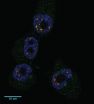
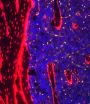
(Press-News.org) The origin of an innate ability the brain has to protect itself from damage that occurs in stroke has been explained for the first time.
The Oxford University researchers hope that harnessing this inbuilt biological mechanism, identified in rats, could help in treating stroke and preventing other neurodegenerative diseases in the future.
'We have shown for the first time that the brain has mechanisms that it can use to protect itself and keep brain cells alive,' says Professor Alastair Buchan, Head of the Medical Sciences Division and Dean of the Medical School at Oxford University, who led the work.
The researchers report their findings in the journal Nature Medicine and were funded by the UK Medical Research Council and National Institute for Health Research.
Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK. Every year around 150,000 people in the UK have a stroke.
It occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is cut off. When this happens, brain cells are deprived of the oxygen and nutrients they need to function properly, and they begin to die.
'Time is brain, and the clock has started immediately after the onset of a stroke. Cells will start to die somewhere from minutes to at most 1 or 2 hours after the stroke,' says Professor Buchan.
This explains why treatment for stroke is so dependent on speed. The faster someone can reach hospital, be scanned and have drugs administered to dissolve any blood clot and get the blood flow re-started, the less damage to brain cells there will be.
It has also motivated a so-far unsuccessful search for 'neuroprotectants': drugs that can buy time and help the brain cells, or neurons, cope with damage and recover afterwards.
The Oxford University research group have now identified the first example of the brain having its own built-in form of neuroprotection, so-called 'endogenous neuroprotection'.
They did this by going back to an observation first made over 85 years ago. It has been known since 1926 that neurons in one area of the hippocampus, the part of the brain that controls memory, are able to survive being starved of oxygen, while others in a different area of the hippocampus die. But what protected that one set of cells from damage had remained a puzzle until now.
'Previous studies have focused on understanding how cells die after being depleted of oxygen and glucose. We considered a more direct approach by investigating the endogenous mechanisms that have evolved to make these cells in the hippocampus resistant,' explains first author Dr Michalis Papadakis, Scientific Director of the Laboratory of Cerebral Ischaemia at Oxford University.
Working in rats, the researchers found that production of a specific protein called hamartin allowed the cells to survive being starved of oxygen and glucose, as would happen after a stroke.
They showed that the neurons die in the other part of the hippocampus because of a lack of the hamartin response.
The team was then able to show that stimulating production of hamartin offered greater protection for the neurons.
Professor Buchan says: 'This is causally related to cell survival. If we block hamartin, the neurons die when blood flow is stopped. If we put hamartin back, the cells survive once more.'
Finally, the researchers were able to identify the biological pathway through which hamartin acts to enable the nerve cells to cope with damage when starved of energy and oxygen.
The group points out that knowing the natural biological mechanism that leads to neuroprotection opens up the possibility of developing drugs that mimic hamartin's effect.
Professor Buchan says: 'There is a great deal of work ahead if this is to be translated into the clinic, but we now have a neuroprotective strategy for the first time. Our next steps will be to see if we can find small molecule drug candidates that mimic what hamartin does and keep brain cells alive.
'While we are focussing on stroke, neuroprotective drugs may also be of interest in other conditions that see early death of brain cells including Alzheimer's and motor neurone disease,' he suggests.
###
Notes to Editors
* The paper 'TSC1 (hamartin) confers neuroprotection against ischemia by inducing autophagy' by Michalis Papadakis and colleagues is to be published in the journal Nature Medicine with an embargo of 18:00 UK time / 13:00 US Eastern time on Sunday 24 February 2013.
* The main funders of the study were the UK Medical Research Council and the UK National Institute for Health Research.
* The Medical Research Council has been at the forefront of scientific discovery to improve human health. Founded in 1913 to tackle tuberculosis, the MRC now invests taxpayers' money in some of the best medical research in the world across every area of health. Twenty-nine MRC-funded researchers have won Nobel prizes in a wide range of disciplines, and MRC scientists have been behind such diverse discoveries as vitamins, the structure of DNA and the link between smoking and cancer, as well as achievements such as pioneering the use of randomised controlled trials, the invention of MRI scanning, and the development of a group of antibodies used in the making of some of the most successful drugs ever developed. Today, MRC-funded scientists tackle some of the greatest health problems facing humanity in the 21st century, from the rising tide of chronic diseases associated with ageing to the threats posed by rapidly mutating micro-organisms. www.mrc.ac.uk
The MRC Centenary Timeline chronicles 100 years of life-changing discoveries and shows how our research has had a lasting influence on healthcare and wellbeing in the UK and globally, right up to the present day. www.centenary.mrc.ac.uk
* The National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) is funded by the Department of Health to improve the health and wealth of the nation through research. Since its establishment in April 2006, the NIHR has transformed research in the NHS. It has increased the volume of applied health research for the benefit of patients and the public, driven faster translation of basic science discoveries into tangible benefits for patients and the economy, and developed and supported the people who conduct and contribute to applied health research. The NIHR plays a key role in the Government's strategy for economic growth, attracting investment by the life-sciences industries through its world-class infrastructure for health research. Together, the NIHR people, programmes, centres of excellence and systems represent the most integrated health research system in the world. For further information, visit the NIHR website.
* Oxford University's Medical Sciences Division is one of the largest biomedical research centres in Europe, with over 2,500 people involved in research and more than 2,800 students. The University is rated the best in the world for medicine, and it is home to the UK's top-ranked medical school.
From the genetic and molecular basis of disease to the latest advances in neuroscience, Oxford is at the forefront of medical research. It has one of the largest clinical trial portfolios in the UK and great expertise in taking discoveries from the lab into the clinic. Partnerships with the local NHS Trusts enable patients to benefit from close links between medical research and healthcare delivery.
