Body's ibuprofen, SPARC, reduces inflammation and thus bladder cancer development and metastasis
Tumors flourish in inflammed tissue; readdition of SPARC reduces inflammation and stops proliferation
2013-01-16
(Press-News.org) Cancer researchers are increasingly aware that in addition to genetic mutations in a cancer itself, characteristics of the surrounding tissue can promote or suppress tumor growth. One of these important tissue characteristics is inflammation – most cancers prosper in and attach to inflamed tissue and so many cancers have developed ways to create it.
A University of Colorado Cancer Center study published today in the Journal of Clinical Investigation shows that the protein SPARC (Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine) acts much like an anti-inflammatory drug, attempting to heal tissues inflamed by tumors. Likewise, cancers – for example, bladder cancer in this study – have developed ways to turn off the production of SPARC, thus allowing growth and metastasis, especially to the lung where bladder cancer is frequently fatal.
"In fact, we show the effects of SPARC go beyond even this anti-inflammatory role. Additionally, the protein is involved in disallowing migrating cancer cells from attaching at possible metastasis sites and stopping the production of new blood vessels needed to feed tumor tissue," says Dan Theodorescu, MD, PhD, director of the University of Colorado Cancer Center and the study's senior author.
The study started by evaluating SPARC levels in human bladder cancer samples. In less aggressive cancers, both the tumor and the surrounding tissue made SPARC. In more aggressive cancers, it was just the surrounding tissue that made SPARC – the aggressive tumor itself had suppressed production of the protein. In these human bladder cancer tumors, more SPARC was associated with longer survival.
This distinction between SPARC made in the tumor and SPARC made in the surrounding tissue largely explains previous work that found high SPARC in aggressive tumors and so suggested a possible tumor-promoting role for the protein. Instead, it seems that surrounding healthy tissue may respond to a growing tumor by increasing SPARC production, which it hopes will mute the tumor. Thus high SPARC that is in fact an attempt at tumor suppression can be coincidentally associated with aggressive tumors when the entire tumor is examined.
Healthy tissue turns up SPARC to mute tumors. Aggressive cancers turn down SPARC to promote tumors.
Then Theodorescu and colleagues turned to animal models without the ability to manufacture SPARC. Not only was bladder cancer quicker to develop in these models, but the cancer was also more likely to travel to invade lung tissue. When SPARC was added to these models, tumor growth and metastasis was reduced.
"This is a comprehensive portrait of SPARC function using human and murine bladder cancer as a model, and the first to clearly distinguish between the role of SPARC generated in the tumor and the role of the protein generated in the surrounding tissue," says Theodorescu. "We hope this provides the rational basis for further exploring manipulation of SPARC as a therapeutic intervention."
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2013-01-16
Could probiotics help HIV patients?
Antiretroviral (ARV) drugs are the first line therapy for patients with HIV; however, ARV-treated, HIV-infected individuals still have a higher mortality rate than uninfected individuals. During the course of infection, HIV patients develop inflammation that damages the walls of the intestines, known as the gut mucosa, allowing intestinal microbes to escape and enter the blood stream to cause a life-threatening systemic infection. The health of the gut mucosa is significantly influenced by the complement of bacteria in the gut and ...
2013-01-16
Antiretroviral (ARV) drugs are the first line therapy for patients with HIV; however, ARV-treated, HIV-infected individuals still have a higher mortality rate than uninfected individuals. During the course of infection, HIV patients develop inflammation that damages the walls of the intestines, known as the gut mucosa, allowing intestinal microbes to escape and enter the blood stream to cause a life-threatening systemic infection. The health of the gut mucosa is significantly influenced by the complement of bacteria in the gut and there is mounting evidence that probiotic ...
