(Press-News.org) BUFFALO, N.Y. – University at Buffalo engineers have created a more efficient way to catch rainbows, an advancement in photonics that could lead to technological breakthroughs in solar energy, stealth technology and other areas of research.
Qiaoqiang Gan, PhD, an assistant professor of electrical engineering at UB, and a team of graduate students described their work in a paper called "Rainbow Trapping in Hyperbolic Metamaterial Waveguide," published Feb. 13 in the online journal Scientific Reports.
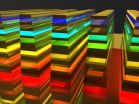
They developed a "hyperbolic metamaterial waveguide," which is essentially an advanced microchip made of alternate ultra-thin films of metal and semiconductors and/or insulators. The waveguide halts and ultimately absorbs each frequency of light, at slightly different places in a vertical direction (see image at http://www.buffalo.edu/news/releases/2013/02/016.html), to catch a "rainbow" of wavelengths.
Gan is a researcher within UB's new Center of Excellence in Materials Informatics.
"Electromagnetic absorbers have been studied for many years, especially for military radar systems," Gan said. "Right now, researchers are developing compact light absorbers based on optically thick semiconductors or carbon nanotubes. However, it is still challenging to realize the perfect absorber in ultra-thin films with tunable absorption band.
"We are developing ultra-thin films that will slow the light and therefore allow much more efficient absorption, which will address the long existing challenge."
Light is made of photons that, because they move extremely fast (i.e., at the speed of light), are difficult to tame. In their initial attempts to slow light, researchers relied upon cryogenic gases. But because cryogenic gases are very cold – roughly 240 degrees below zero Fahrenheit – they are difficult to work with outside a laboratory.
Before joining UB, Gan helped pioneer a way to slow light without cryogenic gases. He and other researchers at Lehigh University made nano-scale-sized grooves in metallic surfaces at different depths, a process that altered the optical properties of the metal. While the grooves worked, they had limitations.
For example, the energy of the incident light cannot be transferred onto the metal surface efficiently, which hampered its use for practical applications, Gan said.
The hyperbolic metamaterial waveguide solves that problem because it is a large area of patterned film that can collect the incident light efficiently. It is referred to as an artificial medium with subwavelength features whose frequency surface is hyperboloid, which allows it to capture a wide range of wavelengths in different frequencies including visible, near-infrared, mid-infrared, terahertz and microwaves.
It could lead to advancements in an array of fields.
For example, in electronics there is a phenomenon known as crosstalk, in which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. The on-chip absorber could potentially prevent this.
The on-chip absorber may also be applied to solar panels and other energy-harvesting devices. It could be especially useful in mid-infrared spectral regions as thermal absorber for devices that recycle heat after sundown, Gan said.
Technology such as the Stealth bomber involves materials that make planes, ships and other devices invisible to radar, infrared, sonar and other detection methods. Because the on-chip absorber has the potential to absorb different wavelengths at a multitude of frequencies, it could be useful as a stealth coating material.
INFORMATION:
Additional authors of the paper include Haifeng Hu, Dengxin Ji, Xie Zeng and Kai Liu, all PhD candidates in UB's Department of Electrical Engineering. The work was sponsored by the National Science Foundation and UB's electrical engineering department.
To view this story online, with downloadable images, go to www.buffalo.edu/news.
Forget about leprechauns, engineers are catching rainbows
By creating a material that slows light, engineers open new possibilities in solar energy, military technology and other fields of research
2013-02-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
IOM 'Evaluation of PEPFAR' to release Feb. 20
2013-02-16
Evaluation of PEPFAR, a new report from the Institute of Medicine, presents the results of an assessment of the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief as requested by Congress in its reauthorization of funding for the initiative in 2008. The report includes recommendations for how PEPFAR and its partner countries can most effectively sustain and advance gains made in preventing and treating the HIV/AIDS epidemic worldwide. Congress will review the initiative later this year.
The report will be released at a public briefing starting at 9 a.m. EST Wednesday, Feb. 20 ...
Early education closes achievement gap, brings societal benefits
2013-02-16
The founder of a decades-long scientific study that has proved the enduring benefits of early education today (Feb. 15, 2013) applauded President Barack Obama's recent call for universal access to high-quality preschool in the United States.
"Investing in high-quality early education has dramatic and sustained payoffs not just for the children directly involved, but for society as well," said Craig Ramey, Ph.D., the originator and founding principal investigator of the Abecedarian Project, a scientific study of the potential benefits of early childhood education for economically ...
