(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS -- Advances in electronic medical record systems and health information exchange are shifting efforts in public health toward greater use of information systems to automate disease surveillance, but a study from the Regenstrief Institute has found that these technologies' capabilities are underutilized by those on the front lines of preventing and reporting infections.
The new study measured the awareness, adoption and use of electronic medical record systems and health information exchange by hospital-based infection preventionists (formerly known as infection control professionals) to report and share information critical to public health. Infection preventionists are often responsible for reporting information on patients diagnosed with health-care-acquired infections like Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or MRSA, as well as sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia.
Prior research at Regenstrief and other academic institutions has shown that health information exchange can increase the completeness and timeliness of infection reporting to local and state health agencies. In this study, the researchers found that half of the infection preventionists surveyed were unaware of whether their hospital or health system participated in a health information exchange. Only 10 percent of infection preventionists indicated that their organizations were formally engaged in health information exchange activities.
While 70 percent of infection preventionists surveyed reported access to an electronic medical record system, less than 20 percent were involved in the design, selection or implementation of the system. Without such involvement, those surveyed indicated the information systems often did not include modules or components that supported infection control activities.
"There is a push from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to reduce hospital-acquired infections and increase the use of electronic health record systems," said lead author Brian Dixon, MPA, Ph.D., Regenstrief Institute investigator and assistant professor in the School of Informatics and Computing at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis. "The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are encouraging local and state health departments to use health information technologies to improve infectious disease reporting and prevention activities. We found that while hospital-based infection preventionists -- the people on the front line -- may have access to health information technology, they lack specially designed computer tools needed to sift through the massive amounts of data in electronic medical records.
"We learned that hospital infection preventionists are frustrated with inefficient lists of patients whose electronic medical charts they must examine individually," said Dr. Dixon, who is also a health research scientist with the Richard Roudebush Veterans Affairs Medical Center. "They say they want electronic alerts and reminders when the system detects something of potential importance. There needs to be concerted R&D to meet this gap in decision support."
In addition to Dr. Dixon, co-authors of the study are Josette Jones, Ph.D., of the School of Informatics and Computing; and Shaun Grannis, M.D., M.S., of the Regenstrief Institute and the IU School of Medicine. The Regenstrief Institute is the home of internationally recognized centers of excellence in biomedical and public health informatics, aging, and health services and health systems research.
"Infection Preventionists' Awareness of and Engagement in Health Information Exchange to Improve Public Health Surveillance" was published online on Feb. 18 in the American Journal of Infection Control. The study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
"Well-designed and supported electronic medical records systems and health information exchange can provide tools that can help prevent and halt the spread of infection among hospitalized patients," Dr. Dixon said. "But to do so effectively, infection preventionists must be made part of the selection and implementation of health information technologies."
INFORMATION:
Regenstrief study: Informatics tools underutilized in prevention of hospital-acquired infection
2013-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
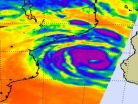
3 NASA satellites see wide-eyed Cyclone Haruna
2013-02-21
VIDEO:
The TRMM satellite flew above Haruna on Feb. 20 at 0717 UTC. Some powerful storms Haruna's northern edge showed rainfall over 108 mm (~4.25 inches) per hour and cloud tops...
Click here for more information.
Cyclone Haruna strengthened into a cyclone and quickly developed an eye that became apparent on visible and infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite. NASA's TRMM satellite analyzed Haruna's heavy rainfall, and NASA and NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a ...
Low-pitched song indicates fairy-wren size
2013-02-21
AUDIO:
This is an example of a trill song type that tells listeners how big the singer is. Their larger physical size means that bigger male purple-crowned fairy-wrens can sing this...
Click here for more information.
A male fairy-wren's low pitch song indicates body size, a new international study has shown.
The study led by University of Melbourne researcher Dr Michelle Hall, is the first to show that the larger the male fairy wren, the lower the pitch of his song.
"This ...
Genome-wide imaging study identifies new gene associated with Alzheimer's plaques
2013-02-21
INDIANAPOLIS -- A study combining genetic data with brain imaging, designed to identify genes associated with the amyloid plaque deposits found in Alzheimer's disease patients, has not only identified the APOE gene -- long associated with development of Alzheimer's -- but has uncovered an association with a second gene, called BCHE.
