(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
This movie shows running mice (bred-for-athleticism mouse on the left, regular mouse on the right).
Click here for more information.
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Is athleticism linked to brain size? To find out, researchers at the University of California, Riverside performed laboratory experiments on house mice and found that mice that have been bred for dozens of generations to be more exercise-loving have larger midbrains than those that have not been selectively bred this way.
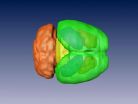
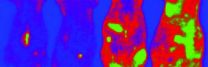
Theodore Garland's lab measured the brain mass of these uniquely athletic house mice, bred for high voluntary wheel-running, and analyzed their high-resolution brain images. The researchers found that the volume of the midbrain — a small region of the brain that relays information for the visual, auditory, and motor systems — in the bred-for-athleticism mice was nearly 13 percent larger than the midbrain volume in the control or "regular" mice.
"To our knowledge, this is the first example in which selection for a particular mammalian behavior — high voluntary wheel running in house mice in our set of experiments — has been shown to result in a change in size of a specific brain region," said Garland, a professor of biology and the principal investigator of the research project.
Study results appeared online Jan. 16 in The Journal of Experimental Biology.
In Garland's lab, selection for high voluntary wheel running in lab house mice has been ongoing for nearly 20 years — or more than 65 generations of house mice. To analyze brain mass and volume on independent samples of house mice, the researchers dissected the brains into two different regions, the cerebellum, a region of the brain crucial for controlling movement, and the non-cerebellar areas. They then weighed these sections separately.
The cerebellum is important for coordination. The midbrain, a part of the non-cerebellar area that contains a variety of sensory and motor nuclei, is essential for reward learning, motivation and reinforcing behavior. Previously, species of mammals and birds with larger brains have been shown to have higher survivability in novel environments.
The researchers found that compared to regular mice, those mice that had been selectively bred for high voluntary wheel-running had significantly greater midbrain volume as well as larger non-cerebellar brain mass, but not larger cerebella or total brain mass.
The primary question the researchers sought to answer in their study is whether selection on a particular behavioral trait, such as voluntary exercise, using an experimental evolution paradigm, has resulted in a change in brain size. An additional question they posed is whether any change in brain size involves the entire brain or is "mosaic," that is, involving only a section or some sections of the brain.
"Our finding that mice bred for high levels of voluntary exercise have an enlarged non-cerebellar brain mass and an enlarged midbrain, but do not show a statistically significant increase in overall brain mass or volume supports the mosaic theory of brain evolution," Garland said.
What implications the current research has for humans is not immediately clear.
"It is possible that individual differences in the propensity or ability for exercise in humans are associated with individual differences in the size of the midbrain, but no one has studied that," Garland said. "If it were possible to take MRIs of babies' midbrains before these babies started 'exercising' and then follow these babies through life, it may be that inherent, genetically-based differences in midbrain size detected soon after birth will influence how much they would be likely to exercise as adults."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by a grant to Garland from the National Science Foundation.
Next, the researchers plan to conduct another mouse study to investigate whether increased exercise activity impacts brain size.
Garland was joined in the study by the following researchers at UCR: E. M. Kolb, E. L. Rezende, L. Holness, A. Radtke, S. K. Lee, and A. Obenaus.
The University of California, Riverside is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment has exceeded 21,000 students. The campus will open a medical school in 2013 and has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Center. The campus has an annual statewide economic impact of more than $1 billion. A broadcast studio with fiber cable to the AT&T Hollywood hub is available for live or taped interviews. UCR also has ISDN for radio interviews. To learn more, call 951-UCR-NEWS.
Is athleticism linked to brain size?
UC Riverside research on mice shows that exercise-loving mice have larger midbrains
2013-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fighting sleep: UGA discovery may lead to new treatments for deadly sleeping sickness
2013-01-17
Athens, Ga. – While its common name may make it sound almost whimsical, sleeping sickness, or African trypanosomiasis, is in reality a potentially fatal parasitic infection that has ravaged populations in sub-Saharan Africa for decades, and it continues to infect thousands of people every year.
Few drugs have been developed to treat sleeping sickness since the 1940s, and those still in use are highly toxic, sometimes causing painful side effects and even death. But researchers at the University of Georgia have made a discovery that may soon lead to new therapies for this ...
Critically ill flu patients saved with artificial lung technology treatment
2013-01-17
TORONTO (January 17, 2013 ) - In recent weeks the intensive critical care units at University Health Network's Toronto General Hospital have used Extra Corporeal Lung Support (ECLS) to support five influenza (flu) patients in their recovery from severe respiratory problems.
