(Press-News.org) This press release is available in German.
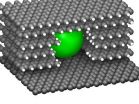
The world's smallest tunnels have a width of a few nanometers only. Researchers from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and Rice University, USA, have dug such tunnels into graphite samples. This will allow structuring of the interior of materials through self-organization in the nanometer range and tailoring of nanoporous graphite for applications in medicine and battery technology. Results are now presented in the scientific journal Nature Communications (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2399).
The tunnels are manufactured applying nickel nanoparticles to graphite which then is heated in the presence of hydrogen gas. The surface of the metal particles, that measure a few nanometers only, serves as a catalyst removing the carbon atoms of the graphite and converting them by means of hydrogen into the gas methane. Through capillary forces, the nickel particle is drawn into the "hole" that forms and bores through the material. The size of the tunnels obtained in the experiments was in the range of 1 to 50 nanometers, which about corresponds to one thousandth of the diameter of a human hair.
To furnish proof of the real existence of these graphite tunnels, the researchers have made use of scanning electron and scanning tunneling microscopy. "Microscopes, in fact, image only the upper layers of the sample," the principal authors of the study, Maya Lukas and Velimir Meded from KIT's Institute of Nanotechnology, explain. "The tunnels below these upper layers, however, leave atomic structures on the surface whose courses can be traced and which can be assigned to the nanotunnels by means of the very detailed scanning tunneling microscopy images and based on computerized simulations." In addition, the depth of the tunnels was determined precisely by means of a series of images taken by a scanning electron microscope from different perspectives.
Porous graphite is used, for example, in the electrodes of lithium ion batteries. The charge time could be reduced using materials with appropriate pore sizes. In medicine, porous graphite could serve as a carrier of drugs to be released over longer periods of time. Replacing graphite by nonconductive materials, e.g. boron nitride, with atomic structures similar to that of graphite, the tunnels could serve as basic structures for nanoelectronic components such as novel sensors or solar cells.
INFORMATION:
The graphite tunnel study was carried out by the study groups headed by Pulickel M. Ajayan from Rice University, USA, and Ralph Krupke and Wolfgang Wenzel from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology.
For further information on research by the KIT study groups, please refer to http://www.int.kit.edu.
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is a public corporation according to the legislation of the state of Baden-Württemberg. It fulfills the mission of a university and the mission of a national research center of the Helmholtz Association. KIT focuses on a knowledge triangle that links the tasks of research, teaching, and innovation.
This press release is available on the internet at www.kit.edu.
The photo of printing quality may be downloaded under www.kit.edu or requested by email or phone. The photo may be used in the context given above exclusively.
Nanoparticles digging the world's smallest tunnels
Tiny metal balls etching into graphite tunnels with diameters of only one-thousandth that of a human hair / porous graphite as a material in medicine and battery technology
2013-01-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers create self-healing, stretchable wires using liquid metal
2013-01-23
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed elastic, self-healing wires in which both the liquid-metal core and the polymer sheath reconnect at the molecular level after being severed.
"Because we're using liquid metal, these wires have excellent conductive properties," says Dr. Michael Dickey, an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State and co-author of a paper on the work. "And because the wires are also elastic and self-healing, they have a lot of potential for use in technologies that could be exposed to high-stress ...
Learn to be more understanding by watching The Bachelor (this season, anyway)
2013-01-23
A new USC study finds evidence suggesting that the brain works hard to understand those who have different bodies when watching them in action.
According to the study's lead author, the finding supports initiatives to include more individuals with physical differences in mainstream media – such as Sarah Herron, a contestant on ABC's The Bachelor this season, who was born with a foreshortened left arm.
"Generally, it's considered impolite to stare. But what these results suggest is that we need to look. It's through this visual experience that we're able to make sense ...
New way to identify 'smoked' grapes and wines
2013-01-23
With climate change sparking concern about an increased risk of wildfires, scientists are reporting development of a way to detect grapes exposed to smoke from those fires, which otherwise could be vented into bad-tasting wine. Their report on the method for detecting smoke taint in both grapes and wine appears in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
Yoji Hayasaka and colleagues point out that Australia and other areas of the world are experiencing an increase in bush and wildfires, which may continue and intensify with global climate change. Smoke from those ...
Scientists underestimated potential for Tohoku quake. Now what?
2013-01-23
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The massive Tohoku, Japan, earthquake in 2011 and Sumatra-Andaman superquake in 2004 stunned scientists because neither region was thought to be capable of producing a megathrust earthquake with a magnitude exceeding 8.4.
Now earthquake scientists are going back to the proverbial drawing board and admitting that existing predictive models looking at maximum earthquake size are no longer valid.
In a new analysis published in the journal Seismological Research Letters, a team of scientists led by Oregon State University's Chris Goldfinger describes how ...
Putting the squeeze on cells
2013-01-23
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. — Living cells are surrounded by a membrane that tightly regulates what gets in and out of the cell. This barrier is necessary for cells to control their internal environment, but it makes it more difficult for scientists to deliver large molecules such as nanoparticles for imaging, or proteins that can reprogram them into pluripotent stem cells.