Is there a Neanderthal in the house?
2013-02-16
Bunions bothering you? How about lower back pain, or impacted wisdom teeth?
As we humans evolved over the millennia to walk on two legs, grow larger brains and shorter jaws, bear big babies and live longer, we've also experienced some negative consequences on our way to becoming the world's most successful primate, at nearly 7 billion strong.
But keeping our evolutionary history in mind can help us better deal with issues from obesity to difficult childbirth in a much more productive way, according to Karen Rosenberg, professor and chair of the Department of Anthropology ...
Novel herbal compound offers potential to prevent and treat Alzheimer's disease
2013-02-16
Amsterdam, NL, February 15, 2013 – Administration of the active compound tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside (TSG) derived from the Chinese herbal medicine Polygonum multiflorum Thunb, reversed both overexpression of α-synuclein, a small protein found in the brain, and its accumulation using a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. These results, which may shed light on the neuropathology of AD and open up new avenues of treatment, are available in the current issue of Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience.
Aberrant accumulation of α-synuclein can form insoluble aggregates ...
Research shows long-term effects of traumatic brain injury
2013-02-16
Research shows long-term effects of traumatic brain injury
Article provided by B. L. Jensen, L.P.
Visit us at http://www.bjensenlaw.com
In recent years, researchers and health care providers have been devoting increased attention to the long-term effects of traumatic brain injuries, or TBIs. In the past, it was thought that most TBIs cleared up on their own with no lasting consequences. However, modern research has revealed that even relatively mild TBIs often result in physical and cognitive problems that may persist for years after the initial injury.
A traumatic ...
Getting to yes: five ways to improve your SSDI claim
2013-02-16
Getting to yes: five ways to improve your SSDI claim
Article provided by The Bollinger Law Firm, P.C.
Visit us at http://www.bollingerlawfirmnc.com
Permanent disability can cause devastating economic results and significant changes to your ability to work (or end it altogether). To assist in these cases, Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), managed by the Social Security Administration (SSA), was created to provide life-long financial support to workers who become disabled.
Although SSDI benefits are designed to help, the application process can be frustrating, ...
Sleeping in car can result in DWI charge
2013-02-16
Sleeping in car can result in DWI charge
Article provided by Glenn R. Bruno, Esq.
Visit us at http://www.hudsonvalleycriminallaw.com
New York residents know a DWI charge comes with devastating consequences. Along with hefty fines and potential jail time, a DWI charge results in a significant loss of freedom. A driver's license is normally suspended or revoked, and installation of an ignition interlock device is usually required.
Man charged with DWI after found sleeping in car
Recently, a 48-year-old man was charged with a DWI after officers found him sleeping ...
California grandparents can take steps to continue relationships
2013-02-16
California grandparents can take steps to continue relationships
Article provided by Lerner o Poole, LLP
Visit us at http://www.cafamilylaw.com/
Like in most states, grandparents in California do not automatically have custody or visitation rights over their grandchildren. In the event a grandparent wishes to be awarded either custody or visitation, they must receive an order from the court. Of course, there are several different factors the court will consider in determining whether such arrangements will be allowed.
When can a grandparent request visitation?
When ...
Surge in student debt prompts Congress to reconsider bankruptcy laws
2013-02-16
Surge in student debt prompts Congress to reconsider bankruptcy laws
Article provided by John Christopher Robinson
Visit us at http://www.debtfreeky.com
Go to college, get a good job. Unfortunately, this old maxim may no longer hold true. In these tough economic times getting a college degree does not always lead to a job, let alone a good one.
The national unemployment rate continues to hover around 8 percent and college graduates are struggling to find employment after graduation. Unemployment rates for college graduates over 25 were estimated at 4.1 percent ...
Divorce and finances, bankruptcy may offer a fresh start
2013-02-16
Divorce and finances, bankruptcy may offer a fresh start
Article provided by John Christopher Robinson
Visit us at http://www.debtfreeky.com
When a couple gets a divorce, most property accumulated by the couple is divided. This includes any debts accumulated by the couple. This can lead to financial stresses in a number of ways. The most common stressor comes from the fact that the same amount of money now needs to support two households. Additional issues can arise if accounts were not properly managed during the divorce process.
If, for example, confusion existed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
[Press-News.org] Forget about leprechauns, engineers are catching rainbowsBy creating a material that slows light, engineers open new possibilities in solar energy, military technology and other fields of research