(Press-News.org) Chagas disease, a deadly tropical infection caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi and transmitted by biting insects called "kissing bugs," has begun to spread around the world, including the U.S. Yet current treatment is toxic and limited to the acute stage.
In The Journal of Infectious Diseases (JID), Galina Lepesheva, Ph.D., and her colleagues at Vanderbilt University and Meharry Medical College report curing both the acute and chronic forms of the infection in mice with a small molecule, VNI.
VNI specifically inhibits a T. cruzi enzyme essential for cell multiplication and integrity. In mouse models of Chagas disease, VNI achieved cures with 100 percent survival and without toxic side effects.
The discovery "represents a possible new way to combat a serious worldwide threat, for which there are currently few good therapeutic options," said Richard Okita, Ph.D., of the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which helped support the research.
About 8 million people have been infected by T. cruzi, mostly in Latin America, but kissing bugs have been found across the southern United States, according to a recent report.
Because the parasite is in the insect's feces, it can also be transmitted through contaminated food and drink, through blood and from mother to child.
The most common symptom of the acute phase of the infection is fever, but the parasite also can trigger inflammation of the heart and brain, which can be fatal. In the chronic phase, Chagas disease most severely affects the heart and gastrointestinal tract.
###Fernando Villalta, Ph.D., chair of Microbiology and Immunology at Meharry, is first author on the paper published in JID. Lepesheva, research associate professor of Biochemistry at Vanderbilt and a member of the Vanderbilt Institute for Global Health, is corresponding author.
Other senior authors from Vanderbilt are Jeffrey Johnston, Ph.D., Stevenson Professor of Chemistry, and Michael Waterman, Ph.D., professor of Biochemistry, emeritus, and former chair of the department.
The research was supported by NIH grant GM067871, by a pilot project grant from the Vanderbilt Institute of Chemical Biology, and in part by NIH grants GM084333 and AI080580.
*Attached photo of kissing bug courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Cure in sight for kissing bug's bite
2013-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cleveland Clinic develops clinical screening program for no.1 genetic cause of colon cancer
2013-02-14
Wednesday, February 13, 2013, Cleveland: Cleveland Clinic researchers have found that colorectal cancer outcomes could be improved with regular genetic screening for Lynch syndrome, the most common hereditary, adult-onset cause of colorectal cancer, as published in the online version of the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Lynch syndrome is the most common genetic cause of colon cancer in adults. The study found that a universal screening program of all colorectal cancers surgically removed at Cleveland Clinic resulted in increased identification of Lynch syndrome patients ...
A little molecule's remarkable feat -- prolonging life
2013-02-14
NEW YORK, Feb. 14, 2013 – Nitric oxide, the versatile gas that helps increase blood flow, transmit nerve signals, and regulate immune function, appears to perform one more biological feat— prolonging the life of an organism and fortifying it against environmental stress, according to a new study.
The study reveals that a roundworm called Caenorhabditis elegans, an animal widely used in laboratory studies of aging, lives significantly longer when fed bacteria capable of manufacturing nitric oxide. The tantalizing observation points to one of the mechanisms by which the ...
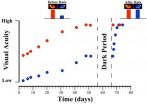
Vision restored with total darkness
2013-02-14
Restoring vision might sometimes be as simple as turning out the lights. That's according to a study reported on February 14 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, in which researchers examined kittens with a visual impairment known as amblyopia before and after they spent 10 days in complete darkness.
Researchers Kevin Duffy and Donald Mitchell of Dalhousie University in Canada believe that exposure to darkness causes some parts of the visual system to revert to an early stage in development, when there is greater flexibility.
"There may be ways to increase ...
New study of the molecular roots of recurrent bladder infections could lead to a vaccine
2013-02-14
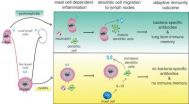
Urinary-tract infections are the second most common bacterial infection in humans, and many of them are recurrent. A study published by Cell Press on February 14th in the journal Immunity reveals the cellular and molecular basis of recurrent bladder infections and suggests possible treatment strategies, such as vaccines, to prevent this common problem.
"Our study shows for the first time that the bladder is unable to mount an effective immune response to bacteria, which could explain the high frequency of recurrent infections," says senior study author Soman Abraham ...
Roots of language in human and bird biology
2013-02-14
BOSTON, MA -- The genes activated for human speech are similar to the ones used by singing songbirds, new experiments suggest.
These results, which are not yet published, show that gene products produced for speech in the cortical and basal ganglia regions of the human brain correspond to similar molecules in the vocal communication areas of the brains of zebra finches and budgerigars. But these molecules aren't found in the brains of doves and quails -- vocal birds that do not learn their sounds.
"The results suggest that similar behavior and neural connectivity for ...
2 Cell studies reveal genetic variation driving human evolution
2013-02-14
VIDEO:
A pair of studies published by Cell Press on February 14th in the journal Cell sheds new light on genetic variation that may have played a key role in human...
Click here for more information.
A pair of studies published by Cell Press on February 14th in the journal Cell sheds new light on genetic variation that may have played a key role in human evolution. The study researchers used an animal model to study a gene variant that could have helped humans adapt to humid ...
Bilingual babies know their grammar by 7 months
2013-02-14
Babies as young as seven months can distinguish between, and begin to learn, two languages with vastly different grammatical structures, according to new research from the University of British Columbia and Université Paris Descartes.
Published today in the journal Nature Communications and presented at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) in Boston, the study shows that infants in bilingual environments use pitch and duration cues to discriminate between languages – such as English and Japanese – with opposite word ...
First animal model of recent human evolution
2013-02-14
The first animal model of recent human evolution reveals that a single mutation produced several traits common in East Asian peoples, from thicker hair to denser sweat glands, an international team of researchers reports.
The team, led by researchers from Harvard Medical School, Harvard University, the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Massachusetts General Hospital, Fudan University and University College London, also modeled the spread of the gene mutation across Asia and North America, concluding that it most likely arose about 30,000 years ago in what is today ...
Defect in immune memory may cause repeat bladder infections
2013-02-14
DURHAM, N.C. – Recurrent bladder infections, which are especially common among women, may result from a defect among the bladder's immune fighters that keeps them from remembering previous bacterial infections. The immune memory lapse can hamper a timely and effective attack, according to researchers at Duke Medicine and Duke-National University of Singapore.
Their study, which involved mice, may provide a new route to develop vaccines and treatments for urinary tract infections, which are the second-most common infection and account for more than 8 million health care ...
Discovery in HIV may solve efficiency problems for gene therapy
2013-02-14
A research team from Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine has discovered an approach that could make gene therapy dramatically more effective for patients.
Led by professor Eric Arts, PhD, the scientists discovered that the process of gene therapy is missing essential elements thereby reducing the effectiveness of this treatment. Re-introducing this element into their model system suggests that improvements for gene therapy areon the horizon.
The findings are detailed in the article, "A new genomic RNA packaging element in retroviruses and the interplay ...