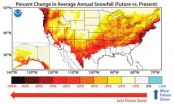
(Press-News.org) A new climate model predicts an increase in snowfall for the Earth's polar regions and highest altitudes, but an overall drop in snowfall for the globe, as carbon dioxide levels rise over the next century.
The decline in snowfall could spell trouble for regions such as the western United States that rely on snowmelt as a source of fresh water.
The projections are the result of a new climate model developed at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL) and analyzed by scientists at GFDL and Princeton University. The study was published in the Journal of Climate.
The model indicates that the majority of the planet would experience less snowfall as a result of warming due to a doubling of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Observations show that atmospheric carbon dioxide has already increased by 40 percent from values in the mid-19th century, and, given projected trends, could exceed twice those values later this century. In North America, the greatest reductions in snowfall will occur along the northeast coast, in the mountainous west, and in the Pacific Northwest. Coastal regions from Virginia to Maine, as well as coastal Oregon and Washington, will get less than half the amount of snow currently received.
In very cold regions of the globe, however, snowfall will rise because as air warms it can hold more moisture, leading to increased precipitation in the form of snow. The researchers found that regions in and around the Arctic and Antarctica will get more snow than they now receive.
The highest mountain peaks in the northwestern Himalayas, the Andes and the Yukon region will also receive greater amounts of snowfall after carbon dioxide doubles. This finding clashes with other models which predicted declines in snowfall for these high-altitude regions. However, the new model's prediction is consistent with current snowfall observations in these regions.
The model is an improvement over previous models in that it utilizes greater detail about the world's topography – the mountains, valleys and other features. This new "high-resolution" model is analogous to having a high-definition model of the planet's climate instead of a blurred picture.
INFORMATION:
The study was conducted by Sarah Kapnick, a postdoctoral research scientist in the Program in Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Princeton University and jointly affiliated with NOAA's Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory in Princeton, and Thomas Delworth, senior physical scientist at GFDL.
The paper, "Controls of Global Snow Under a Changed Climate," was published online by the Journal of Climate Feb. 6.
This work was supported by the Cooperative Institute for Climate Science, a collaborative institute between Princeton University and GFDL.
Forecast is for more snow in polar regions, less for the rest of us
2013-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The lifetime journeys of manure-based microbes
2013-02-22
This press release is available in Spanish.
Studies at the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) are shedding some light on the microbes that dwell in cattle manure—what they are, where they thrive, where they struggle, and where they can end up.
This research, which is being conducted by Agricultural Research Service (ARS) scientists at the agency's Agroecosystems Management Research Unit in Lincoln, Neb., supports the USDA priority of ensuring food safety. ARS is USDA's chief intramural scientific research agency.
In one project, ARS microbiologist Lisa Durso ...
Catheters linked with high risk of infections, heart problems, and death in dialysis patients
2013-02-22
Highlights
Dialysis patients using catheters to access the blood have the highest risks for death, infections, and cardiovascular events compared with patients using other types of vascular access.
Higher quality studies are needed to determine the true safety of different types of vascular access used for hemodialysis.
Worldwide, more than 1.5 million people are treated with hemodialysis.
Washington, DC (February 21, 2013) — Dialysis patients using catheters to access the blood have the highest risks for death, infections, and cardiovascular events compared with ...
Certain mutations affect kidney disease risk and prognosis
2013-02-22
Highlights
Certain mutations and combinations of mutations in immune-related genes affect individuals' risk of developing a rare but serious kidney condition.
These mutations also affect patient prognosis following different treatments.About half of patients with the condition, called atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, develop kidney failure.
Washington, DC (February 21, 2013) — Certain gene mutations affect individuals' risk of developing a serious kidney condition, as well as their prognosis after being diagnosed with the disease, according to a study appearing in ...
Penn researchers develop protein 'passport' that help nanoparticles get past immune system
2013-02-22
VIDEO:
Penn's Dennis Discher explains how his lab designed a protein that acts a "passport " for the body's immune system. Nanoparticles equipped with this passport last longer in the bloodstream than...
Click here for more information.
PHILADELPHIA — The body's immune system exists to identify and destroy foreign objects, whether they are bacteria, viruses, flecks of dirt or splinters. Unfortunately, nanoparticles designed to deliver drugs, and implanted devices ...
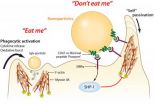
Stem cell 'homing' signal may help treat heart failure patients
2013-02-22
In the first human study of its kind, researchers activated heart failure patients' stem cells with gene therapy to improve their symptoms, heart function and quality of life, according to a study in the American Heart Association journal Circulation Research.
Researchers delivered a gene that encodes a factor called SDF-1 to activate stem cells like a "homing" signal.
The study is unique because researchers introduced the "homing" factor to draw stem cells to the site of injury and enhance the body's stem cell-based repair process. Generally, researchers extract and ...
Floral signs go electric
2013-02-22
Flowers' methods of communicating are at least as sophisticated as any devised by an advertising agency, according to a new study, published today in Science Express by researchers from the University of Bristol. The research shows for the first time that pollinators such as bumblebees are able to find and distinguish electric signals given out by flowers. However, for any advert to be successful, it has to reach, and be perceived by, its target audience.
Flowers often produce bright colours, patterns and enticing fragrance to attract their pollinators. Researchers ...
Research suggests malaria can be defeated without a globally led eradication program
2013-02-22
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Malaria does not have to be eradicated globally for individual countries to succeed at maintaining elimination of the disease, according to research from the University of Florida's Emerging Pathogens Institute and department of geography, to be published in the journal Science Feb. 22.
Researchers Andrew Tatem and Christina Chiyaka found that those countries that have eliminated malaria have maintained their malaria-free states with remarkable stability, going against traditional theory. Between 1945 and 2010, 79 countries eliminated malaria and ...
Researchers propose new way to probe Earth's deep interior
2013-02-22
Researchers from Amherst College and The University of Texas at Austin have described a new technique that might one day reveal in higher detail than ever before the composition and characteristics of the deep Earth.
There's just one catch: The technique relies on a fifth force of nature (in addition to gravity, the weak and strong nuclear forces and electromagnetism) that has not yet been detected, but which some particle physicists think might exist. Physicists call this type of force a long-range spin-spin interaction. If it does exist, this exotic new force would ...
New flu drug stops virus in its tracks
2013-02-22
A new class of influenza drug has been shown effective against drug-resistant strains of the flu virus, according to a study led by University of British Columbia researchers.
Published online today in the journal Science Express, the study details the development of a new drug candidate that prevents the flu virus from spreading from one cell to the next. The drug is shown to successfully treat mice with lethal strains of the flu virus.
In order to spread in the body, the flu virus first uses a protein, called hemagglutinin, to bind to the healthy cell's receptors. ...
A promising new method for next-generation live-attenuated viral vaccines against Chikungunya virus
2013-02-22
Researchers have successfully applied a novel method of vaccine creation for Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) using a technique called large scale random codon re-encoding. Using this approach, a group from the UMR_D 190, Emerging viruses Department in Marseille, France in collaboration with the University of Sydney, Australia, demonstrated that the engineered viruses exhibit a stable phenotype with a significantly decreased viral fitness (i.e., replication capacity), making it a new vaccine candidate for this emerging viral disease. This new report publishes on February 21 in ...