(Press-News.org) Edmonton—Ever wonder how sometimes people still get through security with explosives on their person? Research done in the University of Alberta's Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering has revealed a new way to better detect these molecules associated with explosive mixtures.
A team of researchers including post-doctoral fellows Seonghwan Kim, Dongkyu Lee and Xuchen Liu, with research associate Charles Van Neste, visiting professor, Sangmin Jeon from the Pohang University of Science and Technology (South Korea), and Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering professor Thomas Thundat, has found a method of using receptor-free nanomechanical infrared spectroscopy to increase recognition of chemical molecules in explosive mixtures.
Detecting trace amounts of explosives with mixed molecules presents a formidable challenge for sensors with chemical coatings. The nanomechanical infrared spectroscopy used by the Univesity of Alberta research team provides higher selectivity in molecular detection by measuring the photothermal effect of the absorbed molecules.
Thundat, who holds the Canadian Excellence Research Chair in Oil Sands Molecular Engineering, says the spectroscopy looks at the physical nature of the molecule and "even if there are mixed molecules, we can detect specific molecules using this method."
Seonghwan (Sam) Kim explained that conventional sensors based on coatings generally cannot detect specific molecules in complex mixtures if the concentration of interfering molecules is five times greater than the target molecules. The detection sensitivity and selectivity are drastically increased using the high-power infrared laser because the photothermal signal comes from the absorption of infrared photons and nonradiative decay processes. Using this method, a few trillionths of a gram of explosive molecules can now be detected in a complex mixture even if there is a higher concentration of other interfering molecules.
The research team's findings are published in Scientific Reports by Nature Publishing Group on January 23, 2013.
The research team's current work looks at detecting biomolecules and hydrocarbons in the oil industry and nerve gas stimulants (DMMP), which can be found in household radiators, gasoline, and fabric softeners, for example. The team also hopes to develop a hand-held device for chemical detection that could be utilized in fields such as security, health care and environmental protection.
### END
Explosive breakthrough in research on molecular recognition
Researchers discover new detection technique
2013-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lower autism risk with folic acid supplements in pregnancy
2013-02-13
Women who took folic acid supplements in early pregnancy almost halved the risk of having a child with autism. Beginning to take folic acid supplements later in pregnancy did not reduce the risk. This is shown in new findings from the ABC Study and Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study published in the Journal of The American Medical Association (JAMA).
Women who took folic acid supplements from four weeks before conception to eight weeks into pregnancy had a 40 per cent lower risk of giving birth to children with childhood autism (classic autism). Use of folic acid ...
NASA sees Cyclone Gino wind up to wind down later
2013-02-13
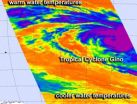
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Cyclone Gino as the storm continues to wind up in the southern Indian Ocean, consolidating and strengthening. Infrared data shows the storm has strengthened but it is headed for cooler waters which will weaken it in coming days.
On Feb. 12 at 0841 UTC, NASA Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard the Aqua satellite captured infrared imagery of Cyclone Gino that showed the storm developed a large area of very cold, high cloud top temperatures around its center indicating powerful thunderstorms. Cloud top temperatures ...
NASA provides satellite views of nor'easter lifespan
2013-02-13
NASA and NOAA satellites have provided animations and images of the coupling of two low pressure areas that created the now historic winter-time nor'easter that brought more than two feet of snow to portions of the New England states on Feb. 8 and 9, 2013. NASA released an animation of NOAA satellite imagery that shows the lifetime of the historic nor'easter.
The nor'easter dropped between 2 and 3 feet of snowfall over the U.S. Northeast and left more than 650,000 without power in eight states, according to the Associated Press. Several governors established travel bans ...
NASA satellites find freshwater losses in Middle East
2013-02-13
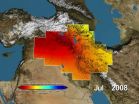
A new study using data from a pair of gravity-measuring NASA satellites finds that large parts of the arid Middle East region lost freshwater reserves rapidly during the past decade.
Scientists at the University of California, Irvine; NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.; and the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colo., found during a seven-year period beginning in 2003 that parts of Turkey, Syria, Iraq and Iran along the Tigris and Euphrates river basins lost 117 million acre feet (144 cubic kilometers) of total stored freshwater. That ...
Gaps in mental health infrastructure for youth identified in many US communities
2013-02-13
ATLANTA- Mental health facilities that provide outpatient specialty services for youth are a critical element of the mental health care infrastructure, especially for youth who are uninsured or publically insured.
In a Viewpoint article in the February 13 issue of JAMA, Janet Cummings, PhD, assistant professor of health policy and management at Emory's Rollins School of Public Health, presents data from the 2008 National Survey of Mental Health Treatment Facilities and examines the extent to which gaps exist in the mental health treatment system for youth.
Based ...
In some dystonia cases, deep brain therapy benefits may linger after device turned off
2013-02-13
LOS ANGELES (Feb. 12, 2013) – Two patients freed from severe to disabling effects of dystonia through deep brain stimulation therapy continued to have symptom relief for months after their devices accidentally were fully or partly turned off, according to a report published online Feb. 11 in the journal Movement Disorders.
"Current thought is that symptoms will worsen within hours or days of device shut-off, but these two young men continued to have clinical benefit despite interruption of DBS therapy for several months. To our knowledge, these two cases represent the ...
Novel test streamlines testing for Huntington Disease
2013-02-13
Philadelphia, PA, February 13, 2013 – A new test may help to streamline genetic testing for Huntington Disease (HD) by generating accurate results, avoiding unnecessary additional testing, and improving turnaround time. The test, which uses chimeric or triplet repeat primed PCR (TP PCR) methodology, yielded results that were 100% concordant with standard genotyping methods in an analysis of 246 samples. The high sensitivity and specificity of the test could reduce the number of false negative results and facilitate both diagnosis and prognosis by correctly sizing the genetic ...
Scientists should advance management of behavioral norms
2013-02-13
Researchers should study how people's social and personal norms are influenced by behavior and use their insights to help governments promote pro-environmental actions, a distinguished group of scholars writes in the March issue of BioScience. The authors maintain that effective policies induce not only short-term changes in behavior but also long-term changes in norms. More effective management of social norms will be necessary, they write, to persuade the public to accept the inconvenience and expense of many environmental policies.
The interdisciplinary group, led by ...
Colorado DUI checkpoints lead to over 1,300 arrests in one weekend
2013-02-13
Colorado DUI checkpoints lead to over 1,300 arrests in one weekend
Article provided by James L. Finegan, P.C.
Visit us at http://www.fineganduilaw.com
The Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT) reports that over 26,000 people in the state are arrested for driving under the influence, or DUI, every year. These arrests are not just from enforcement officers pulling over obviously impaired drivers or issuing tickets after an accident, but also the result of officers testing drivers at DUI checkpoints.
The state uses these checkpoints throughout the year, often ...
Slips, trips and falls: Serious hazard for nursing home residents
2013-02-13
Slips, trips and falls: Serious hazard for nursing home residents
Article provided by Ginsberg & Katsorhis, P.C.
Visit us at http://www.gkf-law.com
When we must place a loved one in the care of a nursing home, we must rely on the facility to protect the physical safety of the resident from a wide range of potential hazards. Falls are one of the most common risks to a resident's safety in these environments.
In fact, recent research from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration has revealed that nursing homes are also especially hazardous for the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Explosive breakthrough in research on molecular recognitionResearchers discover new detection technique