped or ruptured disc – than nonobese patients, obesity increases operative time, blood loss and length of hospital stay, according to new research published in the January 2013 Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (JBJS). Overall, obese patients had poorer outcomes with surgical and nonsurgical treatments for lumbar disc herniation than nonobese patients.
The study included 854 nonobese patients with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of less than 30 kg/m², and 336 ...
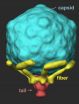
Virus caught in the act of infecting a cell
2013-01-11
AUSTIN, Texas — The detailed changes in the structure of a virus as it infects an E. coli bacterium have been observed for the first time, report researchers from The University of Texas at Austin and The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UT Health) Medical School this week in Science Express.
To infect a cell, a virus must be able to first find a suitable cell and then eject its genetic material into its host. This robot-like process has been observed in a virus called T7 and visualized by Ian Molineux, professor of biology at The University of Texas ...
Stem cells found to heal damaged artery in lab study
2013-01-11
Scientists at the Texas Biomedical Research Institute have for the first time demonstrated that baboon embryonic stem cells can be programmed to completely restore a severely damaged artery. These early results show promise for eventually developing stem cell therapies to restore human tissues or organs damaged by age or disease.
"We first cultured the stem cells in petri dishes under special conditions to make them differentiate into cells that are the precursors of blood vessels, and we saw that we could get them to form tubular and branching structures, similar to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
University of Miami business technology department ranked No. 1 in the nation for research productivity
Researchers build ultra-efficient optical sensors shrinking light to a chip
Why laws named after tragedies win public support
Missing geomagnetic reversals in the geomagnetic reversal history
EPA criminal sanctions align with a county’s wealth, not pollution
“Instead of humans, robots”: fully automated catalyst testing technology developed
Lehigh and Rice universities partner with global industry leaders to revolutionize catastrophe modeling
Engineers sharpen gene-editing tools to target cystic fibrosis
Pets can help older adults’ health & well-being, but may strain budgets too
First evidence of WHO ‘critical priority’ fungal pathogen becoming more deadly when co-infected with tuberculosis
World-first safety guide for public use of AI health chatbots
Women may face heart attack risk with a lower plaque level than men
Proximity to nuclear power plants associated with increased cancer mortality
Women’s risk of major cardiac events emerges at lower coronary plaque burden compared to men
Peatland lakes in the Congo Basin release carbon that is thousands of years old
Breadcrumbs lead to fossil free production of everyday goods
New computation method for climate extremes: Researchers at the University of Graz reveal tenfold increase of heat over Europe
Does mental health affect mortality risk in adults with cancer?
EANM launches new award to accelerate alpha radioligand therapy research
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
[Press-News.org] Immunotherapy reduces allergic patients' sensitivity to peanutsPlacing peanut protein under a patient’s tongue helps dampen allergic reactions