(Press-News.org) Charged particle accelerators have become crucially important to modern day life, be it in health care for cancer treatment or for answering important fundamental scientific questions like the existence of the HIGGS boson, the so called 'God particle'. In a simple picture, charged particles like electrons and protons are accelerated between two end plates across which an electrical voltage is applied. High energies need high voltages (millions and billions of volts) and long acceleration paths in giant sized machines – for instance the trillion volt machine called the 'large hadron collider' (LHC) which discovered the Higgs boson, circles over 27 km underground in Geneva! A new concept for a compact accelerator was discovered in the last decade using high powered, short pulses of laser light. Alternating large electric fields of the light can be transformed in plasmas to create quasi static fields that can produce hundreds of millions volt accelerating voltages just over millimeter lengths on a table top!
How do we accelerate neutral particles- i.e. particles that cannot be energized by electrical voltages? And do it over millimeters rather than hundreds of meters and moreover using lasers? Research at Ultra Short Pulse High Intensity Lab in TIFR has now found a novel scheme that can do precisely this. The concept uses the ability of powerful lasers to strip nearly 8 electrons per atom in a nano sized, cooled aggregate of argon atoms- a nano piece of ice. A 40,000 atom cluster of argon is charged to 320,000 by a laser that lasts only a 100 billionth of a millionth of a second. Such a super highly charged ice piece explodes soon after, accelerating the charged atoms (Ions) to a million electron volts of energy. The TIFR research now found that all the expelled electrons can be put back into the charged ion that has been accelerated so that it now reverts to being a neutral atom but at high energies. To top it all, this process is nearly 100% efficient at neutralizing the speeding ions and converting them to fast atoms!
Accelerated neutral atoms are very important for many applications. Unaffected by electric or magnetic fields, they penetrate deeper in solids than electrons/ions and thereby create high finesse microstructures for novel electronics and optical devices. Fast atoms are used both as diagnostics and heating sources in Tokomak machines like the ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor) in France, that are being developed to create sustained thermo-nuclear fusion. The TIFR scheme can produce a point source of fast neutral atoms close to the location of an intended application.
As the old adage goes, staying neutral under extreme provocation certainly has its advantages!
INFORMATION:
Accelerating neutral atoms on a table top
2013-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rice technique points toward 2-D devices
2013-01-28
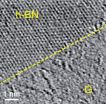
HOUSTON – (Jan. 28, 2013) – Rice University scientists have taken an important step toward the creation of two-dimensional electronics with a process to make patterns in atom-thick layers that combine a conductor and an insulator.
The materials at play – graphene and hexagonal boron nitride – have been merged into sheets and built into a variety of patterns at nanoscale dimensions.
Rice introduced a technique to stitch the identically structured materials together nearly three years ago. Since then, the idea has received a lot of attention from researchers interested ...
Cities affect temperatures for thousands of miles
2013-01-28
BOULDER – Even if you live more than 1,000 miles from the nearest large city, it could be affecting your weather.
In a new study that shows the extent to which human activities are influencing the atmosphere, scientists have concluded that the heat generated by everyday activities in metropolitan areas alters the character of the jet stream and other major atmospheric systems. This affects temperatures across thousands of miles, significantly warming some areas and cooling others, according to the study in Nature Climate Change.
The extra "waste heat" generated from ...
Stem cells aid recovery from stroke
2013-01-28
Stem cells from bone marrow or fat improve recovery after stroke in rats, finds a study published in BioMed Central's open access journal Stem Cell Research & Therapy. Treatment with stem cells improved the amount of brain and nerve repair and the ability of the animals to complete behavioural tasks.
Stem cell therapy holds promise for patients but there are many questions which need to be answered, regarding treatment protocols and which cell types to use. This research attempts to address some of these questions.
Rats were treated intravenously with stem cells or ...
Measuring the consequence of forest fires on public health
2013-01-28
Pollution from forest fires is impacting the health of people with asthma and other chronic obstructive lung diseases, finds a study in Biomed Central's open access journal Environmental Health. This study uses data from pharmacies and dispensaries to measure the increase in drugs needed to alleviate symptoms associated with pollution.
Forest fires burn nearly 1000 km2 of trees in British Columbia every year. The Ministry of Environment keeps a close watch on levels of particulate matter in the air caused by these fires but it is harder to measure the impact of this ...
Poor sleep in old age prevents the brain from storing memories
2013-01-28
The connection between poor sleep, memory loss and brain deterioration as we grow older has been elusive. But for the first time, scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, have found a link between these hallmark maladies of old age. Their discovery opens the door to boosting the quality of sleep in elderly people to improve memory.
UC Berkeley neuroscientists have found that the slow brain waves generated during the deep, restorative sleep we typically experience in youth play a key role in transporting memories from the hippocampus – which provides short-term ...
In breast cancer metastasis, researchers identify possible drug target
2013-01-28
The spread of breast cancer to distant organs within the body, an event that often leads to death, appears in many cases to involve the loss of a key protein, according to UC San Francisco researchers, whose new discoveries point to possible targets for therapy.
In the January 27, 2013 online edition of Nature Cell Biology, UCSF scientists describe for the first time how the protein, known as GATA3 — which is abnormal or absent in many cases of human breast cancer — normally acts downstream in biochemical pathways to prevent the distant spread of cancer, an event called ...
Less invasive treatment may increase survival in early stage breast cancer
2013-01-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- Patients with early stage breast cancer who are treated with lumpectomy plus radiation have a better chance of survival compared with those who undergo mastectomy, according to Duke Medicine research.
The study, which appears online Jan. 28, 2013, in the journal CANCER, demonstrates the effectiveness of breast-conserving therapies such as lumpectomy, where only the tumor and surrounding tissue are surgically removed.
"Our findings support the notion that less invasive treatment can provide superior survival to mastectomy in stage I or stage II breast ...
Better survival rates seen with lumpectomy compared with mastectomy for early breast cancer
2013-01-28
A new analysis has found that lumpectomy plus radiation for early breast cancer may provide patients with a better chance of survival than mastectomy. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the results provide confidence in the efficacy of breast-conserving treatments even among patients with aggressive, early disease.
Lumpectomy combined with radiation is a good treatment choice for women with early breast cancer; however, over the past 10 years, a growing number of women have been choosing mastectomy even for very small ...
First guidelines for brain amyloid imaging in Alzheimer's released
2013-01-28
CHICAGO, January 28, 2013 – Only recently has it become possible to create high-quality images of the brain plaques characteristic of Alzheimer's disease in living people through positron emission tomography (PET). Even so, questions remain about what can be learned from these PET images and which people should have this test.
To provide guidance for physicians, individuals and families affected by Alzheimer's, and the public, the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) and the Alzheimer's Association have jointly published the first criteria for the ...
Economic analysis finds penicillin, not "the pill," may have launched the sexual revolution
2013-01-28
PThe rise in risky, non-traditional sexual relations that marked the swinging '60s actually began as much as a decade earlier, during the conformist '50s, suggests an analysis recently published by the Archives of Sexual Behavior.
"It's a common assumption that the sexual revolution began with the permissive attitudes of the 1960s and the development of contraceptives like the birth control pill," notes Emory University economist Andrew Francis, who conducted the analysis. "The evidence, however, strongly indicates that the widespread use of penicillin, leading to a rapid ...