(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. – A new study has concluded that sports fans love to root for a hero and against a villain, but if the game is exciting, they'll enjoy it no matter who wins.
The research, recently published in the Journal of Media Psychology, examines emotional experiences, outcome satisfaction, and enjoyment of athletic events, particularly ones featuring individual athletes rather than team sports.
Lead author Colleen Bee, an assistant professor of marketing at Oregon State University, said the Olympics are a good example of an event where fans often cheer for little-known athletes competing in little-watched sports. The allure for these casual fans is not necessarily the sport itself. The spectacle and inherent drama associated with an athletic event is enough to make fans watch.
"Knowing something about the personal lives and personalities of these athletes gives the casual fan a reason to root for or against someone," Bee said. "The stories matter here. It magnifies the experience of watching the game, and gives people a reason to watch."
In the study, Bee had participants watch speed skating competitions. She confirmed that none of the participants were familiar with the athletes before watching the event. Then she provided participants with one of two fictitious scenarios. In one scenario, an athlete was given heroic qualities such as working with ill children, a commitment to the cause of cancer prevention, dedicating his performance to his mother, and being gracious and considerate. In the second scenario, the athlete was imbued with unfavorable qualities, such as testing positive for performance enhancing drugs, being arrested for public intoxication, and being ungracious and inconsiderate.
She found that viewers of the game rooted for the heroic athlete and of course hoped that the "villain" would lose. Yet, she found that all the study participants reported enjoying the game regardless of the moral qualities of the winning athlete.
"There are people who enjoy watching famous athletes compete even though they may not like them personally, or feel like they aren't good people," Bee said. "Yet, because they are exciting to watch, and in many cases because they have an exciting story, sports fans still enjoy watching them compete."
While the participants felt disappointed when the "villainous" athlete won, and similarly relieved when the heroic athlete won, they all reported enjoying the game despite the outcome.
"Casual sport fans often enjoy the experience of a highly competitive event even when the outcome is not desirable, due to the entertaining and exciting nature of suspense," Bee said, pointing to her last study which found that winning or losing games did not matter so much as whether or not the game was close.
Bee is an expert on sports marketing, particularly in the areas of sports and emotions and gender/consumer responses.
Robert Madrigal, associate professor of marketing at the University of Oregon, is co-author of the study.
###
Photo: A high resolution photo of Bee is available at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/oregonstateuniversity/6854100683/
For sports fans, the story -- not the victor -- makes the difference in enjoyment
2013-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify ways to improve quality of care measurement from electronic health records
2013-01-16
NEW YORK (January 15, 2013) -- Health care providers and hospitals are being offered up to $27 billion in federal financial incentives to use electronic health records (EHRs) in ways that demonstrably improve the quality of care. The incentives are based, in part, on the ability to electronically report clinical quality measures. By 2014, providers nationwide will be expected to document and report care electronically, and by 2015, they will face financial penalties if they don't meaningfully use EHRs.
A new, federally-funded study by Weill Cornell Medical College in ...
International study: Where there's smoke or smog, there's climate change
2013-01-16
In addition to causing smoggy skies and chronic coughs, soot – or black carbon – turns out to be the number two contributor to global warming. It's second only to carbon dioxide, according to a four-year assessment by an international panel.
The new study concludes that black carbon, the soot particles in smoke and smog, contributes about twice as much to global warming as previously estimated, even by the 2007 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
"We were surprised at its potential contribution to climate," said Sarah Doherty, a University of Washington atmospheric ...
New American Chemical Society podcast: Leaves of carob tree fight food-poisoning bacteria
2013-01-16
The latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS') award-winning Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions podcast series reports that an antibacterial extract from the leaves of the carob tree (the source of a popular chocolate substitute) could fight the microbe responsible for the serious form of food poisoning called listeriosis.
Based on a report by Pierluigi Caboni, Ph.D., Nadhem Aissani and colleagues in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, the new podcast is available without charge at iTunes and from www.acs.org/globalchallenges.
