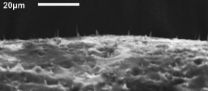
(Press-News.org) Tropical Storm Narelle is growing weaker as it continues to track in a southerly direction parallel to the coast of Western Australia. NASA's Aqua and TRMM satellites captured visible data and rainfall rates on Narelle and noticed the storm was less intense than it was, however, warnings are still up as Narelle continues moving down the coast.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone Narelle on Jan. 12 at 0615 UTC (1:15 a.m. EST) and Jan. 13 at 0655 UTC (1:55 a.m. EST) and captured these visible images of the storm. The imagery on Jan. 12 showed that Narelle weakened and its eye had become cloud-filled. On Jan. 13, the imagery showed that the southeastern quadrant of the storm was over the northern coast of Western Australia.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite captured rainfall rates in Cyclone Narelle on Jan. 14 at 0404 UTC. There were no areas of heavy rainfall in the tropical storm. A large area of moderate rainfall was occurring south of the center of circulation, where rainfall rates were near 30 mm (1.18 inches) per hour. TRMM also showed that cloud heights had fallen below 10 kilometers (6.2 miles), indicating weakening in the uplift of air that helps create the thunderstorms that make up the cyclone. Infrared satellite imagery confirmed that the cloud tops were warming, which is another indication of falling cloud heights. The colder a cloud top is, the higher it is, and the stronger the thunderstorm. When cloud tops warm, they're not as high in the atmosphere, and the storms are weaker.
On January 14 at 1200 UTC (7 a.m. EST), Tropical Storm Narelle had maximum sustained winds near 45 knots (51.7 mph/83.3 kph). Narelle's center was located near 28.8 south latitude and 110.1 east longitude, about 430 nautical miles (494.8 miles/796.4 km) south-southwest of Learmonth, Australia and is moving to the south at 15 knots (17.2 mph/27.7 kph).
The Australian Bureau of Meteorology (ABM) noted on Jan. 14 that Narelle is not expected to produce gales on the coast. However, west coast tides are likely to rise above the normal high tide mark and coastal flooding is possible in low lying areas.
ABM issue a Strong Wind Warning on Monday, Jan. 14 for the following areas: Gascoyne Coast and Geraldton Coast. For Tuesday, Jan. 15, the Strong Wind Warning will be in effect for: Perth Local Waters, West Kimberley Coast, Gascoyne Coast, Geraldton Coast, Lancelin Coast, Perth Coast, Bunbury Geographe Coast and Leeuwin Coast.
Adverse atmospheric conditions and cooler sea surface temperatures are taking a toll on Narelle as it continues to move in a southerly direction and parallel the coast of Western Australia. Narelle is forecast to turn toward the southeast and become extra-tropical in the next day.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees Tropical Storm Narelle winding down near western Australia
2013-01-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Simple intervention helps doctors communicate better when prescribing medications
2013-01-15
When it comes to prescribing medications to their patients, physicians could use a dose of extra training, according to a new study led by a UCLA researcher.
In previous studies, Dr. Derjung Tarn and her colleagues found that when doctors prescribed medicines, the information they provided to patients was spotty at best, they rarely addressed the cost of medications and they didn't adequately monitor their patients' medication adherence.
The logical next step, Tarn said, was to devise an intervention aimed at improving how physicians communicate to their patients ...
Childhood trauma leaves its mark on the brain
2013-01-15
It is well known that violent adults often have a history of childhood psychological trauma. Some of these individuals exhibit very real, physical alterations in a part of the brain called the orbitofrontal cortex. Yet a direct link between such early trauma and neurological changes has been difficult to find, until now.
Publishing in the January 15 edition of Translational Psychiatry, EPFL Professor Carmen Sandi and team demonstrate for the first time a correlation between psychological trauma in pre-adolescent rats and neurological changes similar to those found in ...
Kaiser Permanente study: Change in PSA levels over time can help predict aggressive prostate cancer
2013-01-15
PASADENA, Calif., January 15, 2013 – Measurements taken over time of prostate specific antigen, the most commonly used screening test for prostate cancer in men, improve the accuracy of aggressive prostate cancer detection when compared to a single measurement of PSA, according to a Kaiser Permanente study published today in the British Journal of Urology International.
