(Press-News.org) Boston, MA – Having adequate levels of vitamin D during young adulthood may reduce the risk of adult-onset type 1 diabetes by as much as 50%, according to researchers at Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH). The findings, if confirmed in future studies, could lead to a role for vitamin D supplementation in preventing this serious autoimmune disease in adults. The study was published online February 3, 2013 and will appear in the March 1 print edition of the American Journal of Epidemiology.
"It is surprising that a serious disease such as type 1 diabetes could perhaps be prevented by a simple and safe intervention," said lead author Kassandra Munger, research associate in the Department of Nutrition at HSPH.
This study provides the strongest findings to date to suggest that vitamin D may be protective against type 1 diabetes.
In type 1 diabetes (once called juvenile-onset or insulin-dependent diabetes), the body's immune system attacks and permanently disables the insulin-making cells in the pancreas. About 5% of the estimated 25.8 million people in the United States with diabetes have type 1, according to the American Diabetes Association. Although it often starts in childhood, about 60% of type 1 diabetes cases occur after age 20.
Previous studies have suggested that a shortage of vitamin D might boost type 1 diabetes risk, although those studies mostly examined the link between vitamin D levels in pregnancy or childhood and the risk of type 1 diabetes in children. Other research, in young adults, uncovered an association between high vitamin D levels and a lowered risk of multiple sclerosis—an autoimmune disease genetically and epidemiologically related to type 1 diabetes—suggesting that inadequate vitamin D in adulthood may be an important risk factor for autoimmune diseases in general.
Long-term study of military personnel
The researchers conducted a prospective case-control study of U.S. military personnel on active duty, using blood samples from the Department of Defense Serum Repository, which contains more than 40 million samples collected from 8 million military personnel since the mid-1980s. Identifying 310 individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes between 1997 and 2009, the team examined blood samples taken before onset of the disease, and compared the samples with those of 613 people in a control group.
The researchers found that white, non-Hispanic, healthy young adults with higher serum levels (>75 nmol/L) of vitamin D had about half the risk of developing type 1 diabetes than those with the lowest levels of vitamin D ( END
Low vitamin D levels may increase risk of Type 1 diabetes
2013-02-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate change impacts to US coasts threaten public health, safety and economy
2013-02-05
According to a new technical report, the effects of climate change will continue to threaten the health and vitality of U.S. coastal communities' social, economic and natural systems. The report, Coastal Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerabilities: a technical input to the 2013 National Climate Assessment, authored by leading scientists and experts, emphasizes the need for increased coordination and planning to ensure U.S. coastal communities are resilient against the effects of climate change.
The recently-released report examines and describes climate change impacts on ...
Scientists find a key element of lupus, suggesting better drug targets
2013-02-05
LA JOLLA, CA – February 4, 2013 – A team led by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) has identified specific cellular events that appear key to lupus, a debilitating autoimmune disease that afflicts tens of millions of people worldwide. The findings suggest that blocking this pathway in lupus-triggering cells could be a potent weapon against the disease.
In the new study, described in an online Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences the week of February 4, 2013, the researchers determined that the absence of a certain type ...
Polar bear researchers urge governments to act now and save the species
2013-02-05
(Edmonton) A University of Alberta polar bear researcher along with eleven international co-authors are urging governments to start planning for rapid Arctic ecosystem change to deal with a climate change catastrophe for the animals.
U of A professor Andrew Derocher co-authored a policy perspective in the journal Conservation Letters urging governments with polar bear populations to accept that just one unexpected jump in Arctic warming trends could send some polar bear populations into a precipitous decline.
"It's a fact that early sea ice break-up and late ice freeze-up ...
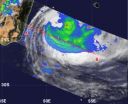
NASA sees the falling of Cyclone Felleng
2013-02-05
Cyclone Felleng traveled through the Mozambique Channel during the week of Jan. 28, 2013 and emerged south into the Southern Indian Ocean where it transitioned into a cold core low pressure area. NASA's TRMM satellite captured a look at the rainfall rates occurring in Felleng as it was making that transition on Feb. 1.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew over Cyclone Felleng on Feb. 1 at 1648 UTC (11:48 a.m. EST) as it was exiting the Mozambique Channel and becoming extra-tropical. TRMM measured a small area of heavy rainfall east of the center ...
Mothers' behavior during playtime linked to young children's engagement with them, researcher says
2013-02-05
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Researchers long have evaluated the roles parents play in children's development. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have found that mothers' directiveness, the extent to which they try to control the content and pace of young children's play, varies based on the children's ages and the mothers' ethnicities. In addition, the study found that the more directive the mothers were during play, the less engaged children were with them and the more negative emotion the children displayed toward their mothers.
"Children flourish when they have opportunities ...
Study finds it actually is better (and healthier) to give than to receive
2013-02-05
BUFFALO, N.Y. – A five-year study by researchers at three universities has established that providing tangible assistance to others protects our health and lengthens our lives.
This, after more than two decades of research failed to establish that the same benefits accrue to the recipients of such help.
Principal investigator Michael J. Poulin, PhD, assistant professor of psychology at the University at Buffalo, says, "This study offers a significant contribution to the research literature on the relationship between social environment and health, and specifically to ...
Benefits of CT outweigh cancer risks in young adults
2013-02-05
OAK BROOK, Ill. – The underlying medical conditions facing young adults who undergo computed tomography (CT) exams represent a significantly greater health risk than that of radiation-induced cancer from CT, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
CT utilization has grown approximately 10 percent annually over the last 15 years in the U.S., raising fears of an increase in radiation-induced cancers. However, discussions of radiation-induced cancer risk often fail to take into account the condition of the patients being imaged, according to ...
Wearable cameras provide new insight into lifestyle behaviors and health
2013-02-05
San Diego, CA, February 5, 2013 – Understanding the relationships between lifestyle behaviors and health outcomes can be enhanced by the use of wearable cameras, concludes a collection of studies in a special theme issue of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine. Three studies report on the latest preventive medicine research using Microsoft's wearable camera, the SenseCam.
"Wearable cameras and their associated software analysis tools have developed to the point that they now appear well suited to measure sedentary behavior, active travel, and nutrition-related ...
Electronic nicotine delivery systems could help reduce smoking
2013-02-05
San Diego, CA, February 5, 2013 – Electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS), or e-cigarettes, debuted in China in 2003 and have since become available globally, particularly through the Internet. While they resemble traditional tobacco cigarettes, they produce fewer toxins in the vapor for the smoker. Still, these novel products have unknown long-term health and addiction consequences, are of varying nicotine content and delivery, and may appeal to nonusers and youth. ENDS have been banned by health authorities in Canada and Australia.
Researchers from the United States, ...
Blowing hot and cold: US belief in climate change shifts with weather
2013-02-05
A University of British Columbia study of American attitudes toward climate change finds that local weather – temperature, in particular – is a major influence on public and media opinions on the reality of global warming.
The study, published today by the journal Climatic Change, finds a strong connection between U.S. weather trends and public and media attitudes towards climate science over the past 20 years – with skepticism about global warming increasing during cold snaps and concern about climate change growing during hot spells.
"Our findings help to explain ...