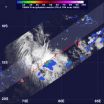
(Press-News.org) Tropical Storm Emang continues to move through open waters in the Southern Indian Ocean and NASA's TRMM satellite noticed one area of heavy rainfall near the center.
On Jan. 16 at 0702 UTC (2:02 a.m. EST) NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over Emang, and captured rainfall rates. TRMM identified that moderate rain was falling throughout most of the tropical cyclone, and heavy rainfall was occurring near the storm's center. TRMM estimated the heavy rain falling at a rate of 2 inches (50 mm) per hour.
On Jan. 16 at 0900 UTC (4 a.m. EST), Tropical Storm Emang had maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph/64.8 kph). Emang was located near 14.2 south latitude and 77.7 east longitude, about 580 nautical miles (667.5 miles/1,074 km) southeast of Diego Garcia. Emang is moving slowly to the west at 3 knots (3.4 mph/5.5 kph). Emang is currently not a threat to any land areas.
Emang is expected track west-southwest and may affect La Reunion Island by Jan. 21. However, as it tracks west, after briefly intensifying, wind shear and cooler water temperatures are expected to weaken the storm.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees 1 area of strength in Tropical Storm Emang
2013-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gene in eye melanomas linked to good prognosis
2013-01-17
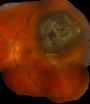
Melanomas that develop in the eye often are fatal. Now, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report they have identified a mutated gene in melanoma tumors of the eye that appears to predict a good outcome.
The research is published in the advance online edition of Nature Genetics.
"We found mutations in a gene called SF3B1," says senior author Anne Bowcock, PhD, professor of genetics. "The good news is that these mutations develop in a distinct subtype of melanomas in the eye that are unlikely to spread and become deadly."
Eye tumors ...
Mayo Clinic: Skin problems, joint disorders top list of reasons people visit doctors
2013-01-17
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A new Mayo Clinic Proceedings study shows that people most often visit their health care providers because of skin issues, joint disorders and back pain. Findings may help researchers focus efforts to determine better ways to prevent and treat these conditions in large groups of people.
"Much research already has focused on chronic conditions, which account for the majority of health care utilization and costs in middle-aged and older adults," says Jennifer St. Sauver, Ph.D., primary author of the study and member of the Population Health Program within ...
Eliminating or curtailing mortgage interest deduction would have modest long-run effects on economy
2013-01-17
Eliminating or curtailing the mortgage interest deduction (MID) would initially result in declines in housing prices and investment but would have only modest aggregate macroeconomic effects in the long run, according to a new paper from Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy.
The MID is the second-largest individual income tax expenditure, according to the congressional Joint Committee on Taxation. Given the severity of the fiscal problems currently faced by the U.S., many recent tax reform proposals have included measures that would curtail or eliminate ...
Recent study suggests bats are reservoir for ebola virus in Bangladesh
2013-01-17
NEW YORK – January 16, 2013 – EcoHealth Alliance, a nonprofit organization that focuses on local conservation and global health issues, released new research on Ebola virus in fruit bats in the peer reviewed journal, Emerging Infectious Diseases, a monthly publication by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The study found Ebola virus antibodies circulating in ~4% of the 276 bats scientists screened in Bangladesh. These results suggest that Rousettus fruit bats are a reservoir for Ebola, or a new Ebola-like virus in South Asia. The study extends the range ...
Tree and human health may be linked
2013-01-17
Evidence is increasing from multiple scientific fields that exposure to the natural environment can improve human health. In a new study by the U.S. Forest Service, the presence of trees was associated with human health.
For Geoffrey Donovan, a research forester at the Forest Service's Pacific Northwest Research Station, and his colleagues, the loss of 100 million trees in the eastern and midwestern United States was an unprecedented opportunity to study the impact of a major change in the natural environment on human health.
In an analysis of 18 years of data from ...
PODEX experiment to reshape future of atmospheric science
2013-01-17
Satellite Earth science missions don't start at the launch pad or even in orbit. They start years before when scientists test their new ideas for instruments that promise to expand our view and understanding of the planet. NASA scientists and engineers are working now to lay the groundwork for the Aerosol-Cloud-Ecosystem (ACE) mission, a satellite that "will dramatically change what we can do from space to learn about clouds and aerosols," said ACE science lead David Starr of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
How should the satellite's instruments be ...
Risk factors identified for prolonged sports concussion symptoms
2013-01-17
Researchers have found clear, identifiable factors that signal whether an athlete will experience concussive symptoms beyond one week. The researchers sought to identify risk factors for prolonged concussion symptoms by examining a large national database of high school athletes' injuries. Previous concussion studies were limited in scope, focusing only on male football players. The information from this study applies to male and female athletes from a number of different sports.
Researchers found that athletes who have four or more symptoms at initial injury were more ...
New research finds slower growth of preterm infants linked to altered brain development
2013-01-17
Preterm infants who grow more slowly as they approached what would have been their due dates also have slower development in an area of the brain called the cerebral cortex, report Canadian researchers in a new study published today in Science Translational Medicine.
The cerebral cortex is a two to four millimetre layer of cells that envelopes the top part of the brain and is involved in cognitive, behavioural, and motor processes.
Researchers analyzed MRI brain scans of 95 preterm infants born eight to 16 weeks too early at
BC Women's Hospital & Health Centre between ...
Mindfulness meditation may relieve chronic inflammation
2013-01-17
MADISON — People suffering from chronic inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and asthma — in which psychological stress plays a major role — may benefit from mindfulness meditation techniques, according to a study by University of Wisconsin-Madison neuroscientists with the Center for Investigating Healthy Minds at the Waisman Center.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction, originally designed for patients with chronic pain, consists of continuously focusing attention on the breath, bodily sensations and mental content while seated, ...
New robotic fish glides indefinitely
2013-01-17
A high-tech robotic fish hatched at Michigan State University has a new look. A new skill. And a new name.
MSU scientists have made a number of improvements on the fish, including the ability to glide long distances, which is the most important change to date. The fish now has the ability to glide through the water practically indefinitely, using little to no energy, while gathering valuable data that can aid in the cleaning of our lakes and rivers.
Designed and built by Xiaobo Tan, MSU associate professor of electrical and computer engineering, and his team, the fish ...