The retrospective study examined the electronic health records of nearly 220,000 men ages 45 and older over a 10-year period who had at least one PSA measurement and no previous diagnosis of prostate cancer. ...
Study documents that some children lose autism diagnosis
2013-01-15
Some children who are accurately diagnosed in early childhood with autism lose the symptoms and the diagnosis as they grow older, a study supported by the National Institutes of Health has confirmed. The research team made the finding by carefully documenting a prior diagnosis of autism in a small group of school-age children and young adults with no current symptoms of the disorder.
The report is the first of a series that will probe more deeply into the nature of the change in these children's status. Having been diagnosed at one time with an autism spectrum disorder ...
Borderline personality disorder: The "perfect storm" of emotion dysregulation
2013-01-15
Philadelphia, PA, January 15, 2013 – Originally, the label "borderline personality disorder" was applied to patients who were thought to represent a middle ground between patients with neurotic and psychotic disorders. Increasingly, though, this area of research has focused on the heightened emotional reactivity observed in patients carrying this diagnosis, as well as the high rates with which they also meet diagnostic criteria for posttraumatic stress disorder and mood disorders.
New research now published in Biological Psychiatry from Dr. Anthony Ruocco at the University ...
Researchers create flexible, nanoscale 'bed of nails' for possible drug delivery
2013-01-15
Researchers at North Carolina State University have come up with a technique to embed needle-like carbon nanofibers in an elastic membrane, creating a flexible "bed of nails" on the nanoscale that opens the door to development of new drug-delivery systems.
The research community is interested in finding new ways to deliver precise doses of drugs to specific targets, such as regions of the brain. One idea is to create balloons embedded with nanoscale spikes that are coated with the relevant drug. Theoretically, the deflated balloon could be inserted into the target area ...
Lack of protein Sp2 disrupts neuron creation in brain
2013-01-15
A protein known as Sp2 is key to the proper creation of neurons from stem cells, according to researchers at North Carolina State University. Understanding how this protein works could enable scientists to "program" stem cells for regeneration, which has implications for neural therapies.
Troy Ghashghaei and Jon Horowitz, both faculty in NC State's Department of Molecular Biomedical Sciences and researchers in the Center for Comparative Medicine and Translational Research, wanted to know more about the function of Sp2, a cell cycle regulator that helps control how cells ...
Never forget a Face(book) -- memory for online posts beats faces and books
2013-01-15
People's memory for Facebook posts is strikingly stronger than their memory for human faces or sentences from books, according to a new study.
The findings shed light on how our memories favour natural, spontaneous writing over polished, edited content, and could have wider implications for the worlds of education, communications and advertising.
The research, authored by academics at the University of Warwick (Dr Laura Mickes) and UC San Diego (including Professors Christine Harris and Nicholas Christenfeld), tested memory for text taken from anonymised Facebook updates, ...
Facebook beats books - and faces - in memory test
2013-01-15
If this were a Facebook post, you would remember it – better than a stranger's face or a line from a published book.
That, in fewer than 140 characters, is the finding of research from the University of California, San Diego and the University of Warwick, published in the Springer journal Memory & Cognition.
Oh, and: The small, social-networking faux pas you were hoping would fade from your friends' memories real soon…? Don't count on it. Sorry. :/
In "Major Memory for Microblogs," the researchers report that Facebook status updates were about one and a half times ...
War was central to Europe's first civilization, contrary to popular belief
2013-01-15
Research from the University of Sheffield has discovered that the ancient civilisation of Crete, known as Minoan, had strong martial traditions, contradicting the commonly held view of Minoans as a peace-loving people.
The research, carried out by Dr Barry Molloy of the University of Sheffield's Department of Archaeology, investigated the Bronze Age people of Crete, known by many as the Minoans, who created the very first complex urban civilisation in Europe.
"Their world was uncovered just over a century ago, and was deemed to be a largely peaceful society," explained ...