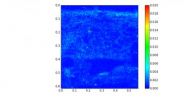
(Press-News.org) Running along the border between the constellations of Canis Major (The Great Dog) and Monoceros (The Unicorn) in the southern sky, the Seagull Nebula is a huge cloud mostly made of hydrogen gas. It's an example of what astronomers refer to as an HII region. Hot new stars form within these clouds and their intense ultraviolet radiation causes the surrounding gas to glow brightly.
The reddish hue in this image is a telltale sign of the presence of ionised hydrogen [1]. The Seagull Nebula, known more formally as IC 2177, is a complex object with a bird-like shape that is made up of three large clouds of gas -- Sharpless 2-292 (eso1237: http://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1237/) forms the "head", this new image shows part of Sharpless 2-296, which comprises the large "wings", and Sharpless 2-297 is a small, knotty addition to the tip of the gull's right "wing" [2].
These objects are all entries in the Sharpless nebula catalogue, a list of over 300 glowing clouds of gas compiled by American astronomer Stewart Sharpless in the 1950s. Before he published this catalogue Sharpless was a graduate student at the Yerkes Observatory near Chicago, USA, where he and his colleagues published observational work that helped to show that the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy with vast, curved arms.
Spiral galaxies can contain thousands of HII regions, almost all of which are concentrated along their spiral arms. The Seagull Nebula lies in one of the spiral arms of the Milky Way. But this is not the case for all galaxies; while irregular galaxies do contain HII regions, these are jumbled up throughout the galaxy, and elliptical galaxies are different yet again -- appearing to lack these regions altogether. The presence of HII regions indicates that active star formation is still in progress in a galaxy.
This image of Sharpless 2-296 was captured by the Wide Field Imager (WFI), a large camera mounted on the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope at ESO's La Silla Observatory in Chile. It shows only a small section of the nebula, a large cloud that is furiously forming hot stars in its interior. The frame shows Sharpless 2-296 lit up by several particularly bright young stars -- there are many other stars scattered across the region, including one so bright that stands out as the gull's "eye" in pictures of the entire complex.
Wide-field images of this region of the sky show a multitude of interesting astronomical objects. The young bright stars within the nebula are part of the nearby star-forming region of CMa R1 in the constellation of Canis Major, which is filled with bright stars and clusters. Also lying close to the Seagull Nebula is the Thor's Helmet Nebula, an object that was imaged using ESO's Very Large Telescope (VLT) on ESO's 50th Anniversary, 5 October 2012, with the help of Brigitte Bailleul -- winner of the Tweet Your Way to the VLT! competition (eso1238a: http://www.eso.org/public/images/eso1238a/).
INFORMATION:
Notes
[1] Astronomers use the term HII to mean ionised hydrogen and HI for atomic hydrogen. A hydrogen atom consists of an electron bound to a proton but in an ionised gas atoms are split into freely moving electrons and positive ions, in this case just single protons.
[2] These objects are officially designated Sh 2-292, Sh 2-296, and Sh 2-297 respectively in the SIMBAD astronomical database.
More information
ESO is the foremost intergovernmental astronomy organisation in Europe and the world's most productive ground-based astronomical observatory by far. It is supported by 15 countries: Austria, Belgium, Brazil, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. ESO carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities enabling astronomers to make important scientific discoveries. ESO also plays a leading role in promoting and organising cooperation in astronomical research. ESO operates three unique world-class observing sites in Chile: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope, the world's most advanced visible-light astronomical observatory and two survey telescopes. VISTA works in the infrared and is the world's largest survey telescope and the VLT Survey Telescope is the largest telescope designed to exclusively survey the skies in visible light. ESO is the European partner of a revolutionary astronomical telescope ALMA, the largest astronomical project in existence. ESO is currently planning the 39-metre European Extremely Large optical/near-infrared Telescope, the E-ELT, which will become "the world's biggest eye on the sky".
Links
Photos of the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope: http://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/search/?adv=&subject_name=mpg
Other photos taken with the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope: http://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/search/?adv=&facility=15
Photos of La Silla: http://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/category/lasilla/
Contacts
Richard Hook
ESO, La Silla, Paranal, E-ELT & Survey Telescopes Press Officer
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6655
Cell: +49 151 1537 3591
Email: rhook@eso.org
The wings of the Seagull Nebula
2013-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study points to possible cause of, and treatment for, non-familial Parkinson's
2013-02-06
New York, NY (February 6, 2013) — Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) researchers have identified a protein trafficking defect within brain cells that may underlie common non-familial forms of Parkinson's disease. The defect is at a point of convergence for the action of at least three different genes that had been implicated in prior studies of Parkinson's disease. Whereas most molecular studies focus on mutations associated with rare familial forms of the disease, these findings relate directly to the common non-familial form of Parkinson's. The study was published ...