A national research team, led by scientists at the Indiana University School of Medicine, reported the results of the study in an article in Molecular Psychiatry posted online Tuesday. The study is believed to be the first genome-wide association ...
Researchers say sunlight yields more efficient carbon dioxide to methanol model
2013-02-21
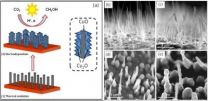
Researchers from The University of Texas at Arlington are pioneering a new method for using carbon dioxide, or CO2, to make liquid methanol fuel by using copper oxide nanowires and sunlight.
The process is safer, simpler and less expensive than previous methods to convert the greenhouse gas associated with climate change to a useful product, said Krishnan Rajeshwar, interim associate vice president for research at UT Arlington and one of the authors of a paper recently published in the journal Chemical Communications. Researchers began by coating the walls of copper oxide, ...
A simple view of gravity does not fully explain the distribution of stars in crowded clusters
2013-02-21
Gravity remains the dominant force on large astronomical scales, but when it comes to stars in young star clusters the dynamics in these crowded environments cannot be simply explained by the pull of gravity.
After analyzing Hubble Space Telescope images of star cluster NGC 1818 in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, researchers at the Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics (KIAA) at Peking University in Beijing found more binary star systems toward the periphery of cluster than in the center – the opposite of what they expected. The ...
Background checks, permanent records needed for all firearm transfers, not just gun sales by retailers
2013-02-21
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — Gun violence in the United States can be substantially reduced if Congress expands requirements for background checks on retail gun sales to cover firearm transfers between private parties, a new report by the director of the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Program concludes.
The report "Background Checks for Firearm Transfers" by Garen Wintemute, who also serves as a professor of emergency medicine, notes that 40 percent of U.S. gun transactions occur between unlicensed private parties, such as people buying and selling at gun shows. That ...
Employees shed pounds in worksite-based weight loss intervention with behavioral counseling
2013-02-21
BOSTON (Wednesday, February 20, 2013)- Workplace-based programs that include dietary advice coupled with behavioral counseling appear to be a promising approach for men and women with significant weight loss goals, based on the results of a pilot study conducted by researchers at the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging (HNRCA) at Tufts University. Employees enrolled in the intervention arm of a randomized controlled trial lost on average, 18 pounds over a six-month period compared to a two pound weight gain in a control group. The study results ...
Perceptions of health improve with pension receipt, researcher says
2013-02-21
COLUMBIA, Mo. – After retirement, pensions provide consistent income to aging individuals. Although the details of pension eligibility and implementation vary by country, receiving pensions can represent a new life stage for individuals. Now, a University of Missouri researcher has studied how older men and women view their health before and after receiving fixed incomes. South African men and women in the study viewed their health more positively when they began receiving their pensions, but the heightened sense of well-being faded over time.
"We looked at individuals' ...
Signaling pathway linked to fetal alcohol risk
2013-02-21
Fetal alcohol syndrome is the leading preventable cause of developmental disorders in developed countries. And fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD), a range of alcohol-related birth defects that includes fetal alcohol syndrome, is thought to affect as many as 1 in 100 children born in the United States.
Any amount of alcohol consumed by the mother during pregnancy poses a risk of FASD, a condition that can include the distinct pattern of facial features and growth retardation associated with fetal alcohol syndrome as well as intellectual disabilities, speech and language ...
Scientists publish analysis of algae parasite impact on algae biofuel in PLOS ONE
2013-02-21
SAN DIEGO, February 20, 2013 – As part of an ongoing effort to improve commercial scale algae biofuel production, a group of scientists, led by crude oil producer Sapphire Energy, Inc., today announced the completion of a collaborative study which identified the morphology, ultrastructure, and life history of A. protococcarum, one of the most difficult to manage algae parasites. Their findings are detailed in "Characterization of Amoeboaphelidium protococcarum: An Algal Parasite New to the Cryptomycota Isolated from an Outdoor Algal Pond Used for the Production of Biofuel," ...