(Press-News.org) Three NASA satellites are keeping tabs on Typhoon Megi and noticed that it was strengthening in the South China Sea today, but increasing wind shear may again weaken the system over the next couple of days.
NASA's TRMM, CloudSat and Aqua satellite captured images of Megi's clouds, rainfall and eye as they passed over the storm and saw clouds higher than 9 miles filled with ice, creating heavy rainfall.
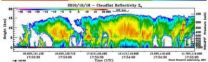
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over Typhoon Megi from its vantage point in space on October 18 at 2321 UTC (7:31 p.m. EDT) and saw that Megi was starting to re-organize after weakening from its encounter with the northern Philippines.
The TRMM team at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. creates rainfall imagery using data from various instruments aboard the satellite. Rain rates in the center of the TRMM swath were created from the TRMM Precipitation Radar (PR), the only spaceborne radar of its kind, while those in the outer portion are from the TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI). To put the image together, the rain rates were then overlaid on infrared data from the TRMM Visible Infrared Scanner. The October 18 TRMM daylight pass showed that Megi's eye was clearer than it was just a few hours earlier and that moderate to heavy rain showers were again completely surrounding the eye indicating it was strengthening at that time.
Also on October 18, NASA's CloudSat satellite passed over Typhoon Megi and the satellite's Cloud Profiling Radar captured a view of the typhoon's clouds from the side. The data gathered from Cloudsat revealed that the cloud tops were over 15 kilometers (9.3 miles) high, and ice was present in them. CloudSat also noticed areas of intense rainfall exceeding 30mm/hr (1.18 inches/hour).
On October 20 at 0530 UTC (1:30 a.m. EDT), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Typhoon Megi as it filled up a large part of the South China Sea. The image revealed an eye filled with high clouds and a very large system.
At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) on October 20, Typhoon Megi's maximum sustained winds had increased to 110 knots (126 mph). It was about 285 nautical miles south-southeast of Hong Kong, China near 18.7 North and 117.2 East. It was moving north at 8 mph (7 knots). Water vapor imagery has shown that its northern edge is eroding from strong upper level westerly winds. Infrared imagery, such as that from NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on the Aqua satellite revealed that deep convection around the northern rim of the eyewall is decreasing indicating a weakening trend.
Typhoon Megi is forecast to make landfall on October 23 east of Hong Kong and then rapidly dissipate as a significant tropical cyclone.
INFORMATION:
3 NASA satellites capture Typhoon Megi strengthening again
2010-10-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
GOES-13 sees system 99L organizing tropically
2010-10-21
The GOES-13 satellite keeps a continuous eye over the eastern U.S., the Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic Ocean, and noticed that System 99L is much better organized today, October 20, hinting that it could become a tropical depression later today.
At 8 a.m. EDT on Wednesday, October 20, System 99L, a low pressure system about 150 miles southwest of Grand Cayman appears to be getting organized as it drifts eastward in the Caribbean Sea.
System 99L is showing more organization than it did yesterday, despite strong upper-level winds that are currently inhibiting ...
New search method tracks down influential ideas
2010-10-21
Princeton computer scientists have developed a new way of tracing the origins and spread of ideas, a technique that could make it easier to gauge the influence of notable scholarly papers, buzz-generating news stories and other information sources.
The method relies on computer algorithms to analyze how language morphs over time within a group of documents -- whether they are research papers on quantum physics or blog posts about politics -- and to determine which documents were the most influential.
"The point is being able to manage the explosion of information made ...
Magic tricks reveal surprising results about autism
2010-10-21
Magicians rely on misdirection—drawing attention to one place while they're carrying out their tricky business somewhere else. It seems like people with autism should be less susceptible to such social manipulation. But a new study in the U.K. finds that people with autism spectrum disorder are actually more likely to be taken in by the vanishing ball trick, where a magician pretends to throw a ball in the air but actually hides it in his hand.
In the vanishing-ball illusion, a magician throws a ball in the air a few times. On the last throw, he merely pretends to throw ...
Exploring Africa's success stories
2010-10-21
Conventional wisdom has long been negative on Africa. Historically, it has been seen as a failing continent, plagued by deep-rooted problems — poverty, corruption, war, and disease. But after four decades of relative stagnation, Africa has been growing rapidly. Since the 1990s, many African countries have seen economic and political improvements, more transparent elections, increased democracy and freedom of press. But these successes are not well understood.
In 2007, the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), the leading nonprofit economics research organization ...
Colorful brains, cooling lasers, disease-detecting lights and more
2010-10-21
WASHINGTON, Oct. 20 -- Scientists and engineers from around the world will gather on the shores of Lake Ontario in Rochester, N.Y. next week to discuss some of the latest breakthroughs in lasers and optics and their applications to cutting-edge science, the development of new materials, and medicine.
Journalists are invited to Frontiers in Optics (FiO) 2010/Laser Science XXVI -- the 94th annual meeting of the Optical Society (OSA), which is being held together with the annual meeting of the American Physical Society (APS) Division of Laser Science at the Rochester Riverside ...
Burn injuries rapidly deplete vitamin E
2010-10-21
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Severe burn injuries in children have been shown to rapidly deplete the levels of vitamin E in their body's adipose, or fat tissues, a new clinical study has found.
Stored levels of this important antioxidant were reduced more in a few weeks than might normally be possible in years.
An analysis of eight children with third-degree burns over much of their body found they lost almost half of their stored vitamin E in three weeks, even though they were being given about 150 percent of the recommended daily allowance of vitamin E and other nutrients in ...
Coral algae (symbiodinium) discovered in black corals at never seen before depths
2010-10-21
Researchers at the Hawai'i Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB), an organized research unit in the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa's School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology have made a remarkable new discovery.
When most people envision coral, they typically think of shallow-water reef-building corals found along beaches and tropical nearshore habitats. These "typical" corals are dependent upon photosynthetic algae (also known as Symbiodinium or zooxanthellae) found in their tissues to obtain nutrients to live off of. In deeper less known waters, closely related ...
Conventional, annual Pap smear cost-effective follow-up after cervical lesion treatment
2010-10-21
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — A study of the options for reducing cancer incidence and mortality among women who have been treated for precancerous cervical lesions found that an annual conventional Pap smear is a cost effective strategy.
Joy Melnikow, professor in the Department of Family and Community Medicine and colleagues tested several follow-up screening strategies for the 500,000 American women diagnosed and treated for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), abnormal cervical cell growth that can lead to cervical cancer. The first comprehensive study of its kind, ...
Researchers develop first implanted device to treat balance disorder
2010-10-21
A University of Washington Medical Center patient on Thursday, Oct. 21, will be the world's first recipient of a device that aims to quell the disabling vertigo associated with Meniere's disease.
The UW Medicine clinicians who developed the implantable device hope that success in a 10-person surgical trial of Meniere's patients will lead to exploration of its usefulness against other common balance disorders that torment millions of people worldwide.
The device being tested – a cochlear implant and processor with re-engineered software and electrode arrays – represents ...
Virtual colonoscopy option could improve colorectal cancer screening rates, patient survey suggests
2010-10-21
Providing computed tomography colonography (CTC) — otherwise known as virtual colonoscopy — as an alternative to conventional colonoscopy could improve colorectal cancer (CRC) screening rates, according to a study in the November issue of the American Journal of Roentgenology (www.ajronline.org).
CRC is the second leading cause of cancer in the U.S. "While colonoscopy is currently the preferred test for CRC screening, the invasive and time-consuming characteristics of the test are often cited as reasons for noncompliance with screening," said Fouad J. Moawad, lead author ...