X-rays reveal uptake of nanoparticles by soya bean crops
2013-02-06
Scientists have, for the first time, traced the nanoparticles taken up from the soil by crop plants and analysed the chemical states of their metallic elements. Zinc was shown to dissolve and accumulate throughout the plants, whereas the element cerium did not dissolve into plant tissue. The results contribute to the controversial debate on plant toxicity of nanoparticles and whether engineered nanoparticles can enter into the food chain. The study was published on 6 February 2013 in the journal ACS Nano.
The international research team was led by Jorge Gardea-Torresdey ...
Earth-like planets are right next door
2013-02-06
Using publicly available data from NASA's Kepler space telescope, astronomers at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) have found that six percent of red dwarf stars have habitable, Earth-sized planets. Since red dwarfs are the most common stars in our galaxy, the closest Earth-like planet could be just 13 light-years away.
"We thought we would have to search vast distances to find an Earth-like planet. Now we realize another Earth is probably in our own backyard, waiting to be spotted," said Harvard astronomer and lead author Courtney Dressing (CfA).
Dressing ...
Study: Firms that purport to value shareholders pay CEOs more
2013-02-06
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Ever wonder why CEOs at poorly performing companies continue to receive exorbitant pay packages? According to a study from a University of Illinois labor professor, firms that trumpet how much they value shareholders actually pay their CEOs more, regardless of the quality of their performance as executives.
Using compensation data from 290 chief executives at large U.S. firms over an 11-year period, Taekjin Shin, a professor of labor and employment relations at Illinois, shows that CEOs at firms with the appearance of a "shareholder-value orientation" ...
Environmental factors determine whether immigrants are accepted by cooperatively breeding animals
2013-02-06
Cichlid fish are more likely to accept immigrants into their group when they are under threat from predators and need reinforcements, new research shows. The researcher suggests that there are parallels between cooperatively breeding fish's and humans' regulation of immigrants. The research was published today, 6 February 2013, in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
The Princess of Lake Tanganyika (Neolamprologus pulcher), a cichlid fish which is popular in home aquariums, are cooperatively breeding fish with a dominant breeding pair and several 'helper' ...
Nothing fishy about swimming with same-sized mates
2013-02-06
Have you ever wondered why, and how, shoals of fish are comprised of fish of the same size? According to new research by Ashley Ward, from the University of Sydney in Australia, and Suzanne Currie, from Mount Allison University in Canada, fish can use a variety of different sensory cues to locate shoal-mates, but they are able to use chemical cues to find other fish of the same size as themselves. Using these cues, they can form a group with strength in numbers. The work is published online in Springer's journal, Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
Forming groups is ...
Biocontrol research on Brazilian peppertree in Florida discovers new cryptic species
2013-02-06
Dr Michael Pogue, a Research Entomologist in the ARS Systematic Entomology Laboratory, at the Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC, was sent a series of moth specimens from Bahia, Brazil, for identification. The insects were under consideration as a possible biocontrol agent for the invasive Brazilian peppertree in Florida.
'The species was initially identified as a common species, but when comparisons were made, it became evident that there were multiple species involved' said Dr. Pogue. Using characters from the moths' male and female genitalia, Dr. Pogue determined ...
Widely used nanoparticles enter soybean plants from farm soil
2013-02-06
Two of the most widely used nanoparticles (NPs) accumulate in soybeans — second only to corn as a key food crop in the United States — in ways previously shown to have the potential to adversely affect the crop yields and nutritional quality, a new study has found. It appears in the journal ACS Nano.
Jorge L. Gardea-Torresdey and colleagues cite rapid increases in commercial and industrial uses of NPs, the building blocks of a nanotechnology industry projected to put $1 trillion worth of products on the market by 2015. Zinc oxide and cerium dioxide are among today's most ...
Study of a rare disease making people look like a woman but having male genitals under study
2013-02-06
University of Granada researchers have designed a guideline for physicians and patients on the Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS), a rare disease that makes the subject develop reverse sex, which occurs when a subject looks like a woman but has male genes.
AIS has low prevalence (it only affects one in 2000 people), and it is characterized by the inability of tissues to respond to the action of male hormones. This prevents individuals with XY sex hormones (i.e. 46,XY) to develop male genitalia. This disorder is caused by a mutation in the gene that codifies the receptor ...
Being overweight linked to higher risk of gum disease
2013-02-06
CHICAGO (Feb. 6, 2013)—Impacting approximately one-third of the U.S. population, obesity is a significant health concern for Americans. It's a risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain forms of cancer, and now, according to an article published in the January/February 2013 issue of General Dentistry, the peer-reviewed clinical journal of the Academy of General Dentistry (AGD), it also may be a risk factor for gum disease.
"We know that being overweight can affect many aspects of a person's health," says Charlene Krejci, DDS, MSD, lead author ...