2013-01-16
Viruses prompt oncogenic transformation by genetically altering infected cells. Several recent studies have demonstrated that viruses alter the expression of microRNAs, non-coding RNA molecules that can block the expression of target genes. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Xiaoje Xu and colleagues at the Beijing Institute of Biotechnology report that miR-148a is repressed by hepatitis B virus (HBV) X protein (HBx) to promote growth and metastasis of liver cancer. In normal liver cells, miR-148a represses the expression of the oncogenic protein HPIP, ...
2013-01-16
PHILADELPHIA - One of the most insidious ways that parasitic diseases such as malaria and toxoplasmosis wreak their havoc is by hijacking their host's natural cellular processes, turning self against self. Researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania and Johns Hopkins University, led by Doron Greenbaum, Ph.D., assistant professor of Pharmacology at Penn, have identified the cell signaling pathway used by these parasites to escape from and destroy their host cells and infect new cells -- pointing the way toward possible new strategies to ...
2013-01-16
On the left of this new image there is a dark column resembling a cloud of smoke. To the right shines a small group of brilliant stars. At first glance these two features could not be more different, but they are in fact closely linked. The cloud contains huge amounts of cool cosmic dust and is a nursery where new stars are being born. It is likely that the Sun formed in a similar star formation region more than four billion years ago.
This cloud is known as Lupus 3 and it lies about 600 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Scorpius (The Scorpion). The section ...
2013-01-16
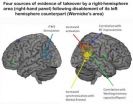
PITTSBURGH—For the first time, scientists at Carnegie Mellon University's Center for Cognitive Brain Imaging (CCBI) have used a new combination of neural imaging methods to discover exactly how the human brain adapts to injury. The research, published in Cerebral Cortex, shows that when one brain area loses functionality, a "back-up" team of secondary brain areas immediately activates, replacing not only the unavailable area but also its confederates.
"The human brain has a remarkable ability to adapt to various types of trauma, such as traumatic brain injury and stroke, ...
2013-01-16
WASHINGTON, DC, January 16, 2013 — Psychiatric disorders are prevalent among current and former inmates of correctional institutions, but what has been less clear is whether incarceration causes these disorders or, alternatively, whether inmates have these problems before they enter prison. A study co-authored by Jason Schnittker, an associate professor of sociology at the University of Pennsylvania, shows that many of the most common psychiatric disorders found among former inmates, including impulse control disorders, emerge in childhood and adolescence and, therefore, ...
2013-01-16
Mass poultry vaccination programmes introduced to combat Salmonella infections have led to a dramatic fall in the number of cases since the late 1990s, according to a researcher at the University of Liverpool.
Salmonella are important food-borne pathogens worldwide, causing diarrhoea, vomiting, nausea, fever and abdominal pain. There are currently around 6 million cases of illness from Salmonella across the EU each year, the majority of which are linked to food items such as eggs, chicken, beef, pork, salad vegetables and dairy products.
Between 1981 and 1991, the ...
2013-01-16
This press release is available in French.
Quebec City, January 16, 2013—Genetics plays a major role in peer rejection and victimization in early elementary school, according to a study recently published on the website of the journal Child Development by a team directed by Dr. Michel Boivin, a research professor at Université Laval's School of Psychology.
To come to this conclusion, Boivin and his team tested over 800 twins at three time points: when they were in kindergarten, Grade 1, and Grade 4. This sample consisted of 41% monozygotic twins—"true" twins who share ...
2013-01-16
Since 1992 the number of deaths linked to breast cancer in Spain has decreased among young and middle aged patients but not among the elderly. Spanish researchers also predict that it will continue to decline over the next decade, although more slowly as observed up until now.
A new study headed by a team of Spanish researchers has analysed breast cancer mortality in Spain among different age groups from 1981 to 2007, setting a valid prediction up until 2023.
Studying this age-related tendency is interesting because any improvement could have significant social and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Body's ibuprofen, SPARC, reduces inflammation and thus bladder cancer development and metastasis
Tumors flourish in inflammed tissue; readdition of SPARC reduces inflammation and stops proliferation