In the ...
Novel approach to track migration of arctic-breeding avian species
2013-01-16
Animals move around the globe in billions, sometimes - like the snow bunting - one of the iconic Arctic-breeding species, covering huge distances and enduring the most extreme frigid weather conditions. In this conspicuously white sparrow-sized bird, animal migration epitomizes a stunning success of biological adaptation – with Snow Bunting representing the only songbird to breed as far north as the Arctic Circle. Indeed, there is nothing north of the snow bunting's breeding ground except the North Pole and the polar ice cap. These passerines thrive in chilly, alpine conditions, ...
Studies provide new insights into brain-behavior relationships
2013-01-16
Amsterdam, NL, January 15, 2013 – Approximately half a million individuals suffer strokes in the US each year, and about one in five develops some form of post-stroke aphasia, the partial or total loss of the ability to communicate. By comparing different types of aphasia, investigators have been able to gain new insights into the normal cognitive processes underlying language, as well as the potential response to interventions. Their findings are published alongside papers on hemispatial neglect and related disorders in the January, 2013 issue of.
The January issue of ...
NASA finds 2012 sustained long-term climate warming trend
2013-01-16
NASA scientists say 2012 was the ninth warmest of any year since 1880, continuing a long-term trend of rising global temperatures. With the exception of 1998, the nine warmest years in the 132-year record all have occurred since 2000, with 2010 and 2005 ranking as the hottest years on record.
NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York, which monitors global surface temperatures on an ongoing basis, released an updated analysis Tuesday that compares temperatures around the globe in 2012 to the average global temperature from the mid-20th century. The ...
Choline supplementation during pregnancy presents a new approach to schizophrenia prevention
2013-01-16
AURORA, Colo. (Jan. 15, 2013) — Choline, an essential nutrient similar to the B vitamin and found in foods such as liver, muscle meats, fish, nuts and eggs, when given as a dietary supplement in the last two trimesters of pregnancy and in early infancy, is showing a lower rate of physiological schizophrenic risk factors in infants 33 days old. The study breaks new ground both in its potentially therapeutic findings and in its strategy to target markers of schizophrenia long before the illness itself actually appears. Choline is also being studied for potential benefits ...
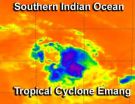
Infrared NASA imagery shows sinking air, elongation in Tropical Storm Emang
2013-01-16
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite provides valuable data to tropical cyclone forecasters, and revealed sinking air, a small area of powerful thunderstorms, and a slightly elongated Tropical Storm Emang.
Infrared data on Tropical Storm Emang's cloud top temperatures was captured by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on Jan. 15 at 0823 UTC (3:23 a.m. EST). AIRS data showed that the largest area of powerful thunderstorms were in the northern half of the storm. That area showed cold cloud top temperatures of -63F ...
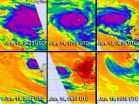
NASA satellites see Cyclone Narelle torn apart
2013-01-16
NASA's TRMM and Aqua satellites showed how Tropical Cyclone Narelle has fallen far from being a powerful cyclone in the Southern Indian Ocean. A time series of infrared images from an Aqua satellite instrument provides a clear picture of Narelle's former power and its recent demise, while TRMM 3-D data showed falling cloud heights and weaker rainfall.
Narelle, once a powerful tropical cyclone with winds of 115 knots (~132 mph), was equivalent to a category 4 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson scale. The storm has continued to steadily weaken as it made its way southward ...
Surgical-site infections may increase risk of deadly blood clots after colorectal surgery
2013-01-16
Despite receiving blood thinners and other clot prevention treatment, some patients still develop potentially lethal blood clots in the first month after their operations anyway, especially if they developed a surgical-site infection while in the hospital, according to results of a study at Johns Hopkins.
The research, described in a report published in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons, found that patients who experience a surgical-site infection after their abdominal surgery are four times more likely than infection-free patients to develop a deep-vein ...