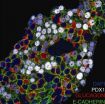
(Press-News.org) CHAPEL HILL, N.C. - Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the seventh most common form of cancer in the United States, but other than an association with the human papillomavirus, no validated molecular profile of the disease has been established. By analyzing data from DNA microarrays, a UNC-led team has completed a study that confirms the presence of four molecular classes of the disease and extends previous results by suggesting that there may be an underlying connection between the molecular classes and observed genomic events, some of which affect known cancer genes. The clinical relevance of the classes and certain genomic events was demonstrated, thus paving the way for further studies and possible targeted therapies.
The study was published in the Feb. 22, 2013 issue of the journal PLOS ONE.
Neil Hayes, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine and senior author, says, "Cancer is a disease caused by alteration in the DNA and RNA molecules of tumors. A cancer results when broken molecules initiate a cascade of abnormal signals that ultimately results in abnormal growth and spread of tissues that should be under tight control within the body.
"However, most common tumors, including head and neck cancer, have relatively little information in the public record as to how these signals coordinate to create different patterns of abnormalities. This study is among the largest ever published to document reproducible molecular tumor subtypes. Subtypes, such as those we describe, represent attractive models to understand and attack cancers for treatment and prognosis."
Dr. Hayes is a member of UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center and national co-chair of the Data Analysis Sub-Group for The Cancer Genome Atlas, a program of the National Institutes of Health.
The team, composed of investigators from UNC and five other institutions, analyzed a set of nearly 140 HNSCC samples. By searching for recurrent patterns known as gene expression signatures, they were able to detect four gene expression subtypes. The subtypes are termed basal, mesenchymal, atypical, and classical based on similarities to established gene expression subtypes in other tumor types and expression patterns of specific genes.
In spite of being the seventh most common form of cancer in the United States, HNSCC is relatively under-studied in comparison to other tumor types, e.g. breast and lung. By leveraging the similarities found in the gene expression subtypes, the results of this study provide a connection to a range of well-established findings and additional insight into the disease.
INFORMATION:
Other UNC authors are: Vonn Walter, PhD; Xiaoying Yin, MD; Matthew Wilkerson, PhD; Christopher Cabanski, PhD, now at Washington University at St. Louis; Ni Zhao, MS; Ying Du,PhD; Mei-Kim Ang, MD, now at the National Cancer Center in Singapore; Michele Hayward, RD; Ashley Salazar, BA; Katherine Hoadley, PhD; Mark Weissler, MD; William Shockley, MD; Adam Zanation, MD; Trevor Hackman, MD; Leigh Thorne, MD; William Funkhouser, MD; Andrew Olshan, PhD; Scott Randell, PhD; and Carol Shores, MD, PhD.
Other institutions are the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, the University of Toledo in Toledo, Ohio, and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in Little Rock.
Funding for the study was provided by a Clinical/Translational Award from the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, the University Cancer Research Fund, and a grant from the National Institutes of Health (K12-RR-023248).
UNC-led study documents head and neck cancer molecular tumor subtypes
2013-02-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Reprogramming cells to fight diabetes
2013-02-23
PHILADELPHIA – For years researchers have been searching for a way to treat diabetics by reactivating their insulin-producing beta cells, with limited success. The "reprogramming" of related alpha cells into beta cells may one day offer a novel and complementary approach for treating type 2 diabetes. Treating human and mouse cells with compounds that modify cell nuclear material called chromatin induced the expression of beta cell genes in alpha cells, according to a new study that appears online in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
"This would be a win-win situation ...
Color in fossil insects, diamonds from the ancient ocean floor and modeling the world's largest rivers
2013-02-23
Boulder, Colo., USA – Geology articles posted online ahead of print on 20 Feb. 2013 include several modeling and simulation studies as well as studies on the Exmouth Sub-basin, Australia; the West Kunlun Range, northern Tibetan Plateau; Krakenes Lake, Norway; the Azores islands; and the hot springs of Colorado. The 12 new papers cover a variety of topics:
Taking the easiest pathway to Earth's surface
A challenge to climate change and biotic factors to explain post-glacial lake acidification
Upper-crustal shortening in the Tibetan Plateau
Analysis of diamonds with ...
