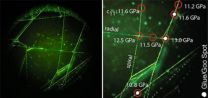
(Press-News.org) Pasadena, CA—Type II supernovae are formed when massive stars collapse, initiating giant explosions. It is thought that stars emit a burst of mass as a precursor to the supernova explosion. If this process were better understood, it could be used to predict and study supernova events in their earliest stages. New observations from a team of astronomers including Carnegie's Mansi Kasliwal show a remarkable mass-loss event about a month before the explosion of a type IIn supernova. Their work is published on February 7 in Nature.
Several models for the supernova-creation process predict pre-explosion outbursts, but it has been difficult for scientists to directly observe this process. Observations of emission lines radiating out form type IIn supernovae are thought to represent interactions between the mass ejected during and prior to the star's explosion
The Palomar Transient Factory team, led by Eran Ofek of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel, observed an energetic outburst from a supernova called SN2010mc that radiated at least 6x1040th joules of energy and released about 2x1028th kilograms (one hundredth of a solar mass). This mass-loss was observed 40 days before the supernova exploded.
"What is surprising is the short time between the precursor eruption and the eventual supernova explosion--one month is an extremely tiny fraction of the ten million-year lifespan of a star," Kasliwal said.
Probability modeling showed that there was only a 0.1 percent chance that the outburst was due to random chance, indicating that the outburst and explosion are likely causally related. At the very least, such outbursts are two orders of magnitude more likely to occur in the immediate run-up to the star's explosion than at other times in a star's life.
By comparing their observations to three proposed models for the mechanism by which this mass is ejected the team they found that one model provided the best match. The high velocities lend credence to the idea that the mass is driven out to the envelope that form's the star's atmosphere by the propagation and dissipation of excited gravity waves, although more work is necessary to confirm this model.
"Our discovery of SN2010mc shows that we can mark the imminent death of a massive star. By predicting the explosion, we can catch it in the act," Kasliwal said.
###
The VLA is operated by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, a facility of the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc. This paper is based on observations obtained with the Samuel Oschin Telescope as part of the Palomar Transient Factory project. The authors acknowledge support from the Arye Dissentshik career development chair, the Helen Kimmel Center for Planetary Science, the Israeli Ministry of Science, the Royal Society, the NSF, the Israeli Science Foundation, the German-Israeli Foundation, ERC, the U.S. Department of Energy, Gary &Cynthia Bengier, the Richard & Rhoda Goldman Fund, the Christopher R. Redlich Fund,and the TABASGO Foundation.
The Carnegie Institution for Science is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.
Forecasting a supernova explosion
2013-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Frequently prescribed drug used in concerning ways with harmful side effects
2013-02-07
TORONTO, Feb. 6, 2013—A popular class of drugs commonly used to treat sleep and mood symptoms continues to be frequently prescribed despite being known to have potentially life-threatening side effects.
Previous studies have linked benzodiazepines – a medication class that may be used in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to treat symptoms of insomnia, depression, anxiety and shortness of breath – with adverse outcomes, but until now there has been little information on how frequently it's prescribed or who is using it.
COPD, also known as emphysema or chronic ...
11,000 elephants slaughtered in national park
2013-02-07
LIBREVILLE, GABON (February 6, 2013): The Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) announced today that a national park, once home to Africa's largest forest elephant population, has lost a staggering 11,100 individuals due to poaching for the ivory trade.
The shocking figures come from Gabon's Minkebe Park, where recent surveys of areas within the park revealed that two thirds of its elephants have vanished since 2004. The majority of these losses have probably taken place in the last five years.
Gabon contains over half of Africa's forest elephants, with a population estimated ...
Children with ACL injuries require special treatment
2013-02-07
Until a child's bones have fully matured (in girls, typically by age 14; in boys, age 16), an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)—the primary, stabilizing ligament of the knee joint—requires special consideration, treatment and care to ensure appropriate healing and to prevent long-term complications.
According to a review article in the February 2013 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (JAAOS), ACL injuries once were considered rare in children and adolescents. However, the number of ACL injuries in young athletes is on the ...
Study: Buying luxury -- hedonistic or just French?
2013-02-07
A young woman in Tokyo pays 243,000 Yen for a Louis Vuitton suitcase emblazoned with the company's iconic monogram. A continent away, another woman purchases the same suitcase at the company's store on New York's 5th Avenue for the equivalent price in dollars, $3000. Why? What motivates their purchases? And, do those motivations hinge on their location?
That is precisely what Professor Jaehee Jung and her collaborators at universities in 9 other countries sought to answer. Their findings published recently in the journal, Psychology & Marketing, compared consumers' ...
Smartphones, tablets help scientists improve storm forecasts
2013-02-07
The next advance in weather forecasting may not come from a new satellite or supercomputer, but from a device in your pocket. University of Washington atmospheric scientists are using pressure sensors included in the newest smartphones to develop better weather forecasting techniques.
"With this approach we could potentially have tens or hundreds of thousands of additional surface pressure observations, which could significantly improve short-term weather forecasts," said Cliff Mass, a UW professor of atmospheric sciences.
Owners of certain new Android smartphones and ...
Happiness increases with age, across generations
2013-02-07
Psychological well-being has been linked to many important life outcomes, including career success, relationship satisfaction, and even health. But it's not clear how feelings of well-being change as we age, as different studies have provided evidence for various trends over time.
A new report published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, reveals that self-reported feelings of well-being tend to increase with age, but that a person's overall level of well-being depends on when he or she was born.
Psychological scientist ...
Tiny capsule effectively kills cancer cells
2013-02-07
A tiny capsule invented at a UCLA lab could go a long way toward improving cancer treatment.
Devising a method for more precise and less invasive treatment of cancer tumors, a team led by researchers from the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science has developed a degradable nanoscale shell to carry proteins to cancer cells and stunt the growth of tumors without damaging healthy cells.
In a new study, published online Feb. 1 in the peer-reviewed journal Nano Today, a group led by Yi Tang, a professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and ...
Personalized health care will revolutionize 21st century medicine, says NJIT professor
2013-02-07
A closer look at personalized or point-of-care healthcare was the focus of a recent international conference in India organized and chaired by NJIT Distinguished Professor Atam Dhawan. The IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS) International Special Topic Conference in point-of-care healthcare technologies, broadcast around the world, focused on topics ranging from 21st century medicine with new smart cross-and trans-disciplinary technologies to how wireless communications will change how physicians care for patients.
"The last century witnessed a ...
Stanford researcher sheds new light on the mysteries of spider silk
2013-02-07
As fibers go, there's never been anything quite like spider silk. Stretch it. Bend it. Soak it. Dry it out. Spider silk holds up. It is five times stronger than steel and can expand nearly a third greater than its original length and snap right back like new. Ounce-for-ounce spider silk is even stronger than Kevlar, the man-made fiber used in bulletproof vests.
It would be understandable to think that science knows all there is to know about the remarkable physics of spider silk, but the truth is far from that. Now, using a long-known-but-underutilized spectroscopy technique, ...
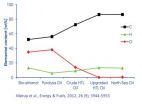
Hydrothermal liquefaction -- the most promising path to a sustainable bio-oil production
2013-02-07
To emphasize, the HTL process accepts all biomasses from modern society – sewage sludge, manure, wood, compost and plant material along with waste from households, meat factories, dairy production and similar industries.
It is by far the most feedstock flexible of any liquid fuel producing process, including pyrolysis, bio-ethanol, gasification with Fischer-Tropsch or catalytic upgrading of different vegetable or agro-industrial residual oils, and does not carry higher costs than these.
Hydrothermal liquefaction is basically pressure cooking, but instead of cooking the ...