Researchers from MIT have now found a safe and efficient way to get large molecules through the cell membrane, by squeezing the cells through a narrow constriction that opens up tiny, temporary holes in the membrane. ...
Panel recommends changing name of common disorder in women
2013-01-23
An independent panel convened by the National Institutes of Health has concluded that the name of a common hormone disorder in women, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), causes confusion and is a barrier to research progress and effective patient care. The current name focuses on a criterion — ovarian cysts — which is neither necessary nor sufficient to diagnose the syndrome. In a report released today, the panel recommended assigning a new name that more accurately reflects the disorder.
"The name PCOS is a distraction that impedes progress. It is time to assign a name ...
Better outlook for dwindling black macaque population in Indonesia
2013-01-23
Since at least the 1970s, the population of critically endangered Sulawesi black macaques living in an Indonesian nature reserve has been dropping. But a new study by researchers at the University of Washington and in Indonesia shows that the population has stabilized over the past decade.
The findings, published in the January issue of the American Journal of Primatology, are from the longest ongoing survey of Macaca nigra and are among the first evidence that the monkeys may be in better shape.
"Fifteen years ago it looked like this macaque population would continue ...
Treatment targeting PI3K may delay resistance to anti-HER2 therapy in breast cancer patients
2013-01-23
PHILADELPHIA — Patients with HER2-positive breast cancer being treated with anti-HER2 therapy may be able to prevent or delay resistance to the therapy with the addition of a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase inhibitor to their treatment regimens.
The data, published in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, indicated that failure of the anti-HER2 antibody trastuzumab to block HER2 from activating the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway can lead to resistance to treatment. Therefore, dual simultaneous inhibition of ...
Global plant diversity hinges on local battles against invasive species
2013-01-23
In Missouri forests, dense thickets of invasive honeysuckle decrease the light available to other plants, hog the attention of pollinators and offer nutrient-stingy berries to migrating birds. They also release toxins that decrease the germination of nearby native plants. Why, then, do studies of invasive species come to different conclusions about their effects and lead some organizations to suggest we accept their presence?
Biologists Kristin Powell, Tiffany Knight and Jon Chase of Washington University in St. Louis have found an answer.
Most studies of the effects ...
More efficient way to make popular prescription medication
2013-01-23
In a demonstration of the power of green chemistry, scientists are reporting development of a new and more efficient process for making one of the most costly and widely used medications for severe mental illness. Described in a report in the journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, it produces larger amounts of the medication than the existing commercial process while reducing the use of solvents and other potentially toxic substances.
Vijayavitthal T. Mathad and colleagues point out that paliperidone, marketed under the brand name Invega, is one of a new generation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Exploring the link between hearing loss and cognitive decline
Machine learning tool can predict serious transplant complications months earlier
Prevalence of over-the-counter and prescription medication use in the US
US child mental health care need, unmet needs, and difficulty accessing services
Incidental rotator cuff abnormalities on magnetic resonance imaging
Sensing local fibers in pancreatic tumors, cancer cells ‘choose’ to either grow or tolerate treatment
Barriers to mental health care leave many children behind, new data cautions
Cancer and inflammation: immunologic interplay, translational advances, and clinical strategies
Bioactive polyphenolic compounds and in vitro anti-degenerative property-based pharmacological propensities of some promising germplasms of Amaranthus hypochondriacus L.
AI-powered companionship: PolyU interfaculty scholar harnesses music and empathetic speech in robots to combat loneliness
Antarctica sits above Earth’s strongest “gravity hole.” Now we know how it got that way
Haircare products made with botanicals protects strands, adds shine
Enhanced pulmonary nodule detection and classification using artificial intelligence on LIDC-IDRI data
Using NBA, study finds that pay differences among top performers can erode cooperation
Korea University, Stanford University, and IESGA launch Water Sustainability Index to combat ESG greenwashing
Molecular glue discovery: large scale instead of lucky strike
Insulin resistance predictor highlights cancer connection
Explaining next-generation solar cells
Slippery ions create a smoother path to blue energy
Magnetic resonance imaging opens the door to better treatments for underdiagnosed atypical Parkinsonisms
National poll finds gaps in community preparedness for teen cardiac emergencies
One strategy to block both drug-resistant bacteria and influenza: new broad-spectrum infection prevention approach validated
Survey: 3 in 4 skip physical therapy homework, stunting progress
College students who spend hours on social media are more likely to be lonely – national US study
Evidence behind intermittent fasting for weight loss fails to match hype
How AI tools like DeepSeek are transforming emotional and mental health care of Chinese youth
Study finds link between sugary drinks and anxiety in young people
Scientists show how to predict world’s deadly scorpion hotspots
ASU researchers to lead AAAS panel on water insecurity in the United States
ASU professor Anne Stone to present at AAAS Conference in Phoenix on ancient origins of modern disease
[Press-News.org] Nanoparticles digging the world's smallest tunnelsTiny metal balls etching into graphite tunnels with diameters of only one-thousandth that of a human hair / porous graphite as a material in medicine and battery technology