A great strength of Oxford medicine is its long-standing network of clinical research units in Asia and Africa, enabling world-leading research on the most pressing global health challenges such as malaria, TB, HIV/AIDS and flu. Oxford is also renowned for its large-scale studies which examine the role of factors such as smoking, alcohol and diet on cancer, heart disease and other conditions.
Ability of brain to protect itself from damage revealed
2013-02-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UN sustainable energy initiative could put world on a path to climate targets
2013-02-25
The new study in Nature Climate Change shows that reaching the 3 energy-related objectives proposed by the United Nations in their Sustainable Energy for All (SE4All) initiative, launched in 2011, would reduce emissions of greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change and, in combination with other measures, could help keep global temperature rise from exceeding the internationally agreed target level of 2°C.
"Achievement of the 3 objectives would provide an important entry point into stringent climate protection," says Joeri Rogelj, ETH Zurich researcher and IIASA-affiliated ...
Pain from the brain
2013-02-25
Psychogenic diseases, formerly known as 'hysterical' illnesses, can have many severe symptoms such as painful cramps or paralysis but without any physical explanation. However, new research from the University of Cambridge and UCL (University College London) suggests that individuals with psychogenic disease, that is to say physical illness that stems from emotional or mental stresses, do have brains that function differently. The research was published today, 25 February, in the journal Brain.
Psychogenic diseases may look very similar to illnesses caused by damage to ...
Laser mastery narrows down sources of superconductivity
2013-02-25
UPTON, NY – Identifying the mysterious mechanism underlying high-temperature superconductivity (HTS) remains one of the most important and tantalizing puzzles in physics. This remarkable phenomenon allows electric current to pass with perfect efficiency through materials chilled to subzero temperatures, and it may play an essential role in revolutionizing the entire electricity chain, from generation to transmission and grid-scale storage. Pinning down one of the possible explanations for HTS—fleeting fluctuations called charge-density waves (CDWs)—could help solve the ...
Researchers at IRB Barcelona discover a general mechanism that accelerates tumor development
2013-02-25
Cancer is characterized by uncontrolled cell division and growth. In order to identify new therapeutic targets through which to tackle the disease, scientists seek to clarify the mechanisms that control the expression of genes that favor the development of tumors, in processes such as uncontrolled cell division. Today, Nature has published a paper by the lab headed by Raúl Méndez, ICREA professor at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona). The study describes a mechanism controlled by the CPEB1 protein that affects more than 200 genes related to cell proliferation ...
Fragments of continents hidden under lava in the Indian Ocean
2013-02-25
The islands Reunion and Mauritius, both well-known tourist destinations, are hiding a micro-continent, which has now been discovered. The continent fragment known as Mauritia detached about 60 million years ago while Madagascar and India drifted apart, and had been hidden under huge masses of lava. Such micro-continents in the oceans seem to occur more frequently than previously thought, says a study in the latest issue of Nature Geoscience ("A Precambrian microcontinent in the Indian Ocean," Nature Geoscience, Vol 6, doi: 10.1038/NGEO1736).
The break-up of continents ...
Quantum algorithm breakthrough
2013-02-25
The team implemented the 'phase estimation algorithm' — a central quantum algorithm which achieves an exponential speedup over all classical algorithms. It lies at the heart of quantum computing and is a key sub-routine of many other important quantum algorithms, such as Shor's factoring algorithm and quantum simulations.
Dr Xiao-Qi Zhou, who led the project, said: "Before our experiment, there had been several demonstrations of quantum algorithms, however, none of them implemented the quantum algorithm without knowing the answer in advance. This is because in the ...
Graphene: A material that multiplies the power of light
2013-02-25
Bottles, packaging, furniture, car parts... all made of plastic. Today we find it difficult to imagine our lives without this key material that revolutionized technology over the last century. There is wide-spread optimism in the scientific community that graphene will provide similar paradigm shifting advances in the decades to come. Mobile phones that fold, transparent and flexible solar panels, extra thin computers... the list of potential applications is endless. Scientists, industries and the European Commission are so convinced of the potential of graphene to revolutionize ...
Scientists find bone-marrow environment that helps produce infection-fighting T and B cells
2013-02-25
DALLAS – Feb. 24, 2013 – The Children's Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern has deepened the understanding of the environment within bone marrow that nurtures stem cells, this time identifying the biological setting for specialized blood-forming cells that produce the infection-fighting white blood cells known as T cells and B cells.
The research found that cells called early lymphoid progenitors, which are responsible for producing T cells and B cells, thrive in an environment known as an osteoblastic niche. The investigation, published online today ...
Distinct niches in bone marrow nurture blood stem cells
2013-02-25
In research that could one day improve the success of stem cell transplants and chemotherapy, scientists have found that distinct niches exist in bone marrow to nurture different types of blood stem cells.
Stem cells in the blood are the precursors to infection-fighting white blood cells and oxygen-carrying red blood cells.
The research, by a team at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, is reported Feb. 24 in the advance online edition of Nature.
The new findings, in mice, suggest that it may be possible to therapeutically target support cells in ...
Analytical trick accelerates protein studies
2013-02-25
MADISON – Researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have found a new way to accelerate a workhorse instrument that identifies proteins. The high-speed technique could help diagnose cancer sooner and point to new drugs for treating a wide range of conditions.
Proteins are essential building blocks of biology, used in muscle, brain, blood and hormones. If the genes are the blueprints, the proteins patterned on them are the hammers and tongs of life.
Proteins are not only numerous — humans have more than a 100,000 varieties — but each one has a complex structure ...