ECLS systems are normally used at the hospital as a bridge to lung transplantation but increasingly, the hospital is using ECLS on patients where the usual breathing machines (ventilators) cannot support the patient whose lungs need time to rest and heal.
The ECLS systems are essentially artificial ...
Drug abuse impairs sexual performance in men even after rehabilitation
2013-01-17
Researchers at the University of Granada, Spain, and Santo Tomas University in Colombia have found that drug abuse negatively affects sexual performance in men even after years of abstinence. This finding contradicts other studies reporting that men spontaneously recovered their normal sexual performance at three weeks after quitting substance abuse.
The results of this study have been published in the prestigious Journal of Sexual Medicine, the official journal of the International Society for Sexual Medicine. The authors of this paper are Pablo Vallejo Medina –a professor ...
Trading wetlands no longer a deal with the devil
2013-01-17
URBANA – If Faust had been in the business of trading wetlands rather than selling his soul, the devil might be portrayed by the current guidelines for wetland restoration. Research from the University of Illinois recommends a new framework that could make Faustian bargains over wetland restoration sites result in more environmentally positive outcomes.
U of I ecologist Jeffrey Matthews explained that under the current policies if a wetland is scheduled for development and a negative impact is unavoidable, the next option is to offset, or compensate, for the destruction ...
UNC researchers use luminescent mice to track cancer and aging in real-time
2013-01-17
Chapel Hill, NC – In a study published in the January 18 issue of Cell, researchers from the University of North Carolina Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center have developed a new method to visualize aging and tumor growth in mice using a gene closely linked to these processes.
Researchers have long known that the gene, p16INK4a (p16), plays a role in aging and cancer suppression by activating an important tumor defense mechanism called 'cellular senescence'. The UNC team led by Norman Sharpless, MD, Wellcome Distinguished Professor of Cancer Research and Deputy Cancer ...
How are middle-aged women affected by burnout?
2013-01-17
New Rochelle, NY, January 17, 2013—Emotional exhaustion and physical and cognitive fatigue are signs of burnout, often caused by prolonged exposure to stress. Burnout can cause negative health effects including poor sleep, depression, anxiety, and cardiovascular and immune disorders. The findings of a 9-year study of burnout in middle-aged working women are reported in an article in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://www.liebertpub.com/jwh.
In ...
Researchers create method for more sensitive electrochemical sensors
2013-01-17
Graphene and related materials hold promise for the future of electrochemical sensors — detectors that measure the concentration of oxygen, toxic gases, and other substances — but many applications require greater sensitivity at lower detection ranges than scientists have been able to achieve.
A Northwestern University research team and partners in India have recently developed a new method for amplifying signals in graphene oxide-based electrochemical sensors through a process called "magneto-electrochemical immunoassay." The findings could open up a new class of technologies ...
Guided care provides better quality of care for chronically ill older adults
2013-01-17
Patients who received Guided Care, a comprehensive form of primary care for older adults with chronic health problems, rated the quality of their care much higher than patients in regular primary care, and used less home care, according to a study by researchers at Johns Hopkins University. In an article published online by the Journal of General Internal Medicine, researchers found that in a 32-month randomized controlled trial, Guided Care patients rated the quality of their care significantly higher than those in normal care, and were 66 percent more likely to rate their ...
New key to organism complexity identified
2013-01-17
The enormously diverse complexity seen amongst individual species within the animal kingdom evolved from a surprisingly small gene pool. For example, mice effectively serve as medical research models because humans and mice share 80-percent of the same protein-coding genes. The key to morphological and behavioral complexity, a growing body of scientific evidence suggests, is the regulation of gene expression by a family of DNA-binding proteins called "transcription factors." Now, a team of researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory ...
Hearing-loss-prevention drugs closer to reality thanks to new UF test
2013-01-17
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — A new way to test anti-hearing-loss drugs in people could help land those medicines on pharmacy shelves sooner. University of Florida researchers have figured out the longstanding problem of how to safely create temporary, reversible hearing loss in order to see how well the drugs work. The findings are described in the November/December 2012 issue of the journal Ear & Hearing.
"There's a real need for drug solutions to hearing loss," said lead investigator Colleen Le Prell, Ph.D., an associate professor in the department of speech, language, and hearing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Is athleticism linked to brain size?UC Riverside research on mice shows that exercise-loving mice have larger midbrains