Geoscience Currents No. 70: Student choices for society membership in the geosciences
2013-02-23
Alexandria, VA – Geoscience Currents #70 presents the final data collected from
the GeoConnection Recruitment Packets distributed from 2009 to 2011. The
packets, which included informational brochures from several of AGI's member
societies, fliers with internship information, and a copy of EARTH Magazine's
"Workforce" edition, also offered students the opportunity to register with up
to five of AGI's professional member societies for free. This endeavor was meant
to increase student participation in the greater geoscience community.
Geoscience Currents #70 details ...
New device better traps viruses, airborne pathogens
2013-02-23
Washington University engineering researchers have created a new type of air-cleaning technology that could better protect human lungs from allergens, airborne viruses and ultrafine particles in the air.
The device, known as the SXC ESP, was created by a team led by Pratim Biswas, PhD, the Lucy & Stanley Lopata Professor and chair of the Department of Energy, Environmental & Chemical Engineering in the School of Engineering & Applied Science.
A recent study of the device, published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, found that it could help to prevent respiratory ...
Cyclone Haruna makes landfall in Madagascar
2013-02-23
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Cyclone Haruna after it made landfall in southwestern Madagascar.
Haruna's center made landfall near Manombo, Madagascar around 0600 UTC (1 a.m. EST/U.S.) The METEO-7 satellite captured a visible image of Haruna at the time of landfall and showed that its eye had already become cloud-filled.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Haruna on Feb. 22 at 1105 UTC (6:05 a.m. EST) after it moved inland and its eye was completed cloud-filled. ...
Flipping the 'off' switch on cell growth
2013-02-23
A protein known for turning on genes to help cells survive low-oxygen conditions also slows down the copying of new DNA strands, thus shutting down the growth of new cells, Johns Hopkins researchers report. Their discovery has wide-ranging implications, they say, given the importance of this copying — known as DNA replication — and new cell growth to many of the body's functions and in such diseases as cancer.
"We've long known that this protein, HIF-1α, can switch hundreds of genes on or off in response to low oxygen conditions," says Gregg Semenza, M.D., Ph.D., ...
PA's adoption laws make it possible for families to grow
2013-02-23
PA's adoption laws make it possible for families to grow
Article provided by The Law Offices of Marguerite Nealon
Visit us at http://www.pafamilylaw.com
Pennsylvania, as a whole, is quite liberal in its policies regarding adoption. For instance, the state does not have any age restrictions, thereby allowing persons above the age of eighteen to be adopted. Furthermore, Pennsylvania allows adoption by both single adults and married couples. Most recently, the state made it legal for same-sex couples to adopt a child. Pennsylvania's liberal adoption regulations make ...
Can sniffs from drug-sniffing dogs establish probable cause?
2013-02-23
Can sniffs from drug-sniffing dogs establish probable cause?
Article provided by Mark K. Tyndall, P.C.
Visit us at http://www.virginiadefenselaw.com
In October, the United States Supreme Court heard two cases regarding the relationship between evidence from a drug-sniffing dog and probable cause. In both cases, the justices will determine if the sniff of a trained drug-sniffing dog can establish probable cause for an officer to obtain a warrant.
Probable cause is the threshold law enforcement must meet to perform a search, request a warrant or make an arrest. ...
NHTSA proposes noise standards for hybrids
2013-02-23
NHTSA proposes noise standards for hybrids
Article provided by Law Offices of Robert Hamparyan
Visit us at http://www.yourcaliforniaaccidentattorney.com
Due to rising gas prices, hybrid vehicles have become more popular in recent years. Although hybrids offer the latest technology and the highest fuel efficiency, they can be dangerous to bicyclists and pedestrians. The reason: they operate so silently at low speeds that it is very difficult to hear them as they approach.
To address the problem, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has recently ...
Recent accidents reveal dangers of pedestrian accidents
2013-02-23
Recent accidents reveal dangers of pedestrian accidents
Article provided by Schiller Law Firm
Visit us at http://www.theschillerlawfirm.com
Walking and biking are enjoyable hobbies for numerous South Carolina residents. However, recent news stories demonstrate how common pedestrian accidents are.
Pedestrian accidents in South Carolina
In one case, an 87-year old man was pinned underneath a pickup truck. According to the Herald Online, the man was walking with a relative outside a VA Medical Center when the pickup truck jumped a curb and struck the man. The ...